Introduction
Up to 40 per cent of patients in hospitals are over the age of 65 years, a population that frequently requires that a range of professionals collaborate on their complex health and social needs (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2015, Canadian Institute for Health Information, 2011; D’Amour, Ferrada-Videla, Rodriguez & Beaulieu, Reference D’Amour, Ferrada-Videla, Rodriguez and Beaulieu2005; Hartgerink et al., Reference Hartgerink, Cramm, Bakker, van Eijsden, Mackenbach and Nieboer2014; Health and Social Care Information, 2015). Interprofessional collaboration is widely accepted as necessary for the provision of efficient, safe, and quality care to people – such as older adults – with complex needs (Ambrose-Miller & Ashcroft, Reference Ambrose-Miller and Ashcroft2016; Fewster-Thuente & Velsoir-Friedrich, Reference Fewster-Thuente and Velsoir-Friedrich2008; Gilbert, J. H. V., Yan, J., & Hoffman, S. J., Reference Gilbert, Yan and Hoffman2010; Martin, Ummenhofer, Manser, & Spirig, Reference Martin, Ummenhofer, Manser and Spirig2010). Providing holistic, collaborative care that is responsive to patients’ needs, defined as patient-centred care, is also a necessary part of providing quality care (Sidani, van Soeren, Hurlock-Chorostechi, Reeves, Fox, & Collins, Reference Sidani, van Soeren, Hurlock-Chorostecki, Reeves, Fox and Collins2016).
At the core of our study was a research project that we conducted to understand professionals’ perspectives on interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care, as well as their learning needs in applying both to working with hospitalized older adults. As part of the process of understanding the data, we explored the similarities and differences between the nursing staff (registered nurses, licensed practical nurses, and health care aides) and related disciplines, which included physiotherapists, occupational therapists, rehabilitation aides, a recreational therapist, and a speech pathologist. We wondered if there would be differences in perspectives between these groups due to differing professional identities and work patterns (e.g., Monday to Friday vs. shift work).
Background
Older adults who commonly have multiple chronic medical conditions with acute illnesses often present atypically and are at risk for preventable functional decline when hospitalized (Dahlke, Hall, & Baumbusch, Reference Dahlke, Hall and Baumbusch2017; Dixon-Woods, Suokas, Pitchforth, & Tarrant, Reference Dixon-Woods, Suokas, Pitchforth and Tarrant2009; Hartgerink et al., Reference Hartgerink, Cramm, Bakker, van Eijsden, Mackenbach and Nieboer2014; Johansson, Eklund, & Gosman-Hedstrom, Reference Johansson, Eklund and Gosman-Hedstrom2010; Long, Brown, Ames, & Vincent, Reference Long, Brown, Ames and Vincent2013). Within hospital environments, there is a focus on rapid resolution of the presenting acute illness or injury rather than a focus on the functional and social needs with which older adults often present. Older adults are often a poor fit with the focus on efficiency that is promoted in hospital environments (Baumbusch, Leblanch, Shaw, & Kjorvin, Reference Baumbusch, Leblanc, Shaw and Kjorvin2016; Dahlke, Reference Dahlke2011; Parke & Chappell, Reference Parke and Chappell2010). Expecting older patients with complex health challenges to be readily accommodated within hospital systems designed for treatment of one acute illness (Baumbusch et al., Reference Baumbusch, Leblanc, Shaw and Kjorvin2016; Covinsky, Pierluissi, & Johnston, Reference Covinsky, Pierluissi and Johnston2011) is institutionally ageist (Dahlke et al., Reference Dahlke, Hall and Baumbusch2017; Sellman, Reference Sellman2009). In addition, scholars have reported that health care providers hold negative perspectives towards older adults (de Almeida Tavares, da Silva, Sá-Couto, Boltz, & Capezuti, Reference de Almeida Tavares, da Silva, Sá-Couto, Boltz and Capezuti2015; Singleton Eymard & Hutto Douglas, Reference Singleton Eymard and Hutto Douglas2012). Moreover, hospital environments are subject to economic constraints leading to larger caseloads that make it difficult for professionals to meet the needs of all hospitalized older adults (Baumbusch et al., Reference Baumbusch, Leblanc, Shaw and Kjorvin2016; Covinsky et al., Reference Covinsky, Pierluissi and Johnston2011; Dahlke et al., Reference Dahlke, Hall and Baumbusch2017; Dahlke, Phinney, Hall, Rodney, & Baumbusch, Reference Dahlke, Phinney, Hall, Rodney and Baumbusch2015; Dixon-Woods et al., Reference Dixon-Woods, Suokas, Pitchforth and Tarrant2009; Parke & Hunter, Reference Parke and Hunter2014; ).
Numerous programs involving interprofessional collaboration have been reported to improve the functional outcomes with hospitalized older adults (Covinsky et al., Reference Covinsky, Palmer, Kresevic, Kahana, Counsell, Fortinsky and Landefeld1998; Covinsky et al., Reference Covinsky, Pierluissi and Johnston2011; Flaherty et al., Reference Flaherty, Tariq, Raghavan, Bakshi, Moinuddin and Morley2003; Hickman, Newton, Halcomb, Chang, & Davidson, Reference Hickman, Newton, Halcomb, Chang and Davidson2007; Inouye, Bogardus, Baker, Leo-Summer, & Cooney, Reference Inouye, Bogardus, Baker, Leo-Summers and Cooney2000). A few other strategies aimed at improving and maintaining hospitalized older adults’ functioning include the Nurses Improving Care to Health System Elders (NICHE) programs (Menzey et al., Reference Menzey, Kobayashi, Grossman, Firpo, Fulmer and Mitty2004) and fighting “pyjama paralysis” which is an emphasis on dressing older patients in street clothes (Oliver, Reference Oliver2017). However, not all older adults are cared for in hospitals that offer these resources. In this study, we focused on interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care.
Interprofessional collaboration has been identified as important in preventing adverse effects within health care institutions (Martin et al., Reference Martin, Ummenhofer, Manser and Spirig2010), reducing duplication and clinical errors, and enhancing the quality of care (Morey et al., Reference Morey, Simon, Jay, Wears, Salisbury, Dukes and Berns2002; Schmitt, Reference Schmitt2001). These benefits result because collaboration among the professionals improves the coordination of care (Martin et al., Reference Martin, Ummenhofer, Manser and Spirig2010). The term collaboration describes a variety of processes among more than one discipline, from parallel practice with consultation to full integration (Perreault & Careau, Reference Perreault and Careau2012). In this study, we used Fox and Reeves’ (Reference Fox and Reeves2015) definition of interprofessional collaboration as meaning two or more disciplines communicating with one another about patient care.
Collaboration among professionals is influenced by relational, processual, organization, and contextual issues (Lee, Doran, Tourganeau, & Fleshner, Reference Lee, Doran, Tourganeau and Fleshner2014; Reeves, Lewin, Espin, & Zwarenstein, Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Relational issues include factors such as professional power and socialization that affect relationships between professionals (Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Processual issues refer to factors such as professionals having the time and space to collaborate (Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Organizational issues refer to factors (e.g., access to resources) within local organizations that influence how professionals collaborate (Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Finally, contextual factors are explained as broader social (e.g., ageism), political, and economic issues that affect how professionals collaborate (Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Professionals collaborate with one another to provide care that is patient-centred for older adults within these complex social, political, and economically constrained hospital environments (Essen, Freshwater, & Cahill, Reference Essen, Freshwater and Cahill2015; Fox & Reeves, Reference Fox and Reeves2015).
Interprofessional collaboration presents unique challenges that can become barriers to communication (Mickan & Rodger, Reference Mickan and Rodger2005). Challenges include professionals’ differing routines (Duner, Reference Duner2013; Elissen, van Raak, & Paulus, Reference Elissen, van Raak and Paulus2011), different knowledge and identities (Baxter & Brumfitt, Reference Baxter and Brumfitt2008), and professional hierarchies and time constraints (Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Rice, Conn, Miller, Kenaszchuk and Zwarenstein2009). Ineffective communication has been recognized as a barrier to collaboration and a major contributor to adverse patient outcomes (Ambrose-Miller & Ashcroft, Reference Ambrose-Miller and Ashcroft2016; Bronk, Reference Bronk2017). Research suggests that communication among professionals can become unidirectional, terse, and focused on medical issues, particularly when time constraints are involved (Baxter & Brumfitt, Reference Baxter and Brumfitt2008; Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Rice, Conn, Miller, Kenaszchuk and Zwarenstein2009). At the same time, however, scholars have also reported that interactions between nursing staff and other health professions (e.g., physiotherapists ([PT] and occupational therapists [OT]) are often in-depth and focused on a breadth of issues related to patient care (Baxter & Brumfitt, Reference Baxter and Brumfitt2008). A perceived power imbalance between team members can be a barrier to interprofessional collaboration (Ambrose-Miller & Ashcroft, Reference Ambrose-Miller and Ashcroft2016). Unequal relationships, particularly those existing between nurses and physicians, have been well-documented within health care (Housden, Browne, Wong, & Dawes, Reference Housden, Browne, Wong and Dawes2017; Speedy, Reference Speedy1997; Zelek & Phillips, Reference Zelek and Phillips2003). Hospitals that report better collaboration between nurses and physicians have lower rates of 30-day patient mortality (Estabrooks, Midodzi, Cummings, Ricker, & Giovannetti, Reference Estabrooks, Midodzi, Cummings, Ricker and Giovannetti2005). Little is known, however, about how nursing staff and other professional team members (e.g., PT, OT, dietician, social workers) view the equality of their collaboration within interprofessional acute care teams.
Older people and their families value delivery of health care that demonstrates interprofessional teams’ consideration of the unique characteristics of the older person (Dahlke et al., Reference Dahlke, Steil, Freund-Heritage, Colborne, Labonte and Wagg2018). Given the complex environments in which professionals work with acutely hospitalized older adults, the process by which they are able to provide patient-centred-care and collaborate effectively is not well understood. Thus, the purpose of this study was to explore staffs’ perceptions of interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care when working in hospital environments.
Methods
This study was part of a larger research project that examined professionals’ perspectives about interprofessional collaboration, patient-centred care, and learning needs related to their work with hospitalized older adults. With these data, we developed and conducted an educational session based on participants espoused learning needs. As part of understanding the data, we explored the similarities and differences between nursing staff and the other disciplines in their perspectives on interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care. In this study, we used a convergence triangulation mixed-methods design to examine differences in the perceptions about interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care between nursing staff and the staff from other disciplines (Creswell & Plano Clark, Reference Creswell and Plano Clark2007).
Research questions included the following: (1) What are the perceptions of team members about interprofessional collaboration? (2) What are their perceptions of their ability to provide patient-centred care? and (3) What are team members’ perceptions about working within interprofessional teams with hospitalized older adults? Questions one and two were answered by survey, and question three through interviews.
Sample and Setting
After receiving ethical approval from the University of Alberta and the participating hospital in Western Canada, we recruited professional groups from three medical units in a tertiary hospital via posters, email, and information sessions. Staff who were included were full- and part-time registered nurses (RNs), licensed practical nurses (LPNs), health care aides (HCAs), physiotherapists (PTs), occupational therapists (OTs), recreational therapist (RT), recreational aides (RAs), and a speech pathologist (SP). The three medical units were chosen because of their similarity to one another and because their patients were people almost entirely older than age 65. In addition, the first author had been communicating with one of the nurse managers for a year to understand their challenges and foster a potential research collaboration. This communication extended to only one of the managers. None of the interprofessional staff were known to the researchers. There were four managers connected to these three medical units: three were nurse managers, one for each of the three units. The fourth manager was a PT who managed the OT, PT, RA, RT, and SP who all worked on the three medical units. The four managers often collaborated on quality improvement and staff education initiatives.
Each unit had 18 patient and two over-capacity beds. One of the units had eight beds designated as geriatric. Patients on all three units were admitted from the emergency department and were acutely ill with a wide range of diagnoses. A small percentage of these patients recovered from their acute illness and remained on the units waiting for a transfer to another living accommodation (such as long-term care), because they were no longer able to return home. Each of the units was staffed with three RNs, two LPNs, and two HCAs on day shifts, and two RNs and two HCAs on nights. The unit with the geriatric beds had an additional LPN and HCA during the evening and a recreational therapist during the day, Monday through Friday. Although each of the medical units had designated positions for nursing staff, casual nursing staff (who filled in for vacation and illnesses) commonly worked on all three units. Three OTs, three PTs, three RAs, and three SPs worked Monday through Friday on all three units. Altogether, the staff who worked on all three units included 34 RNs, 25 LPNs, 25 HCAs, three PTs, three OTs, three RT, one recreational therapist, and three SPs, for a total of 97 staff.
The four managers forwarded an email (which we, as the researchers, had authored) to their respective staff, inviting participation in the study. Accordingly, the nurse managers sent the email invitation to their designated nursing staff, and the PT manager sent it to the other disciplines. The email explained the study and also that participation was confidential, voluntary, and that completing the survey was considered consent. Participation in the survey was achieved by activating an electronic link in the email. The link sent participants to a secure server at the University of Alberta. Staff were sent reminders about the opportunity to participate in the survey every two weeks, (three times) in keeping with Dillman, Smyth, and Christian’s (Reference Dillman, Smyth and Christian2014) method of encouraging participation. As a result, staff had the opportunity to participate in the survey over a 2-month period.
The lead researcher, who was unknown to the staff, conducted information sessions on the units, explaining the study, and answering questions. During the information sessions, some staff asked about receiving payment for attending an interview. It was explained that the funding agency strictly forbade us as the researchers from paying individuals for their time; however, we were willing to accommodate them by interviewing at a quiet time during staff members’ working hours, or during lunch breaks, or at the beginning or end of a workday. Individuals who were interested in participating in interviews contacted the lead researcher. Participation in the survey was not a pre-requisite for participating in an interview. All interprofessional staff who worked full time or part time on any of the units were invited to participate in the study through email invitations, posters on each unit, and information sessions. All participants were given the opportunity to ask questions and then asked to sign an informed consent form prior to an interview. Interviews occurred at a time and place that was mutually agreed upon by the researcher and the participant. Some interviews occurred in a deserted coffee shop after a shift, others occurred in a private space during a lunch break, or during quieter moments of a shift.
Data Collection and Tools
Survey measures included the Patient-Centred Care measure (PCC) (Sidani et al., Reference Sidani, van Soeren, Hurlock-Chorostecki, Reeves, Fox and Collins2016), and the Modified Index of Interdisciplinary Collaboration (MIIC) (Oliver, Wittenberg-Lyles, & Day, Reference Oliver, Wittenberg-Lyles and Day2007). The PCC measure is a 20-item 6-point Likert type scale ranging from 0 to 5 based on three elements: holistic, collaborative, and responsive care (Sidani et al., Reference Sidani, Collins, Harbman, MacMilan, Reeves, Hurlock-Chorostecki and van Soeren2014; Sidani et al., Reference Sidani, van Soeren, Hurlock-Chorostecki, Reeves, Fox and Collins2016). This tool was developed and validated in the Canadian context (Sidani et al., Reference Sidani, Collins, Harbman, MacMilan, Reeves, Hurlock-Chorostecki and van Soeren2014; Sidani et al., Reference Sidani, van Soeren, Hurlock-Chorostecki, Reeves, Fox and Collins2016). The closer the score is to 5, the more patient-centred the response. The MIIC is a 42-item index with four subscales that represent the six domains of interprofessional collaboration: (a) interdependence, (b) flexibility, (c) newly created professional activities, (d) collective ownership of goals, (e) reflection on process, and (f) reflection on interprofessional collaboration; with questions on a 5-point Likert type scale ranging from 1 to 5 (Hong, Bainbridge, & Seow, Reference Hong, Bainbridge and Seow2015, Oliver et al., Reference Oliver, Wittenberg-Lyles and Day2007). The MIIC has also been used and validated in the Canadian context (Hong et al., Reference Hong, Bainbridge and Seow2015). The closer to 5 an item is rated, the more the statement aligns with interdisciplinary collaborative practice. The PCC measure and the MIIC both demonstrated internal consistency reliability in the study sample (alpha coefficients = 0.85 and 0.91 respectively).
Individual and group interviews were conducted so that we could understand participants’ experiences and perceptions about working in teams providing care for older adults. Participants were given the choice of participating either alone or in groups. We asked participants in group interviews to keep confidential any comments that were shared within the group. A semi-structured interview guide informed by survey results and researchers’ knowledge of interprofessional literature was used to examine perceptions about working with hospitalized older people in interprofessional teams. The semi-structured interview guide included the following questions: How would you describe interprofessional collaboration on your unit? How would describe your ability to meet the needs of older patients? What supports your ability to meet the needs of older patients? What supports interprofessional collaboration on your unit? What are the challenges related to meeting the needs of older patients? What are the challenges to interprofessional collaboration? Depending on participants’ responses, we posed further probes to gain a fuller understanding of participants’ experiences. The lead researcher conducted all of the interviews, which were audio-recorded and then transcribed verbatim. Pseudonyms are used in this article to protect confidentiality of participants.
Data Analysis
Missing survey data were handled by listwise deletion, and we used descriptive statistics to examine central tendency and variance of data. Based on the lower numbers of other professionals (PTs, OTs, RAs, and SPs) compared to nursing staff, we created two groups: nursing staff and other professional staff. With independent sample t-tests, we compared the means of nursing and other professional staff on the overall scale scores and individual item scores of the PCC measure and the MIIC. Levene’s test for equality of variances was applied in order to determine if the homogeneity of variances assumption was met prior to running the t-tests (Pallant, Reference Pallant2010). We calculated effect sizes using eta-squared to determine the magnitude of the between-group differences. As proposed by Cohen, 0.2 = small effect size, 0.5 = moderate effect size, and 0.8 or greater = large effect size (Field, Reference Field2016). Levels of significance were set at p values less than or equal to .05. We also examined the means of items that were not significantly different but were related to teamwork.
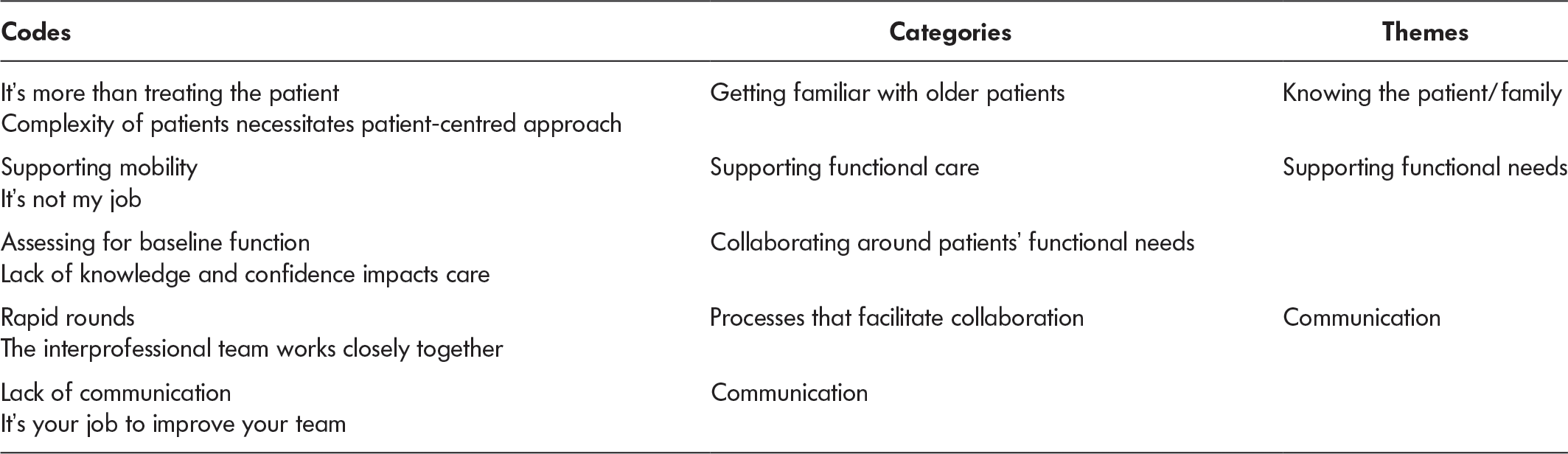
We analysed qualitative data using content analysis, to provide a description of the phenomena whereby the researcher is situated in close proximity to the data and focuses on both subject and context (Graneheim & Lundman, Reference Graneheim and Lundman2004; Graneheim, Lindgren, & Lundman, Reference Graneheim, Lindgren and Lundman2017; Sandelowski, Reference Sandelowski2000). Two of the researchers coded the data using Microsoft Word documents. Similarities and differences within codes and categories were noted by these two researchers and used to develop themes. The themes were circulated among all six members of the research team. Further discussion among the research team enhanced the development of themes that explained perceptions about patient-centred care and interprofessional collaboration in the context of working with hospitalized older adults. The first two authors examined the differences and similarities of the team members’ perspectives and agreed on the themes as described below.
Rigor
To ensure the rigor of our mixed-methods approach, we used Eckhardt and DeVon’s (Reference Eckhardt and DeVon2017) MIXED framework which includes attention to the criteria of method, inference, expertise, evaluation, and design choice. We described our study design method as well as our sampling method. We addressed the criterion of inference by involving all researchers in data analysis and ensuring that findings clearly reflected the data. The expertise criterion was satisfied by our research team’s knowledge and skill with the survey tools and data analysis methods. The evaluation criterion was attended to through our attention to trustworthiness, and our inclusion of a framework to evaluate mixed methods. Finally, we addressed the criterion of design choice by clearly articulating how we employed the triangulation convergence model to explicate the phenomenon we studied. Credibility was enhanced by the attention researchers paid to analysis as illustrated by Table 1. We attended to transferability and dependability by maintaining an audit trail of our decisions made during data collection and analysis (Lincoln & Guba, Reference Lincoln and Guba1985; Wolf, Reference Wolf and Munhall2012). Confirmability was promoted through maintaining a reflexive stance about our inquiry. We compared our findings with literature about interprofessional practice to enhance confirmability (Creswell, Reference Creswell2009; Creswell & Plano Clark, Reference Creswell and Plano Clark2007).
Table 1: Nursing staffs’ perceptions of their learning needs
Findings
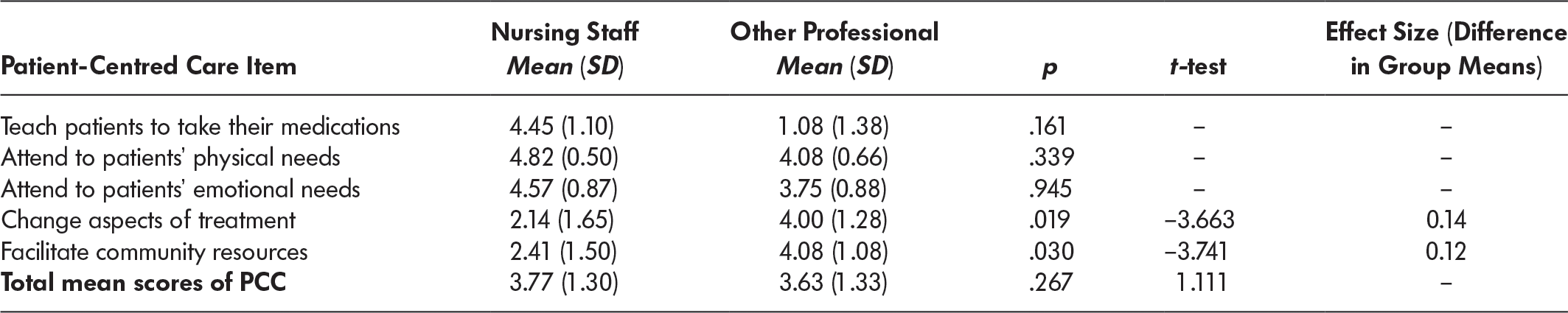
In total, 34 (22 nursing and 12 other disciplines) of 97 eligible staff responded to the survey for a response rate of 35 per cent. There were minimal missing data. The mean (SD) score for the PCC was 3.70 (1.33) indicating perceptions of patient-centred care between neutral and agree. A two-tailed independent t-test compared the mean scores of the nursing staff (µ = 3.75, SD = 1.30) and the other professionals (µ = 3.63, SD = 1.33). The alpha level was set to 0.05, equal variances were assumed, and results showed no significant differences between the two groups (t [675] = 1.111, p = 0.267). Two of the individual items for the PCC were statistically significant for the two groups; these related to changing aspects of patients’ treatment and facilitation resources for patients. A two-tailed independent t-test compared the mean scores of the nursing staff (µ = 2.14, SD = 1.65) and the other professionals (µ = 4.00, SD = 1.28) related to changing aspects of patients’ treatment. The alpha level was set to 0.05, equal variances were not assumed, and results showed a significant difference between the two groups (t [27.86] = –3.663, p = 0.019). The effect size for the difference was minimal at 0.14.
A two-tailed independent t-test compared the mean scores of the nursing staff (µ = 2.41, SD = 1.50) and the other professionals (µ = 4.08, SD = 1.08) related to facilitating community resources for patients. The alpha level was set to 0.05, equal variances were not assumed, and results showed a significant difference between the two groups (t [29.27] = –3.741, p = 0.03). The effect size for the difference was minimal at 0.12. Of note, nursing staff scored high in items such as teaching patients about medication 4.45 (1.10), and tending to the emotional (4.57 [0.87]) and physical (4.82 [1.10]) needs of patients. Other professionals also scored high on attending to patients’ physical needs (4.08 [0.66]); see Table 2. The PCC measure answered our second research question about interprofessional staff’s perceptions about their ability to provide patient-centred care. Two items related to changing aspects of patients’ treatment and facilitating community differences for patients were rated significantly differently between the two groups (nursing staff and other professionals), with the other professionals scoring higher than the nursing staff.
Table 2: Patient-centred care results (PCC)
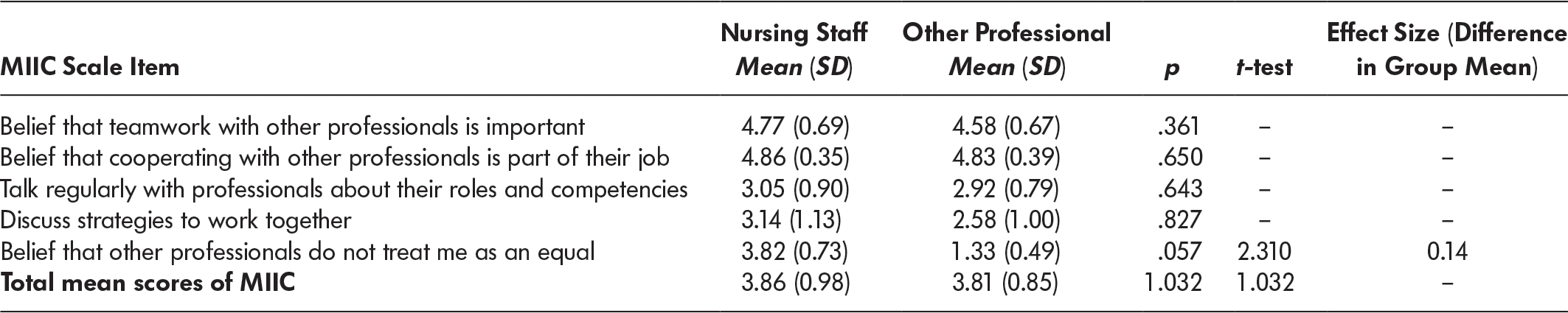
The mean (SD) total score for the MIIC was 3.84 (0.94) indicating that the average participant reported positive interprofessional collaboration between neutral and agree. A two-tailed independent t-test compared mean scores of the nursing staff (µ = 3.86, SD = 0.98) and the other professional members (µ = 3.81, SD = 0.85). The alpha level was set to 0.05, and equal variances were not assumed. Results showed no significant differences between the two groups (t [1156.72] = 1.032, p = 1.032). One item on this scale showed a significant difference between the two groups: a two-tailed independent t-test compared mean scores of the nursing staff (µ = 3.82, SD = 0.73) and of the other professionals (µ = 1.33, SD = 0.49) related to the item believing other professionals treated them differently. The alpha level was set to 0.05, and equal variances were assumed. Results showed a significant difference between the two groups (t [32] = 2.31, p = 0.05). The effect size was small at 0.14. This suggests that nursing staff scored higher than other professionals in believing that other professionals do not treat them as equals.
Of note, both groups valued interprofessional collaboration as evident in their scores exceeding 4.5 in believing that teamwork is important and that cooperating with other professionals was part of their job. Yet both groups scored much lower, 3.1 or lower, in talking regularly with professionals about their roles and competencies and in discussing strategies to work together (see Table 3). Results from the MIIC answered our first question about interprofessional staffs’ perceptions about interprofessional collaboration. Only one item differed between the two groups (nursing staff and other professionals), and that was regarding the belief that other professionals treated them differently. Both groups scored high related to valuing interprofessional collaboration, and their scores were below a neutral response in discussing one another’s roles and strategies about how to work together.
Table 3: Modified Index of Interdisciplinary Collaboration (MIIC) results
Fourteen nursing staff participated in interviews to share their perceptions about working with hospitalized older adults in the context of interprofessional teams. Unfortunately, members of other professional groups informed the first author that they were not interested in being interviewed unless they were paid. Our funding agency as well as hospital policy did not allow us to pay participants for their time.
The following themes were generated by the content analysis: knowing the patient/family, functional needs, and communication processes (see Table 1). These themes provide both context for illustrating how we operationalized the concepts of interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care, and they also provide insight regarding our quantitative data.
Knowing the Patient/Family
Participants explained that, in order to provide individualized care, it was important to familiarize themselves with older patients and to navigate the families’ involvement with the older persons’ care. Participants identified that the complexity of providing patient-centred care in working with older adults required that they develop a foundational understanding of patients’ functional needs, of how functional needs fluctuated throughout a 24-hour period, and of biophysical needs. One participant described the need to “get so close we become familiar with their bowel routine, or the way they eat, and how much dinner they’ll eat and the secrets of how to get them to take their pills” (Sue, RN). Some participants highlighted the importance of talking to families to better understand, for example,
… the patient’s baseline at home. Is she eating [and] drinking? How does she take her medications? How does she walk? How does she go to the bathroom? How does she transfer? So that there is a continuity or we can ask for further assessment from the physiotherapy. (Dee, RN)
If nursing staff understood premorbid function, they were in a better position to tailor care and to engage other professionals to address the patient’s needs.
Supporting Functional Needs
Participants identified the importance of working with other professional team members with respect to supporting older patients’ functional needs. Functional needs (e.g., mobility, nutrition) were identified as requiring collaboration in order to provide care that focused on the patients’ needs. As one participant explained: “They are being assessed first by the physician, [then by] physiotherapy and occupational therapy. If you give them medication, you feed them, [and] you don’t mobilize them, they are not going to get better” (Dee, RN). Implicit in this description is the need for other professionals to be engaged in both assessment of the patient’s needs as well as engaging in care that supports the older adult’s functional needs as part of their recovery from the acute illness.
Supporting older patients’ functional needs started with an assessment. There were differing opinions among participants about whether nurses could assess function or whether or not another profession was needed. For example, one participant believed that “we [are] going to get a more accurate assessment if PT does it. We [nursing staff] might be able to assess basic mobility, but not what aids they might use” (Raj, RN). Raj identified that the type of walker or other aid to be prescribed was within the expertise of the physiotherapist. Another participant observed:
Nurses sometimes have the attitude that it’s not their job to assess mobility, whereas I think they can and it makes the mobilization faster. Sometimes there is the attitude, “Oh the physio hasn’t assessed them, so they are [on] bed rest.” (Peg, RN)
If older patients remained in bed because a PT was first needed to assess whether or not they could mobilize, they were at risk for de-conditioning and loss of function.
Communication
An essential element of providing patient-centred care was clear and effective communication between team members as well as with patients and their family members. As one participant summed up:
The whole interprofessional team communication is very important. When the patient or family asks you a simple question and they have already heard from the physician and you are not on the same page, they’re not really going to trust you. (Sam, LPN)
It was important that all of the professionals understood the plan of care and were giving the same message to patients and families so that they felt supported by the whole team.
Participants described their daily morning meeting as an effective way to facilitate the sharing of information and identification of the need to involve other professionals’ care. “The team meets in the morning, during rapid rounds, and it’s quite easy to get contributions from other members, or to get them involved if you need them involved, physios, OT, or pharmacy” (Peg, RN). These meetings were an efficient way of ensuring that the appropriate team members were involved, and of sharing pertinent information to facilitate optimal care. “We will discover [information about patients] in rapid rounds. I’ll be like ‘the patient is confused’ and they’ll [say] their daughter came in and said ‘my father was taking his car to the shop a week ago’” (Raj, RN). As this participant explained, rapid rounds provided information that could facilitate more effective patient-centred care. With an understanding of patients’ previous function status, staff had a better idea of how to support them in getting back to that level for discharge.
Participants also described communication gaps. They identified that each team member had a responsibility to communicate. If they did not believe that other members were sharing information needed to provide patient-centred care, then it was their responsibility to say something. “If you don’t feel like the communication is good, you have to speak up. It’s up to you to help your team improve” (Louise, RN). Identifying gaps in communication could facilitate team development, which would ultimately improve patient-centred care.
Discussion
There was no statistically significant difference between staff categories in overall scores for either the MIIC or PCC questionnaire. There were, however, statistical differences in the means between the two groups in two items on the PCC measure and one on the MIIC.
Nursing staff’s scores highlighted their emphasis in providing holistic care that focused on attending to patients’ physical, emotional, and social needs as well as teaching them how to take medications and manage their emotional stress. Conversely, other professionals’ scores identified their focus on changing aspects of patients’ treatment and facilitating community resources. These differences highlight the different roles of the professional groups in this setting. Kitson, Marshall, Bassett, and Zeitz’s (Reference Kitson, Marshall, Bassett and Zeitz2013) review and synthesis of the core elements of patient-centred care indicated that different professional groups tend to emphasise different elements of patient-centred care. For example, since nursing staff are responsible for assisting patients with physical and emotional needs (Besner, Reference Besner2006), they are more likely to highly rate those aspects of patient-centred-care. Moreover, nursing staff providing direct patient care on these units were not included in rounds related to discharge planning where other professionals and nurses involved in discharge planning (such as transition coordinators or unit managers) focus on the responsive elements of patient-centred-care. Since OTs and PTs are often in those meetings, it makes sense that those aspects of patient-centred care were rated more highly by other professionals.
The differences in the items on the MIIC highlight nursing staff’s perspective that they are not treated the same as other professional groups. Scholars have reported a belief held by nursing staff that they are there to serve other professionals (Matzke, Houston, Fischer, & Bradshaw, Reference Matzke, Houston, Fischer and Bradshaw2014). This helps to explain why nursing staff scored high on the item related to not being treated the same as other professionals. Effective interprofessional collaboration requires that individuals have both an in-depth understanding of what knowledge to transmit as well as the confidence to actually do so. Having the confidence to “speak up” might be difficult if the person required to do this feels low on the hierarchical structure found within hospitals. If nursing staff feel subservient to other disciplines, they may wait for other professionals’ assessments before engaging in activities that are shared among disciplines. For example, the qualitative data revealed that some nursing staff believed that they could not mobilize older patients until the PT had assessed the patients. Yet assessing patients’ ability to mobilize and then mobilizing patients are fundamental aspects of nursing care (Kitson et al., Reference Kitson, Marshall, Bassett and Zeitz2013) as well as within the disciplinary knowledge of PTs. An integrative review of the literature on nursing perceptions about mobilizing hospitalized older adults suggests nursing staff may believe that mobilizing patients is the PT’s job, not theirs (Constantin & Dahlke, Reference Constantin and Dahlke2018). This review also identified that when nursing staff received education about safely mobilizing patients, they were more likely to mobilize patients. Other researchers have reported improved patient outcomes when professionals worked together to provide early mobilization to patients in intensive care units (Morris et al., Reference Morris, Goad, Thompson, Harry, Passmore, Ross and Haponik2008; Needham et al., Reference Needham, Korupolu, Zanni, Pradhan, Colantuoni, Balmer and Fan2010).
All of the staff’s scores were high (over 4.5 in Table 3) and placed a high value on working with other professionals and in believing it was part of their roles. Yet they scored low on items related to facilitating the development of teams (e.g., talking with other professionals about their roles and how to better work together; see Table 3). This suggests they valued interprofessional collaboration. The qualitative data from nursing staff revealed a belief in rapid rounds as an effective process that supported interprofessional collaboration. Rapid rounds is an efficient process that occurs daily to provide opportunities for professional communication about the needs and discharge plans of patients (Geary, Cale, Quinn, & Winchell, Reference Geary, Cale, Quinn and Winchell2009; Ryan, Scott, Fields, Reference Ryan, Scott and Fields2017). Rapid rounds provided an opportunity for the interprofessional team to meet at patients’ bedsides to discuss patients’ progress and care plan, with each team member providing their disciplinary perspective. In the qualitative data, nurses emphasized the importance of communicating the information they had to share effectively within rapid rounds, requesting more information from other disciplines and working collaboratively. Research has suggested that implementation of rapid rounds improves interprofessional communication, coordination of patient care, reduction in errors and duplications, and staff satisfaction (Geary et al., Reference Geary, Cale, Quinn and Winchell2009; Ryan et al., Reference Ryan, Scott and Fields2017). Other scholars report that professionals view rapid rounds as being of too brief a duration to address patients’ concerns meaningfully (Baxter & Brumfitt, Reference Baxter and Brumfitt2008). Rapid rounds have been identified by nurses elsewhere as suitable to address narrow health issues, such as identifying falls risk, whereas weekly discharge planning rounds are perceived as more comprehensive and suitable to address older patients’ cognitive, physical, and psychosocial needs (Butler & Fox, Reference Butler and Fox2018). Direct care nursing staff on the three units did not participate in weekly discharge planning rounds. This helps explains why rapid rounds were perceived as more valuable to them in enhancing their collaboration with other professionals.
Despite both nursing staff’s and professionals’ perception that interprofessional collaboration was important and part of their work, both groups also reported a score lower than neutral about participating in processes where exploring one another’s roles and how to work better together occurred. Scholars who have studied interprofessional collaboration agree that there is a lack of understanding about the processes by which professionals communicate and collaborate with each other, (Jones & Jones, Reference Jones and Jones2011; Lemieux-Charles & McGuire, Reference Lemieux-Charles and McGuire2006; Paradis et al., Reference Paradis, Leslie, Puntillo, Gropper, Aboumatar, Kitto and Reeves2014; Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010). Reeves et al.’s (Reference Reeves, Lewin, Espin and Zwarenstein2010) interprofessional framework includes the relational, contextual, process, and organizational factors that influence the processes related to interprofessional collaboration. In our study, we are uncertain as to which of these factors may be influencing interprofessional collaboration. Researchers have suggested that professionals frequently collaborate informally (Baxter & Brumfitt, Reference Baxter and Brumfitt2008; Reeves et al., Reference Reeves, Rice, Conn, Miller, Kenaszchuk and Zwarenstein2009). It is unknown if our participants had informal collaboration within the interprofessional team. We suspect they likely did. Because of the lack of participation of professional groups other than nurses in interviews, we were unable to fully explore what unit processes other than rounds supported professional engagement in conversations about their disciplinary roles and how to work together more effectively. Further research is warranted to better understand how discussions about roles and working together could be incorporated into the units’ practices. Further inquiry should include physicians to gain a more complete picture of interprofessional collaboration.
After conducting a critical exploration of the discourses surrounding interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care, Fox and Reeves (Reference Fox and Reeves2015) suggested that equal participation in patient care processes is influenced by legislated scopes of practice, differing educational levels, differing remuneration processes, and institutional structures. They warn that although improved working relationships among professionals are valuable, they may “enhance inequitable relations of power” among members of the interprofessional team (Fox & Reeves, Reference Fox and Reeves2015, p. 116). A hierarchy can at times be an efficient and effective way to work within constrained health care environments. Perhaps what is needed is a balance between professionals’ spending time discussing how best to work together and spending time discussing patients’ needs.
Implications
Managers on individual units could facilitate supportive processes that provide opportunities for professionals to discuss each other’s roles and how best to work together. This could enhance interprofessional collaboration about patient-centred care. If patient-centred care is indeed the goal, then the contributions of each profession must be valued and respected. Accordingly, scholars have promoted interprofessional education as a necessary part of disciplinary education (Thom et al., Reference Thom, Heil, Lindsay, Croft, Duffy, Morgan and Johantgen2016). Organizations must likewise support interprofessional collaboration with continued education and processes that enhance understanding about the roles and contributions of each profession to patient-centred care.
Limitations
This study is limited by size and the fact that the qualitative data represent only the nursing staff’s perspective. Although other professionals were invited to participate in interviews, none did, stating they wished remuneration for participation. During information sessions, physicians were invited to participate, yet none participated and we are not certain as to why they did not participate. Thus, the findings cannot be generalized to other settings or to represent interprofessional collaboration among all professional groups. In future studies, we plan to use gift card incentives for participation as they have been found to increase participation (Kramer, Schmalenberg, & Keller-Unger, Reference Kramer, Schmalenberg and Keller-Unger2009). We also plan to discuss strategies on how to incorporate physician participation with the physician on our research team.
This study is also limited because we did not collect demographic information. Therefore, we cannot report the age, or professional designation, of the sample. Future studies should include questions about demographics. The nursing staff and other professional staff groups were not balanced in size, which may have led to a Type I error. Consequently, findings should be interpreted with caution. The findings do, however, raise questions about processes that contribute to professionals’ being able to discuss their unique roles and come to agreement about how to work together.
Conclusions
This study provided insights into professionals’ perspectives about the importance of interprofessional collaboration and patient-centred care, particularly as to how daily rapid rounds supported such collaboration for achieving patient-centred care. Interprofessional staff scored high in valuing interprofessional collaboration and below neutral related to talking with one another about how to best work together. We suggest that professional staff be supported to explore how to incorporate opportunities for professionals to discuss their unique roles and how to work better together. More inquiry into the role that the organizational context contributes to professionals’ ability to collaborate around patients’ concerns is warranted.





