Introduction
Subsequent to Norby (Reference Norby1976) restudying the type specimens of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 (Fig. 1) and describing newly collected bedding-plane assemblages of Lochriea commutatus (=Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]), several of which we refigure (Fig. 2), the conodont genus Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942 was used to accommodate an increasing number of species and the biostratigraphic zones they define, with only minimal taxonomic and historical underpinnings that led to this usage ever having been presented. Despite assurances (Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, p. 111) that “species of . . . Lochriea . . . are represented by bedding-plane assemblages, hence there are few mysteries about [their] skeletal anatomy,” Lochriea and its apparatus were not nearly as well known then and in the intervening years as Sweet implied. Thus, we provide the foundations and justifications for accommodating certain Carboniferous carminiscaphate P1 conodonts with unornamented or ornamented platforms, and the elements they were biologically associated with, in the genus Lochriea instead of in other genera, including Spathognathodus, Gnathodus, and Paragnathodus. We do so by tracing the generic assignments of the P1 elements of Lochriea commutata and related species, and by re-examining and documenting the element composition, and the number of elements in the apparatus of the type species of the genus Lochriea, Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b).

Figure 1. Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, holotype and paratype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]). Scanning electron micrographs and outline drawing of bedding-plane assemblages on black shale, with interpretation of conodont elements present. Specimens reoriented relative to views shown by Scott (Reference Scott1942), and elements on parts and counterparts numbered sequentially from top down. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA. Scale bars = 0.5 mm. (1, 2) Fecal assemblage of 18 elements; holotype, part and counterpart (i.e., + and − of Scott [Reference Scott1942, pl. 37, figs. 2, 6], respectively), UI X-1318; (3, 4) fecal assemblage of 23 elements; paratype, part and counterpart (i.e., + and − of Scott [Reference Scott1942, pl. 37, figs. 4, 5]), respectively. Part (+) lost; outline drawing (3) based on Scott (Reference Scott1942, fig. 4), UI X-1319.

Figure 2. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b). Scanning electron micrographs (1A, 1B, 2), photomicrograph (4), and line drawings (3, 5) of bedding-plane assemblages on black shale surfaces. Solid lines (3, 5) represent elements and dashed lines, represent imprints of elements. Heath and Tyler formations, Montana, USA. Scale bars = 0.5 mm. (1A, 1B) Natural assemblage of 15 elements in lateral collapse with some rotation of P element complex, numbered diagonally from the upper left to lower right. Only part (i.e., of part and counterpart) is illustrated. Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, ISGS 62P-207A. (2, 3) Natural assemblage of 15 elements in oblique lateral collapse pattern from the side (Purnell and Donoghue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), numbered from the top down. Part and counterpart, respectively, with P1 and P2 element pairs in apposition mostly preserved on part (2), with anterior end of P2?d element preserved on counterpart (3), which was drawn rather than photographed. More detail of S elements is shown on counterpart (3), although some M and S elements are only imprints. Sample H-B-1-B-1, Tyler Formation, locality 3, ISGS 62P-216A and 62P-216B. (4) Natural assemblage of 13 elements in oblique collapse from behind, above, and to one side (Purnell and Donoghue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), numbered from the top down. P1, P2, and Md elements are imprints. S element array is tightly clustered, preventing specific identification of six S elements present; anterior ends of elements 11S–13S further revealed by excavation subsequent to photo. Probable topotype, of which only part is known. Sample H-A-1-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, ISGS 62P-210. (5) Natural assemblage of 13 elements in apparent lateral collapse, but with disrupted architectural pattern, numbered consecutively from the mirror image axis (horizontal dashed line) outward; part (lower) and counterpart (upper) show some scatter. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, ISGS 62P-218A and 62P-218B.
Range and biostratigraphic utility of Lochriea
The genus Lochriea occurs in, and is restricted to, strata of Carboniferous age. Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012) concluded that the genus is monophyletic, biostratigraphically important, and that the first appearances of Lochriea species, and their transitions, are markers for global correlation (aspects of the latter were discussed by Somerville, Reference Somerville2008). Lochriea commutata and other species of Lochriea (some early listings were under the generic names Gnathodus and Paragnathodus) first appear at the base of the Viséan in Europe (Higgins, Reference Higgins, Neale and Brasier1981), in the Arundian of England (Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981; Stone, Reference Stone1991), in the lower Meramecian of North America (Krumhardt et al., Reference Krumhardt, Harris and Watts1996), and in strata of equivalent age elsewhere in the world.
The earliest occurrences of a species of the genus are Lochriea cracoviensis (Belka, Reference Belka1985), at the base of the Viséan in Poland (Belka, Reference Belka1985, chart), and L. cracoviensis and L. saharae Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse, and Weyant, Reference Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse and Weyant2006, from the lower Viséan of Algeria (Nemyrovska et al., Reference Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse and Weyant2006), both species appearing slightly before L. commutata in the latter country. The upper limit of species of Lochriea, including that of L. commutata, is in the earliest Bashkirian (lowermost Morrowan) of Ukraine (Nemirovskaya et al., Reference Nemirovskaya, Poletaev, Vdovenko, Brenckle and Manger1991), Uzbekistan (Nigmadganov and Nemirovskaya, Reference Nigmadganov and Nemirovskaya1992), south China (Wang et al., Reference Wang, Lane, Manger and Wang1987b), southwest Japan (Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997), Spain (Sanz-López and Blanco-Ferrara, Reference Sanz-López and Blanco-Ferrera2012), and the lower Namurian of Britain and Ireland (Higgins, Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, table 7; Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, chart 6). The type species, L. commutata, is long ranging (Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, chart 6) and is of biostratigraphic utility only in a local context. Lochriea commutata and L. homopunctatus (Ziegler, Reference Ziegler1960), were utilized by Metcalfe (Reference Metcalfe1981) and Varker and Sevastopulo (Reference Varker, Sevastopulo, Higgins and Austin1985) to define local-range zones. Other species, such as L. cracoviensis, L. mononodosa (Rhodes, Austin, and Druce, Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969), L. nodosa (Bischoff, Reference Bischoff1957), L. multinodosa (Wirth, Reference Wirth1967), and others, have a more limited range and are therefore stratigraphically more useful (Higgins and Wagner-Gentis, Reference Higgins and Wagner-Gentis1982; Belka, Reference Belka1985, chart; Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, chart 6). Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012) suggested that Lochriea homopunctatus is globally important for marking and recognizing the base of the Viséan, and they indicated that the first appearance of Lochriea ziegleri Nemirovskaya, Perret, and Meischner, Reference Nemirovskaya, Perret and Meischner1994, was under investigation as a marker for the Viséan/Serpukhovian boundary. Qi et al. (Reference Qi, Nemyrovska, Wang, Hu, Wang and Lane2018) provided occurrence data (fig. 2) for ten species of Lochriea at or near the Viséan/Serpukhovian boundary in south China; this data supports Sevastopulo and Barham (Reference Sevastopulo and Barham2014) and others in advocating for the use of the first appearance datum (FAD) of L. ziegleri as a definitive marker for the base of the Serpukhovian Stage. Qi et al. (Reference Qi, Nemyrovska, Wang, Hu, Wang and Lane2018, figs. 3, 4) also illustrated their interpretation of the evolutionary relationships among nine of the 10 Lochriea species recovered by them.
When Mizuno (Reference Mizuno1997) defined his new genus Neolochriea, he recognized four species, each of which was based solely on P1 elements. He interpreted the four species of Neolochriea from Japan to be closely related to Lochriea spp., their morphology and stratigraphic distribution leading him to conclude that Neolochriea evolved from Lochriea. The first appearance of these Neolochriea species in southwest Japan is well within the Bashkirian (Morrowan), and it is above the occurrence of L. commutata in Japan and elsewhere in the world. In Japan, L. commutata ranges into the basal Bashkirian (i.e., into the Declinognathodus noduliferous Zone) (Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997). Although it is known to range higher into the basal Bashkirian of the Donets Basin of the Ukraine (Nemirovskaya et al., Reference Nemirovskaya, Poletaev, Vdovenko, Brenckle and Manger1991) and south China (Wang et al., Reference Wang, Lane, Manger and Wang1987b), the occurrence of L. commutata in Japan (Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997) is higher than has been recorded from Europe or North America.
Taxonomic journey of Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942
Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 298) defined the conodont genus Lochriea as “natural conodont assemblages made up of hindeodells, spathognaths, prioniods, and prioniodells.” With the discovery by Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973, p. 58) of what they believed to be complete conodont animals containing in situ elements in functional position, they amended this definition slightly to “conodont-bearing animals in which conodonts are represented by hindeodellids, spathognathodids, neoprioniodids, and prioniodinids-ozarkodinids.”
Most conodont researchers have worked, and continue to work, on discrete elements recovered by breaking down sedimentary rock with acids and solvents. However, the preceding definitions of the apparatus composition of Lochriea species were based entirely on the study of rare bedding-plane assemblages and, 30 years later in the early 1970s, on conodontophages with elements of Lochriea and other conodont genera in their gut. This created a dichotomy between the taxonomy of ornamented and unornamented P1 conodont elements now accepted to be the P1 elements of Lochriea spp., and the taxonomy based on bedding-plane assemblages. Thus, starting in 1941, the year before Lochriea was first named, and continuing into the 1990s, those workers studying these ornamented and unornamented P1 elements generally assigned P1 elements that have a morphology similar or identical to those present in these rare bedding-plane assemblages to a variety of genera. The earliest of these assignments was by Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941a, Reference Branson and Mehlb), who assigned their new species commutatus to Spathognathodus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b). A year later, Scott (Reference Scott1942)—working at a time when neither a procedure nor an agreement had been established for how to reconcile taxonomies based on discrete isolated conodonts with the very same ones found in bedding-plane assemblages—bypassed Branson and Mehl's Spathognathodus commutatus in favor of his own Lochriea montanaensis.
Ironically, subsequent workers did their own bypassing of Scott's conclusions regarding the bedding-plane assemblage-based Lochriea in favor of the better established, perhaps simpler, and (at the time) less controversial single-element taxonomy, thereby sending Spathognathodus commutatus and some other similar platform elements on a circuitous and complex taxonomic journey. Thus, Hass (Reference Hass1953, p. 80) assigned his new species inornatus, a junior subjective synonym of commutatus, to Gnathodus Pander, Reference Pander1856, and recognized its similarity to Gnathodus commutatus, with Bischoff (Reference Bischoff1957, p. 22) apparently being the first to assign Spathognathodus commutatus to Gnathodus. This was followed by Ziegler in Flügel and Ziegler (Reference Flügel and Ziegler1957, p. 39), Serre and Lys (Reference Serre and Lys1960, p. 39), Wirth (Reference Wirth1967, p. 206), Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 95), Thompson and Goebel (Reference Thompson and Goebel1969, p. 23–24), Marks and Wensink (Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 258), Aisenverg et al. (Reference Aisenverg, Brazhnikova, Vassilyuk, Reitlinger, Fomina, Einor, Wagner, Higgins and Meyen1979, p. 48), Metcalfe (Reference Metcalfe1981), and Dong and Ji (Reference Dong and Ji1988, p. 50) also assigning commutatus to Gnathodus. Bischoff (Reference Bischoff1957), and others who followed, generally did not provide reasons for removing the species commutatus from Spathognathodus, although good reasons for doing so are that: (1) Spathognathodus, a replacement name for the previously occupied Spathodus Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1933, had become a catch-all genus used for a very broad range of bladed P1 conodont elements in animals that evolved over long periods of geologic time; (2) Lochriea commutata P1 elements are morphologically distinct from most spathognathodid P1 elements by having a blade with more uniform denticulation and a subcircular posteriorly-positioned basal cavity; and (3) Spathognathodus primus Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1933, the type species of Spathognathodus, is a middle Silurian multielement conodont species, with its own complex nomenclatural evolution from Spathognathodus primus to Hindeodella confluens (Jeppsson, Reference Jeppsson1969, p. 15), to Ozarkodina typica (Klapper and Philip, Reference Klapper and Philip1971, p. 441, 443), to O. confluens (Klapper, Reference Klapper and Ziegler1973, p. 211, 221), and back to O. typica (see Murphy et al., Reference Murphy, Valenzuela-Rios and Carls2004, for a revision of Silurian spathognathodids). Because the apparatus for O. typica is well known and restricted to the Silurian, neither Spathognathodus nor Ozarkodina can be used to accommodate the Carboniferous species Lochriea commutata.
Among the new conodont species and subspecies, based on P1 elements with or without ornamentation that were being assigned to Gnathodus, were the subspecies Gnathodus commutatus nodosus Bischoff (Reference Bischoff1957, p. 23) and G. commutatus multinodosus Wirth (Reference Wirth1967, p. 208), as well as the species G. glaber Wirth (Reference Wirth1967, p. 210, 211) and G. mononodosus Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 103). However, by the late 1960s, some or all of these gnathodontids were increasingly understood to be morphologically and phylogenetically distinct from species with more complex ornamented P1 elements, such as G. bilineatus (Roundy, Reference Roundy, Roundy, Girty and Goldman1926) and G. girtyi Hass, Reference Hass1953. The result was the informal (Meischner, Reference Meischner1970), and then the formal (Higgins, Reference Higgins1975), naming of the genus Paragnathodus for some of these conodont species. Paragnathodus was first used as a nomen nudum by Meischner (Reference Meischner1970, p. 1173, 1177, fig. 2); Higgins (Reference Higgins1975, p. 70) subsequently defined the genus, with Paragnathodus commutatus as the type species, as follows: “The unit consists of a subrectangular blade and carina and a low, subcircular to subquadrate posterior cup. The oral surface of the blade is denticulate and is not clearly distinguished from the carina; the denticles of the blade increase in width posteriorly when seen in oral view. The aboral side of the cup is excavated.”
The genus Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942, initially based on rare bedding-plane assemblages, was exhumed, in a sense by, Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973) when they named conodontophages containing Lochriea sp. elements in their gut, Lochriea wellsi. Shortly thereafter, Norby (Reference Norby1976, p. 140) brought the genus into taxonomic play when, recognizing the priority of Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) over Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, he applied this priority to designate L. commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) the type species of Lochriea. That conclusion, and the resulting action, required a conciliation of concepts based on bedding-plane assemblages and discrete platform elements—one more than three decades in the making.
Norby's work was not widely available and the generic designation Paragnathodus continued to be used, presumably by those who did not have access to, or who rejected Norby's conclusions. Thus, Higgins (Reference Higgins, Neale and Brasier1981, p. 39, fig. 4.3, 4.6) continued his earlier practice (Higgins, Reference Higgins1975, p. 70) of placing commutatus, nodosus, mononodosus, and cruciformis in Paragnathodus, and adding multinodosus and glaber, the latter species apparently only in Higgins (Reference Higgins, Neale and Brasier1981, fig. 4.6). In that study, he recognized and defined a Paragnathodus nodosus conodont zone in the Brigantian (early Carboniferous) of Britain. In subsequent work, Higgins (Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, pl. 6.1, figs. 7, 8, 11, 12) also placed commutatus and mononodosus in Paragnathodus.
By 1982, Higgins (in Higgins and Wagner-Gentis, Reference Higgins and Wagner-Gentis1982) recognized the probable synonymy of Paragnathodus and Lochriea and commented (p. 335) that “the composition of the multi-element genus [Paragnathodus] is unknown but it is likely to correspond to the natural assemblage Lochriea of Scott Reference Scott1942.” Higgins (Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 214–215) subsequently assigned commutata and mononodosa to Lochriea; however, he continued to recognize Paragnathodus by placing nodosus in that genus while noting that Varker and Sevastopulo (Reference Varker, Sevastopulo, Higgins and Austin1985) assigned that species to Lochriea (Higgins, Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 215, pl. 6.1, fig. 9 [caption under pl. 6.3, fig. 9]). In the same year, Grayson et al. (Reference Grayson, Davidson, Westergaard, Atchley, Hightower, Monoghan and Pollard1985, p. 169) assigned commutatus from southern Oklahoma to Paragnathodus. Belka (Reference Belka1985, p. 40) recognized and described a new species of Paragnathodus, P. cracoviensis, and the next year von Bitter et al. (Reference von Bitter, Sandberg and Orchard1986) referred “simple-cupped gnathodontiform” conodonts to that genus. Krumhardt et al. (Reference Krumhardt, Harris and Watts1996) documented that Ji (Reference Ji1987), Riley et al. (Reference Riley, Varker, Owens, Higgins and Ramsbottom1987), Wang et al. (Reference Wang, Lane, Manger, Brenckle and Lane1987a), Wang and Higgins (Reference Wang and Higgins1989), Nemirovskaya et al. (Reference Nemirovskaya, Poletaev, Vdovenko, Brenckle and Manger1991), Varker et al. (Reference Varker, Owens and Riley1991), Nigmadganov and Nemirovskaya (Reference Nigmadganov and Nemirovskaya1992), and Alekseev and Kononova (Reference Alekseev, Kononova and Tikhomirov1993), among others, continued to assign commutatus to Paragnathodus, and we here add Yanagida et al. (Reference Yanagida, Ota and Sano1992) to that list.
Those authors who did have access to the unpublished work of Norby (Reference Norby1976), and agreed with his conclusion that Lochriea was the earliest valid generic designation available, began to use Lochriea, but without full documentation regarding why the name applies. Horowitz and Rexroad (Reference Horowitz and Rexroad1982, p. 966) may have been the first to do so when they reconstructed a partial apparatus of L. commutata from the Chesterian of the Illinois Basin based on statistical analysis, and when they attempted to extrapolate those results to L. mononodosa Rhodes, Austin, and Druce, Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969. By 1985, a number of authors had recognized either the utility, or the priority, of Lochriea. Varker and Sevastopulo (Reference Varker, Sevastopulo, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 174, 181–183, pl. 5.5, figs. 11–13, 16–18, 20) referred commutata, nodosa, and mononodosa to Lochriea, and applied each of the species names to a conodont zone. They also followed Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 160) and Marks and Wensink (Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 266) in their designation of some M elements as Neoprioniodus montanaensis, and acknowledged (p. 202, pl. 5.6, fig. 13) that Neoprioniodus singularis (Hass, Reference Hass1953), an M element, was “probably the Ne element of Lochriea commutata.”
Norby and Rexroad (Reference Norby and Rexroad1985) discussed similarities and associations of Lochriea with Vogelgnathus. And for the first time, Higgins (Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 215, pls. 6.1, 6.3, and elsewhere) assigned commutata and mononodosa to Lochriea while, as noted earlier, continuing to place nodosus in Paragnathodus (Higgins, Reference Higgins, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 215, pl. 6.3, fig. 9). The next year, Mapes and Rexroad (Reference Mapes and Rexroad1986, p. 118) pointed out that the still widely used Paragnathodus was a junior synonym of Lochriea, an opinion subsequently shared by Stone (Reference Stone1991) and Skompski et al. (Reference Skompski, Alekseev, Meischner, Nemirovskaya, Perret and Varker1995). Mapes and Rexroad (Reference Mapes and Rexroad1986) described some elements of the L. commutata apparatus and noted the general agreement regarding the apparatus composition of the genus. Krumhardt et al. (Reference Krumhardt, Harris and Watts1996) supported the use of Lochriea and documented the gradual acceptance of the genus by numerous workers since 1986, including Armstrong and Purnell (Reference Armstrong and Purnell1987), Grayson (Reference Grayson and Ritter1990), Ramovš (Reference Ramovš1990a, Reference Ramovšb), Rexroad and Horowitz (Reference Rexroad and Horowitz1990), Whiteside and Grayson (Reference Whiteside, Grayson, Suneson, Campbell and Tilford1990), Weibel and Norby (Reference Weibel, Norby, Sutherland and Manger1992), Kolar-Jurkόvsek and Jurkόvsek (Reference Kolar-Jurkόvsek and Jurkόvsek1993), Nemirovskaya et al. (Reference Nemirovskaya, Perret and Meischner1994), and von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb). We add Purnell (Reference Purnell1992) and Varker (Reference Varker1994) to this list, but make no claim that the citations before or after 1996 are either exhaustive or complete.
Lochriea commutata, parataxa, and a natural taxonomy governed by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), the type species of the genus, remains one of the most consistently recognized Carboniferous conodont species, despite its generic journey from Spathognathodus to Gnathodus to Paragnathodus to Lochriea. The principal aspect that prevented placement of commutatus in Lochriea, and indeed its recognition as the type species of Lochriea prior to Norby (Reference Norby1976), was that most Carboniferous conodont workers were working with discrete conodont elements rather than with the much rarer bedding-plane assemblages. A second reason is that the diagnoses of Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 298) and of Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973, p. 58) failed to recognize and acknowledge that elements present in bedding-plane assemblages, or in the gut of conodontophages (Conway Morris, Reference Conway Morris1985, Reference Conway Morris1990; Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, p. 28), had previously been identified and named. Specifically, although Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 300) was probably aware of Branson and Mehl's (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) publication that included a description of Spathognathodus commutatus, he failed to recognize and acknowledge that the “spathognaths” present in Lochriea were both known and named. This resulted in the decades-long use of a dual nomenclature: one based on bedding-plane assemblages or similar uncommon material, and the other based on discrete elements.
Scott (Reference Scott1942, Reference Scott1973) and Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973), studying what they thought were whole taxa, were undoubtedly aware of earlier publications, but, in the thinking of the times, they bypassed the priority of previously named discrete conodonts. Considerable debate had arisen before (e.g., Croneis, Reference Croneis1939) and after (e.g., Moore, Reference Moore, Hass, Häntzschel, Fisher, Howell, Rhodes, Müller and Moore1962), but little agreement was found in how to deal taxonomically with fragmentary versus whole fossil material. One of the proposed solutions was to create and use parataxa (i.e., to maintain a parallel but taxonomically separate classification system independent of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature [ICZN]) for fragmentary fossils such as crinoid ossicles, holothuroid spicules, fish remains, and conodonts. With conodonts the problem was twofold. The first was how to name discrete, individual elements, whether that was according to their shape, denticulation, or other criteria. And second, after conodont bedding-plane assemblages were discovered and named first by Hinde (Reference Hinde1879), and subsequently by Scott (Reference Scott1934) and Schmidt (Reference Schmidt1934b), the question arose of whether the names of previously named discrete conodonts should have nomenclatural priority, when several different kinds of already named conodont elements were present in bedding-plane assemblages. Scott (Reference Scott1942) and fellow conodont workers before and after him were undoubtedly aware of this dilemma and gave it much thought; however, being unable to untie this particular taxonomic Gordian knot, they bypassed previously named taxa based on discrete conodont elements and created new taxonomic categories based on bedding-plane assemblages. Thus, Scott (Reference Scott1942) named Lewistownella for bedding-plane assemblages that contained the earlier-named diagnostic platform element Cavusgnathus Harris and Hollingsworth, Reference Harris and Hollingsworth1933, also bypassing the earlier-named species Spathognathodus commutatus when he named Lochriea montanaensis. As late as a decade later, Rhodes (Reference Rhodes1953) named Scottognathus on the basis of bedding-plane assemblages from the Pennsylvanian of Illinois, bypassing the Law of Priority set by the ICZN, even though Gunnell (Reference Gunnell1931) and Stauffer and Plummer (Reference Stauffer and Plummer1932) had previously named the diagnostic platform elements present in these assemblages Idiognathodus and Streptognathodus, respectively. Much the same situation prevailed with the recognition and naming of Illinella and Duboisella based on bedding-plane assemblages, while avoiding the available and earlier-named Gondolella Stauffer and Plummer, Reference Stauffer and Plummer1932 and Idioprioniodus Gunnell, Reference Gunnell1933, respectively (Rhodes, Reference Rhodes1952).
Conodont workers and other paleontologists of the time continued to wrestle with the paleontological angst created by the question of how to deal taxonomically with isolated fragmentary fossil remains. One result was the proposal to the ICZN by Moore and Sylvester Bradley (Reference Moore and Sylvester-Bradley1957a, p. 5) for the recognition and use of parataxa “as a special category for the classification and nomenclature of discrete fragments or of life-stages of animals which are inadequate for identification of whole-animal taxa, with proposals of procedure for the nomenclature of Parataxa” (see Moore and Sylvester Bradley, Reference Moore and Sylvester-Bradley1957b, regarding the application of parataxa to conodonts). Rhodes (Reference Rhodes, Hass, Häntzschel, Fisher, Howell, Rhodes, Müller and Moore1962, p. W82) described the rather hasty rejection of this proposal by the ICZN in 1958, noting that the body “offered no alternative solution” and that “this action leaves conodont nomenclature in a confused and unstable position.” In discussing the taxonomic problems of a dual nomenclature, Rhodes (Reference Rhodes, Hass, Häntzschel, Fisher, Howell, Rhodes, Müller and Moore1962, p. W81) favored giving “new names to natural conodont assemblages and to retain the existing system of nomenclature for isolated conodonts.” Moore (Reference Moore, Hass, Häntzschel, Fisher, Howell, Rhodes, Müller and Moore1962, p. W92–W97) discussed the illegality of a dual classification and suggested adopting a conservative course such that “species, genera and families distinguished on the basis of discrete conodonts . . . are to be regarded as “natural” taxa, and the species and genera defined on the basis of conodont assemblages likewise.”
The summary refusal of the ICZN may, however, have had the beneficial effect of forcing conodont workers to try harder to reconstruct apparatuses from collections of discrete conodont elements, and to name them according to the priority of the most characteristic named element, generally, but not always, the P1 element. Simultaneous with the debates for and against the use and legality of parataxa, the stirrings of a revolution in conodont taxonomy were taking place in Germany. Here, Tatge (Reference Tatge1956) and Huckriede (Reference Huckriede1958), studying Triassic conodonts, and Walliser (Reference Walliser1964), working on Silurian conodonts, grouped discrete conodonts into tentative apparatuses, but without formally naming them.
By the mid-1960s, American Ordovician conodont workers Webers (Reference Webers1966) and Bergström and Sweet (Reference Bergström and Sweet1966) not only reconstructed apparatuses from discrete conodont collections, but also named them in conformity with the ICZN Law of Priority. Clearly, the revolution in conodont taxonomy was taking hold, and at the 1971 Symposium on Conodont Taxonomy, the Marburg Proposal (Aldridge and von Bitter, Reference Aldridge, von Bitter and Over2009, appendix II), with F.H.T. Rhodes as its prime mover, and its strong emphasis on strict application of the ICZN Code, passed with no further mention of parataxa. Some of the younger Carboniferous conodont workers who participated in the Marburg Symposium, or whose better-financed PhD advisors were there to later pass the ideas and recommendations of that meeting on to their students, correctly read the taxonomic winds that were blowing in conodont taxonomy. They did this by taking up the challenges of multielement taxonomy, and in quick succession (von Bitter, Reference von Bitter1972; Baesemann, Reference Baesemann1973; Perlmutter, Reference Perlmutter1975; Norby, Reference Norby1976) began to reconstruct conodont apparatuses, and gave priority to the earliest validly named genus name, such as Streptognathodus, Idiognathodus, Cavusgnathus, and Gondolella, irrespective of how whole or fragmentary the original material used to describe these genera had been. Subsequent to 1971, even though students of some other fossil groups decided to continue to use parataxa, conodont workers overwhelmingly distanced themselves from parataxa and agreed to use a natural taxonomy governed by the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. This group decision by members of the Pander Society was subsequently recognized by the ICZN (Melville, Reference Melville1981).
Among bedding-plane assemblage-based generic names, such as Scottognathus, Duboisella, and Illinella, practically none are now used or invoked by Carboniferous conodont workers. All three are junior synonyms of earlier named taxa and are now mostly of historical interest. Lochriea, however, is the exception and survives because, unlike these three named bedding-plane assemblages, no previously assigned competing Carboniferous generic name based on discrete element taxonomy was, and is, available.
Taxonomic notes
We conclude, as did Norby (Reference Norby1976), that Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) is the senior subjective synonym of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 and that the two are combined as L. commutata according to priority and availability. First and foremost, that conclusion is based on our detailed comparison and documentation (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a; Fig. 3) of the overall morphology of P1 elements in the type specimens of L. montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 with the P1 elements that are the type specimens of Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a; Fig. 3), and of a wide range of P1 elements from across North America and Europe (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a; Fig. 3). Our determination, based on this wide-ranging material, is that no apparent differences exist in overall P1 morphology of the two taxa. Although the P1 elements of the type specimens of Lochriea montanaensis tend to be longer than those of L. commutata, this observation has yet to be confirmed statistically. Discrete P1 elements from the Heath Formation and from the overlying Tyler Formation of Montana, show considerable variation in morphological features such as the length and number of denticles, variation that we regard as normal phenotypic variation; however, further study may determine that this variation is ecophenotypic, and may be due to environmental differences during the deposition of the Heath and Tyler formations.

Figure 3. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) P1 elements in bedding-plane assemblages on black shale (1–6), as acid residue-derived discrete elements (7–34), and in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (35). All are scanning electron micrographs except (3), which is a photomicrograph. Scale bars (1–6, 35) = 0.2 mm; for the remaining figures, actual specimen lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1) P1s,d element pair in functional apposition, lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus; element pair rotated ~90° from original functional position in apparatus. Anterior ends of elements on right side of figure, posterior on left. See elements 1P1?s and 2P1?d (Fig. 2.2) for apparatus context of P1s,d element pair. Splotchy mottled surface attributable to uneven scanning electron micrograph coating, charging, or both. Sample H-B-1-B-1, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P- 216A. (2) P1s,d element pair in ‘near’ functional position in lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus with anterior ends of elements on right, posterior ends on left. P1s element both ‘flipped’ and rotated ~135° relative to its original functional apposition with P1d element. See elements 1P1s and 2P1d (Fig. 2.1A) for apparatus context of this element pair, and see element 4P2d (Fig. 2.1A) for apparatus context of anterior part of the P2d element on bottom left. Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-207A. (3) P1s,d element imprint pair in ‘near’ functional position, lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus, P1?s (upper) element rotated 180° relative to its original functional apposition with P1?d (lower) element. P1?d element a good imprint, P1?s element a partial imprint only. See elements 1P1?s and 2P1?d (Fig. 2.4) for apparatus context of the P1s,d element pair. Sample H-A-1-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-210. (4) P1s element (in) Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 holotype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]), outer view. See element 2P1s (Fig. 1.1, 1.2) for apparatus context. Previously illustrated by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 2.1, counterpart). Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1318. (5) P1?d element (in) Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 holotype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]), outer view. See element 11P1?d (Fig. 1.1, 1.2) for apparatus context. Previously illustrated by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 2.2). Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1318. (6) P1?d element, (?) inner view. Heath Formation, locality 1, Montana, USA, CM 33965. (7–10) P1s element, upper, lower, outer, and inner views, respectively, of a syntype of Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b). Designated as one of four cotypes and illustrated (with incorrect number UM C552-1) by Lane and Straka (Reference Lane and Straka1974, figs. 40.15, 40.16); catalogue no. UM C552-2 apparently applied by or at UM for series of four syntypes. Re-illustrated and designated lectotype (UM C552-2) of the species (other three specimens designated as paralectotypes and given new numbers) by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 2.6–2.9). Hindsville Formation, locality 4, Oklahoma, USA. Length = 0.91 mm. (11–18) P1s elements (14, 16–18) and P1d elements (11, ?12, 13, 15), upper views of approximate ontogenetic growth series from least to most mature. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1088 to 62P-1092, and 62P-1094 to 62P-1096. Lengths = 0.63, 0.89, 1.00, 0.82, 0.78, 0.62, 0.68, and 0.63 mm, respectively. (19–21) P1d (19), P1?d (20), P1?d (21) elements, upper views of three elements from most to least mature. Samples VS-1, VS-12, and VS-12, respectively, Ridenhower Formation, locality 7, Illinois, USA, ISGS 62P-1201, 62P-1202, and 62P-1093. Lengths = 0.55, 0.47, and 0.43 mm, respectively. (22–27) P1s (22, 23, 26) and P1d (24, 25, 27) elements, upper views of a potential ontogenetic growth series from most to least mature. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593924–593928 and 696950. Lengths = 0.61, 0.60, 0.55, 0.62, 0.61, and 0.43 mm, respectively. (28) P1d element, upper view. Sample Kenk-2-1, Kennetcook Member, Upper Windsor Group, locality 9, Colchester County, Nova Scotia, Canada, ROM 63699. Length = 0.75 mm. (29, 30) P1d elements, upper views. Sample Schälk 42, Herdringen Formation, locality 10, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, ISGS 82P-53 and ISGS 82P-54, respectively. Lengths = 0.54 and 0.37 mm, respectively. (31) P1d element, inner view. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1101. Length = 0.79 mm. (32, 34) P1d element, upper and inner (caudal) views, respectively. Illustrated by Lane and Straka (Reference Lane and Straka1974, fig. 37.1, 37.2), Goddard Formation, locality 6, Oklahoma, USA, SUI 33624. Length = 0.94 mm. (33) P1?d element, (?) inner view of immature element, Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1097. Length = 0.44 mm. (35) P1?s element in ?upper view at posterior end of partial, fused S element array (see Fig. 9.21 for another view of this fused cluster). Apparatus showing several S elements of apparatus inclined toward one another. Collection USGS 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593966.
Second, our conclusion is based on our earlier determination (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994b) that the well-developed microsculpture on the carinal denticles of P1 elements of the type specimens of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, is not a defining characteristic of that taxon. Although this feature is obscured by diagenetic overgrowths on the lectotype and the paralectotypes of Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a), that feature is present and was documented in the same study on more recently collected topotypes of S. commutatus. Additionally, P1 elements of this morphology from a wide range of locations, including those from the Heath and Tyler formations of Montana, the Fayetteville Formation of Oklahoma, and the Herdringen Formation of Germany, exhibit this microsculpture (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb).
The weight of evidence supporting our conclusion that Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 is a subjective junior synonym of Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), was based initially (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a) on our comparison of the characteristics, particularly the micromorphology, of their P1 elements. Conodont P1 elements had long been regarded as the most diagnostic and most quickly evolving elements, and S. commutatus was, when described and named by Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), based solely on P1 elements. We (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a) determined that the macro- and micromorphology of the P1 elements of the two species were identical, concluding that they were synonyms of each other, and with the genus name Lochriea and the species name commutatus each having priority, that its correct name was, after amending the species name ending, Lochriea commutata. We here extend our documentation of L. commutata P1 elements by illustrating specimens from the United States, Canada, and Germany (Fig. 3), and re-illustrating the lectotype of Spathognathodus commutatus from its type stratum and type locality, the Hindsville Formation of Oklahoma at locality 4 (Fig. 3.7–3.10). We had previously illustrated both its lectotype and its three paralectotypes (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2.6–2.15, 3.1–3.12), as well as P1 elements from the overlying Fayetteville Formation at locality 5 (Sutherland and Manger, Reference Sutherland, Manger, Sutherland and Manger1979, fig. 2 correlation chart) (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 5.1–5.12).
Because L. montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, was based on bedding-plane assemblages that contained elements other than P1 elements, the key to confirming our earlier conclusion that L. montanaensis and S. commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) were synonyms of one another, lay in demonstrating that their non-P1 elements (i.e., their P2, M, S0, S1, S2, and S3/4 elements) were also identical. Thus, we re-collected the type locality and type stratum of S. commutatus, the Hindsville Formation at locality 4 in Oklahoma, from which we recovered a few P2, M, S0, and S3/4 elements that we identified as belonging to that species, as well as more than a dozen topotype P1 elements, and compared the non-P1 elements from there with the homologous elements in the type specimens of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 (Scott, Reference Scott1942, pl. 37, figs. 2, 4–6; here re-illustrated in Fig. 1). We continued this process of comparing and documenting non-P1 elements with those homologous elements in topotype specimens of that species collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976) from the Heath Formation, at locality 2, in Montana (Fig. 2). Finally, we examined and documented P2, M, S0, S1, S2, and S3/4 elements, which we here identify and label as those of L. commutata, from a variety of localities in the United States, Canada, and Germany (Figs. 4–9). One of these localities, the Fayetteville Formation at locality 5 in Oklahoma (Sutherland and Manger, Reference Sutherland, Manger, Sutherland and Manger1979, fig. 2), yielded characteristic and slightly better-preserved L. commutata P2, M, S0, and S3/4 elements (Figs. 5.15, 6.12, 9.17, 9.18) than the non-P1 elements we recovered from the Hindsville Formation at locality 4. We conclude, after examining and comparing lower Carboniferous conodont faunas from three countries on two continents, that the P2, M, S0, S1, S2, and S3/4 elements, like the P1 elements of the initially designated S. commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), the subsequently named L. montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, and those of the final combination, L. commutata, show surprisingly little variation within each of the non-P1 elements, confirming that L. montanaensis and L. commutata are indeed synonyms.

Figure 4. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) P2 elements in bedding-plane assemblages on black shale surfaces (1–7), in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (8, 17), and as acid residue-derived discrete elements (9–16, 18–23). All are scanning electron micrographs except (3), which is a photomicrograph. Scale bars (1–8, 17) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining figures, actual specimen lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1) P2s,d element pair in lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus, (upper) P2d element rotated ~135° relative to (lower) P2s element ‘in apposition’ position. See elements 4P2d and 5P2s (Fig. 2.1A) for apparatus context of P2s,d element pair. Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-207A. (2) P2s,d element pair view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus. Anterior part of P2?d element missing, but preserved on counterpart ISGS 62P-216B (Fig. 2.3). See elements 3P2?s and 4P2?d (Fig. 2.2, 2.3) for apparatus context of P2s,d element pair (however, P2s,d elements as shown in Fig. 2.2 are reversed relative to the position shown here). Sample H-B-1-B-1, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-216A. (3) P2s,d element pair in apposition in lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of apparatus. Lower P2?d element is imprint only. See elements 3P2?s and 4P2?d (Fig. 2.4) for apparatus context of P2s,d element pair. Sample H-A-1-1, locality 2, Heath Formation, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-210. (4) P2 element as (mostly) impression in ?inner view; only a few denticle tips of element preserved; posterior termination not preserved. See element 2P2 (Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218B. (5) P2?d element (in) Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 holotype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]) in ?inner view. See element 17P2?d (Fig. 1.1, 1.2) for apparatus context of this element. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1318. (6) P2 element in ?inner view, posterior tip broken and not present. See element 6P2 (lower Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218A. (7) P2?d element, ?inner view. Heath Formation, locality 1, Montana, USA, CM 33965. (8) P2s,d element pair in approximate functional apposition in lateral view along rostrocaudal axis of nearly complete sinistral side of a fused apparatus (see Figs. 5.4, 7.7 for other views of this element pair in this apparatus). USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM-593967. (9–16) P2 elements, ?outer lateral views of two ontogenetic growth series (9–12) and (13–16) from smallest to largest. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593929–593936. Lengths = 0.28, 0.54, 0.60, 0.70, 0.45, 0.45, 0.53, and 0.55 mm, respectively. (17) P2s,d element pair fused in functional apposition, lateral view. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593968. (18) P2d element, inner view. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1102. Length = 0.50 mm. (19–22) P2s elements, inner views. Samples VS-12, VS-5, VS-1, and VS-5, Ridenhower Formation, locality 7, Illinois, USA, ISGS 62P-1117, 62P-1205, 62P-1116, and 62P-1206. Lengths = 0.47, 0.52, 0.44, and 0.61 mm, respectively. (23) P2d element, inner view. Sample HerbR-7-7, Herbert River Limestone, Upper Windsor Group, locality 9, Nova Scotia, Canada, ROM 63700. Length = 0.73 mm.

Figure 5. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) M elements in bedding-plane assemblages (1–3), in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (4, 5), and as acid residue-derived discrete elements (6–22). Scale bars (1–5) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining specimens, actual lengths from cusp tip to anticusp are provided in descriptions below. (1) Md element in Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 holotype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]) in outer (dorsal) view. See element 18Md (Fig. 1.1, 1.2) for apparatus context. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1318. (2) Md element imprint in outer view. See element 15Md (Fig. 2.1B) for apparatus context. Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-207A. (3) Ms element in inner view, Heath Formation, locality 1, Montana, USA, CM 33965. (4) Ms,d elements in outer view of sinistral side of moderately complete apparatus (see Figs. 4.8, 7.7 for other views of this apparatus and element pair). USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593967. (5) Md element in outer view of moderately complete S–M element array (see Fig. 6.6, 6.7 for other views of this apparatus). USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593969. (6–9) Ms elements, inner views of well-preserved ontogenetic growth series. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593937–593940. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.69, 0.85, 0.81, and 0.57 mm, respectively. (10–13) Md elements, inner views of well-preserved ontogenetic growth series. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USNM 593941–593944. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.49, 0.84, 0.76, and 0.76 mm, respectively. (14) Md element, inner view. Sample Schälk 50, Herdringen Formation, locality 10, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, ISGS 82P-45. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.43 mm. (15) Ms element, inner view. Sample 2, Fayetteville Formation, locality 5, Craig Co., Oklahoma, USA, ISGS 82P-46. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.23 mm. (16, 17) Ms elements, inner views, showing crystal overgrowths and surface etching. Sample Kenk-2-1, Kennetcook Member, Upper Windsor Group, locality 9, Colchester Co., Nova Scotia, Canada, ROM 63701 and 63702, respectively. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.44 and 0.49 mm, respectively. (18) Ms element, inner view. Sample Schälk 50, Herdringen Formation, locality 10, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, ISGS 82P-47. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.82 mm. (19, 20) Md elements, inner views. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1112 and 62P-1113, respectively. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.43 and 0.65 mm, respectively. (21, 22) Md elements, inner view. Samples VS-12 and VS-7, Ridenhower Formation, locality 7, Illinois, USA, ISGS 62P-1111 and 62P-1207, respectively. Cusp tip to anticusp = 0.37 and 0.84 mm, respectively.

Figure 6. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) S0 elements in bedding-plane assemblages (1, 2), as acid residue-derived discrete elements (3–5, 11–14), and in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (6–10). Scale bars (1, 2, 7–10) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining specimens, actual lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1) S0 element, anterior view of anterolateral processes, with triangular bevel at base of cusp. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation (not Tyler Formation as per Norby, Reference Norby1976, pl. 11, fig. 15a), locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1103. (2) S0 element, lateral dextral view of cusp and broken stubs of posterior and dextral anterolateral processes. See element 11S0 (Fig. 2.1B) for the apparatus context of this element. Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-207A. (3–5) S0 elements, lateral sinistral views of an ontogenetic series showing a rarely preserved, long posterior process, and shorter sinistral and dextral anterolateral processes. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593945–593947. Horizontal lengths = 0.65, 0.55, and 0.50 mm, respectively. (6–10) S0 elements, USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA. (6, 7) S0 element in moderately complete sinistral and dextral fused S0-4 element array, lateral sinistral and dorsal views, respectively (see Fig. 5.5 for another view of this fused assemblage and of its S0 element), USNM 593969. (8, 9) S0 element with short symmetrical anterolateral processes and long posterior process in fused S element array, oblique dextroventral and ventral views, respectively, of the mostly sinistral side of the rostral apparatus, USNM 593970. (10) S0 element with short symmetrical anterolateral processes and long posterior process in fused S element array, ventral view. Arcuate indentation in upper left is the outline of the scanning electron microscopy mounting medium. USNM 593971. (11) S0 element, dextral view of broken anterolateral lateral and posterior processes, sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1104. Horizontal length = 0.51 mm. (12) S0 element, sinistral view of broken anterolateral and posterior processes. Sample 5, Fayetteville Formation, locality 5, Oklahoma, USA, ISGS 82P-48. Horizontal length = 0.16 mm. (13) S0 element, posterior view of symmetrical anterolateral processes and central stub of broken posterior process. Sample Schälk 50, Herdringen Formation, locality 10, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, ISGS 82P-49. Vertical height = 0.35 mm. (14) S0 element, sinistral view of broken anterolateral process and moderately complete, but relatively short posterior process. Sample VS-4, Ridenhower Formation, locality 7, Illinois, USA, ISGS 62P-1208. Horizontal length = 0.46 mm.

Figure 7. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) S1 elements in bedding-plane assemblages (1–4), in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (5–8), and as acid residue-derived discrete elements (9–18). Scale bars (1–8) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining specimens, actual lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1, 2) S1s element with long posterior process in outer lateral view (1, right), and broken-off anterior process in outer lateral view (1, left, and 2). Sample H-A-2-2, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1114. (3) S1s element in outer lateral view, with an unidentified S element, a remnant of a possible M element crossing the posterior process and a possible P2 element in upper left. See element 5S1s (bottom of Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context of this element. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218A. (4) S1d element stub in inner lateral view. See element 11S1d (upper Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context of this element. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218B. (5–8) S1 elements in fused assemblages. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA. (5, 6) S1d,s element pair in upper and lateral sinistral views, respectively; (6) is rotated around the rostrocaudal axis ~90° from (5), USNM 593972. (7) S1s,d element pair in lower (ventral) view in moderately complete fused apparatus (see Figs. 4.8, 5.4 for other views of this element pair and of this fused cluster), USNM 593967. (8) S1s element in lower (ventral) view with its posterior process fused in functional position against posterior process of S2s element. Partially complete but disrupted apparatus, USNM 593973. (9–18) S1 elements, acid residue-derived discrete elements. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, location 8, West Virginia, USA. (9–11) S1s element in inner views (9, 10) and in upper view (11), USNM 593948. Length = 1.18 mm. (12) S1s element in upper view, USNM 593949. Length = 0.76 mm. (13, 14) S1d element in inner views, USNM 593950. Length = 0.90 mm. (15–18) S1d element tilted to varying degrees in inner views (15–17) and in upper view (18), USNM 593951. Length = 0.93 mm.

Figure 8. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) S2 elements in bedding-plane assemblages (1–4), as acid residue-derived discrete elements (5–11), and in an acid residue-derived fused assemblage (12). Scale bars (1–4, 12) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining specimens, actual lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1, 2) ?S2d element in inner lateral view of anterior end of part and counterpart, respectively. See element 10?S2d (lower and upper Fig. 2.5, respectively), for apparatus context of this element. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218A and 62P-218B. (3) ?S2s element in inner view; see element 9?S2s (lower Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context of this element. Sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218A. (4) ?S2d element, Lochriea montanaensis Scott, holotype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]) in outer view of anterior end; see element 6?S2d (Fig. 1.1, 1.2) for apparatus context of this element. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1318. (5–11) S2s elements (5–7) and S2d elements (8–11) in inner views of two partial ontogenetic series. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593952–593958. Lengths = 1.13, 1.01, 0.86, 1.05, 1.02, 0.74, and 0.76 mm, respectively. (12) S2d element in inner view, fused against the inner surface of an S3d element, which is, in turn, fused against the inner surface of an S4d element. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593974.

Figure 9. Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) S3/4 elements in bedding-plane assemblages on shale surfaces (1–5), as acid residue-derived discrete elements (6–10, 12–20), and in acid residue-derived fused assemblages (11, 21). Scale bars (1–5, 21) = 0.2 mm. For the remaining specimens, actual lengths are provided in descriptions below. (1, 5) S3s and S4s element pair in inner views of part and counterpart, respectively. S3s element closest to viewer lacks most of posterior process, whereas S4s element behind S3s element is only an impression; see elements 7S4s and 8S3s (Fig. 2.5) for apparatus context of this element pair; sample H-A-2-7-1, Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-218A and 62P-218B. (2) S3/4d element, Lochriea montanaensis Scott, paratype (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]) in outer lateral view of anterior end; see element 1S3/4d (Fig. 1.3, 1.4) for apparatus context of this element. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1319. (3, 4) S3/4d element in outer view in S element array. Anterior end of S3/4d element in upper right, posterior end in lower left of (3); close-up of anterior end of S3/4d element in (4) (see element 12S3/4d in Fig. 2.1B for apparatus context of this and associated elements 11S0 and 13?S1s). Sample H-B-1-B, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-207A. (6–10) S3/4s elements in inner lateral views, forming a partial ontogenetic growth series. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593959–593961, 696951, 593962. Lengths = 1.44, 1.45, 1.21, 1.28, and 0.49 mm, respectively. (11) S3d and S4d element pair in inner view in partial fused assemblage; outer surface of S3d element fused in functional position against inner surface of S4d element (see Fig. 8.12 for an almost identical S3d and S4d element pair, except for the additional presence of an S2d element). USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 696952. Length = 1.16 mm. (12–14) S3/4d elements in inner views, that together with USNM 696952 (11) form a partial ontogenetic growth series. USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USA, USNM 593963–593965. Lengths = 1.31, 1.00, and 0.45 mm, respectively. (15–20) S3/4 elements in inner views of anterior ends. (15) S3/4s element. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1109. Length = 0.48 mm. (16) S3/4d element. Sample H-B-1-A, Tyler Formation, locality 3, Montana, USA, ISGS 62P-1107. Length = 0.29 mm. (17) S3/4s element. Sample 5, Fayetteville Formation, locality 5, Afton, Oklahoma, USA, ISGS 82P-50. Height = 0.21 mm. (18) S3/4s element. Sample 5, Fayetteville Formation, locality 5, Afton, Oklahoma, USA, ISGS 82P-51. Height = 0.24 mm. (19) S3/4s element. Sample Schälk 50, Herdringen Formation, locality 10, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, ISGS 82P-52. Height = 0.25 mm. (20) S3/4s element. Sample VS-7, Ridenhower Formation, locality 7, Illinois, USA, ISGS 62P-1209. Length = 0.38 mm. (21) S3/4s pair in ?upper (?dorsal) view of partial S element array (see Fig. 3.35 for another view of this fused cluster). USGS collection 34004-PC, Bluestone Formation, locality 8, West Virginia, USNM 593966.
Previously, we (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb) regarded Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) as having provided the taxonomic foundation for the species Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl. We still do so, despite subsequently having become aware that E.B. Branson and M.G. Mehl had published an article a few months earlier (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941a) in which they used the name S. commutatus for illustrated specimens from the Caney Formation of Oklahoma, but without having fulfilled the requirements for naming a new species. In effect, the authors were using a nomen nudum, a condition they rectified a few months later in Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) when they described, named, and illustrated the species more adequately from material from the “Pitkin limestone” (now Hindsville Formation) of Oklahoma.
In addition to describing Lochriea montanaensis, Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 299) also described a second species of the genus, L. bigsnowyensis. This description was also based on bedding-plane assemblages from the Heath Formation of Montana, the one specimen (the holotype) still available, being composed of a complement of 14 elements (Fig. 10). However, unlike L. commutata, it cannot contribute either to the generic concept of Lochriea or to our knowledge of the apparatus composition and structure of its species. Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 299) described the defining P1 elements (= his spathognaths) of L. bigsnowyensis as “blade wide, thin along aboral margin; denticles short, tips rounded, escutcheon moderately deep” adding (p. 299) that “only imprints and fragments of spathognaths have been found in assemblages of L. bigsnowyensis. As a result no sharp differences can be pointed out at this time.” Presumably, the “sharp differences” he alluded to referred to differences between the P1 elements of this and related species, such as L. commutata.

Figure 10. Lochriea bigsnowyensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, holotype (= an undetermined species of Cavusgnathus Harris and Hollingsworth, Reference Harris and Hollingsworth1933), illustrated by Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 38, fig. 8); paratype UI X-1321 lost. No counterpart known. Scanning electron micrographs of bedding-plane assemblage on black shale, with interpretation of conodont elements present. All elements, notably the P1d element (9P1d), are characteristic of species of Cavusgnathus Harris and Hollingsworth, Reference Harris and Hollingsworth1933. Heath Formation, locality 2, Montana, USA, UI X-1320. Scale bars = 0.5 mm. (1) Fecal assemblage of 14 elements numbered clockwise commencing in upper right. (2) The carminiscaphate P1d element and parts of associated M and S elements. (3) M and S elements below P1d element.
Scanning electron microscopy of the bedding-plane assemblage designated by Scott (Reference Scott1942) as the holotype of L. bigsnowyensis demonstrates (Fig. 10) that it contains one or more carminiscaphate P1 elements, as well as P2, M and S elements (Fig. 10) similar or identical to those present in apparatuses of Cavusgnathus spp. (von Bitter and Merrill, Reference von Bitter and Merrill1990, fig. 1B–D; Purnell and Donohue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig. 15). The bedding-plane assemblage Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 299) designated as the paratype, but did not illustrate, has been lost. We place the discrete L. bigsnowyensis prioniod element of Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 40, fig. 3) in synonymy with the L. commutata M element. The prioniodell elements illustrated by Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 40, figs. 4 and 5) may be L. commutata P2 elements.
We conclude that L. bigsnowyensis was based primarily on a partial bedding-plane assemblage of an as yet unidentified species of Lewistownella Scott, Reference Scott1942, which in turn is a junior synonym of an as yet unidentified species of Cavusgnathus Harris and Hollingsworth, Reference Harris and Hollingsworth1933. Lochriea bigsnowyensis was also, but to a minor degree, based on a misidentified discrete M element that we place in L. commutata and on two P2 elements that may have belonged to L. commutata.
Element composition of the Lochriea commutata apparatus
Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 298, fig.1) concluded that the Lochriea montanaensis apparatus bore a minimum of 22 elements, comprising at least four each of “spathognaths,” “prioniodells,” and “prioniods,” and at least ten “hindeodells” (Fig. 11.1, 11.2), an element terminology that translates into four each of carminiscaphate, angulate, and makellate elements, as well as ten bipennate elements, respectively (Fig. 11.1, 11.2).
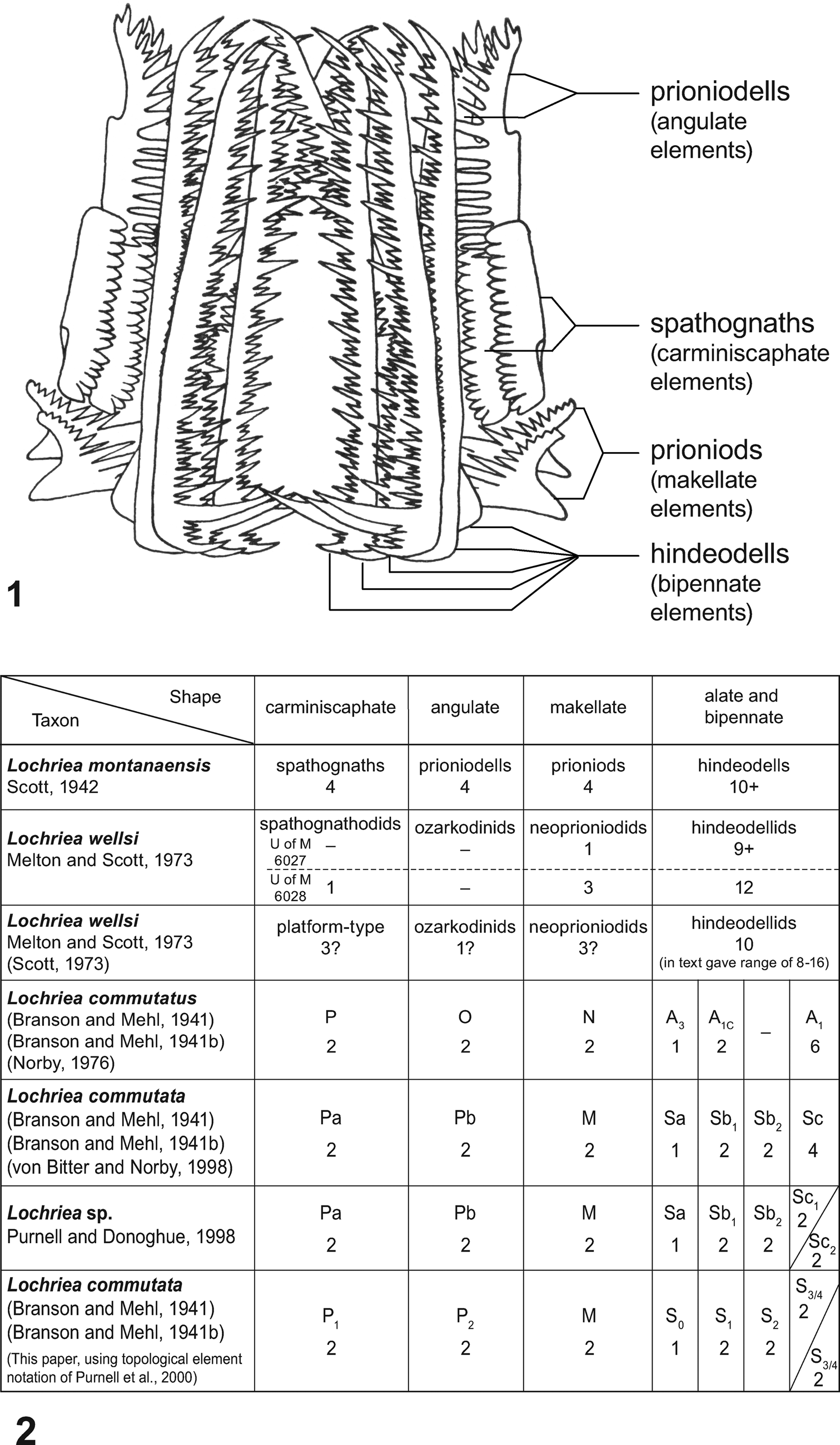
Figure 11. (1) Twenty-two (22+) element apparatus reconstructions of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, a subjective junior synonym of L. commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b); after Scott (Reference Scott1942) and labeled with his terminology for the four element types recognized by him; shape categories used (in parentheses) are those of Sweet (Reference Sweet, Clark, Sweet, Bergström, Klapper, Austin, Rhodes, Müller, Ziegler, Lindström, Miller and Harris1981, Reference Sweet1988). (2) Interpretations of the apparatus composition of Lochriea spp. since 1942, based on bedding-plane assemblages. Lochriea wellsi was named for a conodontophage containing elements of species of Lochriea and other conodont taxa in its gut. The identity of Lochriea sp. of Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998) is indeterminate, and the reconstruction of L. homopunctatus (Ziegler, Reference Ziegler1960) by Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012), based on discrete elements, is not included.
Thirty-one years later, Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973) named newly discovered fossils of a soft-bodied, cigar-shaped animal, Lochriea wellsi, because of conodont elements they recognized as those of a species of Lochriea, in the “deltaenteron,” or midgut, of the animal. Melton and Scott (Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973) referred to these elements as “spathognathodids,” “prioniodinids/ozarkodinids,” “neoprioniodids,” and “hindeodellids” (Fig. 11.2). Scott (Reference Scott1973) in discussing this species, identified the “spathognathodids” as “a platform type” and suggested a possible ratio of the four element types present as 3:1:3:10 (Fig. 11.2), but admitted that the exact number of each was questionable. The species was subsequently assigned to a new genus by Conway Morris (Reference Conway Morris1985), and was interpreted, as Typhloesus wellsi (Melton and Scott), to be a conodontophage (i.e., a conodont-eater) (Conway Morris, Reference Conway Morris1985, Reference Conway Morris1990), an interpretation supported by Sweet (Reference Sweet1988) and by us. Reasons for our support for this conclusion are that: (1) elements of other conodont taxa, including those of Kladognathus Rexroad, Reference Rexroad1958, have been found inside T. wellsi (Conway Morris, Reference Conway Morris1990; Purnell, Reference Purnell1993a); (2) elements of Lochriea observed and reported in T. wellsi are disorganized and jumbled; and (3) there is, notwithstanding the orderliness of the Kladognathus assemblage described by Purnell (Reference Purnell1993a), a general uncertainty and inconsistency regarding the number and identity of Lochriea elements in T. wellsi. We conclude that the identity and apparatus composition of the species of Lochriea present in the gut of T. wellsi has yet to be determined and is presently of no help in elucidating the apparatus structure of L. commutata, or that of the genus Lochriea.
Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 293) wrote that the bedding-plane assemblages he was studying “did not represent accidental accumulations or coprolite material.” Nevertheless, most of the elements in his illustrated bedding-plane assemblages show a definite lack of orientation and are best described as chaotic. The single exception (Scott, Reference Scott1942, pl. 38, fig. 10; vide UI X-1385) is a symmetrical bundle of eight “hindeodells” (= S elements) with “four oriented with the denticles to the left and four to the right,” that he identified (p. 295) as L. montanaensis. This partial S-element assemblage may have been the one of the important clues, along with the presence of sinistral and dextral elements, that Scott (Reference Scott1942, fig. 1) used to arrive at his schematic diagram (Fig. 11.1) (although he did not specifically state that his assemblages represented bilaterally symmetrical apparatuses within the conodont animal, his diagram certainly implies that). Norby (Reference Norby1976) described Scott's apparatuses of Lochriea as having “a scattered arrangement,” and he regarded all but this single specimen as fecal. Proof that Scott's Lochriea assemblages were indeed fecal was provided by the numerous additional assemblages of L. commutata collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976) and the single bedding-plane assemblage collected by R. Lund in the Heath Formation of Montana, Scott's original collecting unit, as well those found by Norby (Reference Norby1976) in the overlying Tyler Formation. The best of Norby's bedding-plane assemblages are natural assemblages in which the elements show good parallel arrangement and pairing (Fig. 2).
Figure 12 illustrates a two-dimensional exploded diagrammatic view of the relative position and arrangement of elements in the three-dimensional functional feeding apparatus of L. commutata. Aldridge et al. (Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987) and Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1997, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig. 1) proposed and reviewed possible three-dimensional arrangements of elements within the functioning ozarkodinid conodont apparatus, with Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998) concluding that their text-figure 1E best explained the position, arrangement, and functional morphology of elements in that apparatus.

Figure 12. The 15 element apparatus of Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) in exploded view using the topological element notation of Purnell et al. (Reference Purnell, Donoghue and Aldridge2000; cf., their fig. 3). This two-dimensional diagrammatic representation of the three-dimensional apparatus shows the apparatus in dorsal view, but does not show the downward (ventrally) sloping anterior (rostral) ends of the S elements or the vertical (dorsoventral) orientation of the P element pairs, whose anterior ends point downward (ventrally). Morphologically, P1 elements are carminiscaphate, P2 elements are angulate, M elements are makellate, the S0 element is alate, and S1–S4 elements are bipennate with three different morphologic types.
Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 299) recognized that the Lochriea montanaensis apparatus contained “at least ten hindeodells” (Fig. 11). This bundle of mostly parallel, elongated ramiform elements intergrade morphologically, and are characteristic of ozarkodinid conodont apparatuses (Aldridge et al., Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987; Sweet, Reference Sweet1988). Functionally, this group of elements was regarded by Hitchings and Ramsay (Reference Hitchings and Ramsay1978) to have served as a sieve basket, but was subsequently interpreted to have had a raptorial grasping function (Purnell, Reference Purnell1993b; Purnell and Donoghue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1997). Norby (Reference Norby1976), using newly collected L. commutatus (= L. commutata) bedding-plane assemblages, recognized three distinct element types in Scott's “ten hindeodells,” one A3 (= S0), two A1c (= S1), and six A1 (= S2/3/4) elements (Fig. 11.2); he did not differentiate an S2 element.
As well as differentiating three types of A (= S) elements in the newly collected bedding-plane assemblages of L. commutatus (= L. commutata), Norby (Reference Norby1976) also determined that the L. commutatus (= L. commutata) apparatus was composed of 15 elements, consisting of pairs of P (= P1), O (= P2), and N (= M) elements, as well as nine A (= S) elements. This conclusion was supported by Aldridge (Reference Aldridge and Aldridge1987) and Aldridge et al. (Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987) when they determined that conodont apparatuses of the Polygnathacea Bassler, Reference Bassler1925, which includes Lochriea commutata, were composed of 15 elements. Each apparatus contained pairs of Pa (= P1), Pb (= P2), M, Sb, and Sd elements, two pairs of Sc elements, as well as an unpaired Sa (= S0) element, which is an element plan that Purnell et al. (Reference Purnell, Donoghue and Aldridge2000) determined to be plesiomorphic for complex conodonts. Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998) illustrated and described a bedding-plane assemblage of an unidentified species of Lochriea from the Namurian of Germany, the part and counterpart of which we re-illustrate in Figure 13.1 and 13.2, respectively. We also re-illustrate a camera lucida drawing of the same specimen (Fig. 14.1), first published by Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), and subsequently amended by them to reflect topological element notation of Purnell et al. (Reference Purnell, Donoghue and Aldridge2000). The three-dimensional apparatus architecture of the German Lochriea sp. specimen was illustrated by Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, p. 76, figs. 11A, B) by juxtaposing a line drawing of Lochriea sp. with a photograph of a model of the apparatus architecture of another polygnathacaean, identified by M. Purnell (personal communication, 2019) as being Idiognathodus, both here re-illustrated as Figure 14.1 and 14.2, respectively.

Figure 13. Lochriea sp. bedding-plane assemblage, counterpart (1) and part (2), as designated by Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, pl. 2). Lüsenberg Formation, locality 11, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany, IMGP Gö 600-36. From the collection of Schmidt and Müller (Reference Schmidt and Müller1964); after Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, pl. 2), and reproduced with permission of the Palaeontological Association. Scale bars = 1 mm.

Figure 14. (1) Lochriea sp., bedding-plane assemblage, composite camera lucida drawing of IMGP Gö 600-36 (counterpart) shown in Figure 13.1. After Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig. 11A), and reproduced with permission the Palaeontological Association. Positional element notation shown was modified and provided by M. Purnell subsequent to the publication of Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), and is used with their permission. (2) Photograph of a model, identified by M. Purnell (personal communication, 2019) as of Idiognathodus sp., taken from right side and slightly in front to simulate the collapse pattern of Lochriea sp. shown in Figures 13 and 14.1. After Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig. 11B), and reproduced with permission of the Palaeontological Association.
Our identification of 18 and 23 elements in the holotype and paratype, respectively, of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 (Fig. 1; Table 1) is clearly at odds with the apparatus composition of Lochriea spp. as determined by Norby (Reference Norby1976), von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1998a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb), and Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998). The anomalously high numbers of elements in the two assemblage specimens chosen by Scott (Reference Scott1942) as the primary types of Lochriea montanaensis, the presence of three and four each of the P1, P2, and M elements, and the anomalously high number of each of S3/4 and S elements in the holotype and paratype, respectively (Table 1), all suggest that the primary types consist of the elements of more than one individual. This, as well as their disorganized state (Fig. 1), suggests that both specimens are fecal composites, a conclusion at odds with those of Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 293), who thought that the bedding-plane assemblages he was studying were not fecal, or accidental accumulations.
Table 1. Conodont elements on the holotype and paratype of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942 (= Lochriea commutata [Branson and Mehl, 1941] [Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b]) from the Heath Formation, and on three and five specimens of Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) from the Heath and Tyler formations, respectively. All 10 specimens are bedding-plane assemblages from Montana, USA. Underlined element designations (i.e., 3P1, 3P2, 3M, 2S1, 1S2, 6S3/4, etc.) are the number of each those elements identified on that assemblage. The parenthetical designations below them—(2P1s, 3?P1, 11P1?d), (4P2, 13P2?s, 17P2?d), and so forth—represent the position of that element in that assemblage, as labeled on Figures 1 and 2, followed by our determination of the identity of that element, preceded or followed by question marks indicating the degree of certainty of our identification. An asterisk (*) indicates only the part is present; other conodont elements may have been present on the counterpart.

The best preserved eight bedding-plane assemblages of Lochriea commutata collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976), and presented here, show a maximum of 15 elements (Fig. 2; Table 1). The presence of two each of the P1, P2, and M elements in all but two of the eight specimens, are in agreement with the number of these elements that other authors, including Norby (Reference Norby1976), Aldridge (Reference Aldridge and Aldridge1987), Aldridge et al. (Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987), and Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1997, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), concluded were present in ozarkodinid conodont apparatuses. Remarkably, the rarely identified S0 element, even though not identified in the type specimens of Lochriea montanaensis, was recognized in three and possibly an additional two of the apparatuses of Lochriea commutata (Table 1). The presence of only a single M element in ISGS 62P-210 and possibly 62P-211 (Table 1) is likely due to either preservational factors, or to our inability to recognize this element. Similarly, we attribute the underrepresentation of one or more of the categories of S1, S2, and S3/4 elements in these eight specimens (Table 1) to the same preservational and human factors, a reality that forced us to place anomalously large numbers of elements into the more generalized and less specific category of S elements (Table 1). The more balanced element maximum of up to 15 elements in the eight assemblages (Table 1) and their less disturbed distribution suggest that they are ‘natural’ bedding-plane assemblages.
That the type species of Lochriea, L. commutata, possessed a food processing apparatus of 15 elements (Norby Reference Norby1976; von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1998a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb) (Figs. 11.2, 12; Table 1) has provided, and continues to provide, an element blueprint for the apparatus of other Lochriea species. That reconstruction was supported and strengthened when Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998) documented the element composition of a well-preserved, but unidentified, species of Lochriea from the Namurian of Germany—a bedding-plane assemblage that, in an outline drawing updated by Purnell and Donoghue (personal communication, 2019), shows paired P1, P2, S1, S2, S3, and S4 elements, as well as a single M element (a second M element was either not preserved, or was covered by other elements), and an S0 element (Figs. 13.1, 13.2, 14.1).
The availability of an apparatus element blueprint for the type species Lochriea commutata resulted in others beginning to reconstruct the apparatuses of species of Lochriea, using a variety of approaches. The simplest approach was perhaps that of Stone (Reference Stone1991), who, using discrete collections, reconstructed a partial L. commutata apparatus by identifying its Pa (= P1), Pb (= P2), M, and Sc1 (= S3/4) elements, based on criteria presented by Norby (Reference Norby1976). Another more complicated approach was that of Horowitz and Rexroad (Reference Horowitz and Rexroad1982), Varker (Reference Varker1994), and Nemyrovska et al. (Reference Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse and Weyant2006), who assumed that one or more species of Lochriea, while distinguished by their Pa (= P1) elements, each bore morphologically identical non-platform elements in their apparatuses. Thus Horowitz and Rexroad (Reference Horowitz and Rexroad1982), in reconstructing a partial apparatus of L. commutata from discrete faunas, assumed (text-fig. 10) that L. mononodosa bore the ‘same’ (i.e., morphologically identical) Pb (= P2), M, and Sc (= S3/4) elements as L. commutata, doing so despite the fact that the rare L. mononodosa Pa (= P1) element was grouped in their cluster analysis in the middle of mostly elements of Idioprioniodus healdi (Roundy, Reference Roundy, Roundy, Girty and Goldman1926) (Horowitz and Rexroad, Reference Horowitz and Rexroad1982, text-fig. 3). Similarly, Varker (Reference Varker1994, p. 310) studying discrete elements and fused clusters, regarded L. commutata, L. mononodosa, and L. nodosa to “share” the same non-Pa elements (i.e., he interpreted the apparatuses of each of the three species to each have borne morphologically identical Pb [= P2], M, Sa [= S0], and Sc [= S3/4] elements). Finally, Nemyrovska et al. (Reference Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse and Weyant2006) concluded that the P2, M, and S elements of three species of Lochriea (L. commutata, L. cracoviensis, and L. saharae) were morphologically the same.
Assumptions of sharing non-platform elements in apparatuses of Lochriea spp., while possibly true, remain unproven, and there has been little success in reconstructing the apparatuses of Lochriea species, other than L. commutata (see Skompski et al., [Reference Skompski, Alekseev, Meischner, Nemirovskaya, Perret and Varker1995] for a key to the up to 10 species of Lochriea, and to which additional species, such as L. saharae have since been added). The major reason for that lack of success is the relative rarity of bedding-plane assemblages and fused clusters of Lochriea spp., and that the reconstruction of conodont apparatuses from discrete collections is largely dependent on the availability of conodont faunas that are composed, if not of the elements of a single conodont species, then of the elements of several species, the components of which can readily be disentangled and identified.
The sole exception to our generalization that there have been few successful attempts to reconstruct the apparatuses of species other than that of L. commutata, involved five samples studied by Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012, p. 1281) that contained “P1 elements of L. homopunctatus along with morphologically distinctive P2, M and S elements that could not be assigned to any of the 11 other co-occurring species.” These authors, in reconstructing most of the apparatus of L. homopunctatus, also concluded that the characteristics of P2, M, and S elements may be as, or more, important in determining and defining Lochriea spp. than those of the traditionally used P1 elements. We concur and contend that the current practice of assigning species to Lochriea almost entirely on the basis of ornamented or unornamented P1 elements leaves those assignments in doubt, at least until the rest of their apparatuses are determined, and found to be similar to that of the type species. Relying solely on P1 elements to carry the taxonomy ignores important taxonomic and phylogenetic information that almost certainly resides in the other elements of their apparatuses. Of interest in this context, and a step forward, was the interpretation by Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012) of an M element, illustrated by Nemyrovska et al. (Reference Nemyrovska, Perret-Mirouse and Weyant2006) from a sample from Algeria containing P1 elements of only a single Lochriea species, L. saharae, as the M element of that species.
Materials and methods
We studied three kinds of conodont fossils, the first, and the most commonly recovered, being individual discrete elements that collectively functioned in the feeding apparatuses of conodonts. Isolated discrete elements were recovered from carbonates or carbonate-rich sediments by standard acid digestion techniques, using either dilute acetic or formic acid (Collinson, Reference Collinson1963, Reference Collinson, Kummel and Raup1965; Stone, Reference Stone and Austin1987) and from organic-rich black shales using a sodium hypochlorite and sodium hydroxide solution (Norby, Reference Norby1976; Duffield and Warshauer, Reference Duffield and Warshauer1979; Stone, Reference Stone and Austin1987) and Stoddard Solvent, a kerosene-derivative, used to process soft clay-rich shales (Collinson, Reference Collinson1963, Reference Collinson, Kummel and Raup1965; Norby, Reference Norby1976). Gentle boiling in water with Quaternary O, a deflocculating agent, was used for all shales and some carbonates (Norby, Reference Norby1976; Duffield and Warshauer, Reference Duffield and Warshauer1979; Stone, Reference Stone and Austin1987). Discrete elements were concentrated using heavy liquids such as tetrabromoethane (Collinson, Reference Collinson1963, Reference Collinson, Kummel and Raup1965; Stone, Reference Stone and Austin1987), then the heavy fractions, occasionally magnetically separated, were subsequently hand-picked for conodont elements using binocular microscopes.
The second, much less common material collected and studied, are bedding-plane assemblages, most commonly preserved on black shale surfaces as groups of conodont elements preserved in close proximity to one another, that are either classified as fecal assemblages, or as natural assemblages, depending on whether or not they had been ingested and gone through the gut of a conodontophage. In rare situations, a conodont assemblage inside the body of a conodontophage is both sufficiently well preserved, and retains enough of its original structure, to be classified as a natural assemblage, one such example being the apparatus of the conodont Kladognathus Rexroad, Reference Rexroad1958, in the midgut of the conodontophage Typhloesus wellsi (Melton and Scott, Reference Melton, Scott and Rhodes1973), and another is the apparatus of the conodont Bispathodus Müller, Reference Müller1962 in the gut of a Devonian shark (Purnell and Donoghue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998).
In this study, bedding-plane assemblages were recovered by hand splitting organic-rich black fissile shales with a thin sharp knife or a cleaver, and then using the naked eye and a hand-lens or a low-powered microscope to locate them; the latter procedure was best accomplished by taking advantage of the reflectivity of the conodont elements in the sun in the field, or of artificial light in the laboratory. The most useful natural assemblages were, and are, those that had not been disturbed, or had only been minimally disturbed, by sedimentologic, taphonomic, or biologic processes, and that preserved important information regarding the number, morphological types, and arrangement of conodont elements in the feeding apparatus of conodonts. Conversely, feeding apparatuses that had been ingested, digested, and excreted, generally preserved a minimum of such information.
The third, and the rarest kind of conodont material studied, were fused clusters, which, depending on their history and on their preservation, may be considered more three-dimensional categories of bedding-plane assemblages, also theoretically being divisible into both ‘natural’ and ‘fecal’ categories. In fused clusters, typically just the elongated bipennate elements are compacted and fused together, and are preserved in their original relative position and orientation within the feeding apparatus. The fused clusters of Lochriea commutata recovered and studied by us are only the second reported occurrence, after Varker (Reference Varker1994), of fused clusters of Lochriea spp. The fused clusters were recovered from carbonate concretions by the standard acid digestion and heavy liquid techniques described above.
Our examination of Scott's (Reference Scott1942) Lochriea montanaensis bedding-plane assemblages suggests that although some represent the feeding apparatus of a single individual and provide information regarding the element composition of the L. commutata feeding apparatus, all appear to be of fecal origin (Fig. 1; Table 1). In contrast, we subjectively categorize the 34 bedding-plane assemblages of L. commutatus (= L. commutata) collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976) from the Heath Formation of Montana, as three natural, two ?natural, 23 fecal, and six ?fecal. Similarly, of the 81 assemblages collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976) from the Tyler Formation of Montana, we categorize five as natural, 29 as ?natural, 19 as fecal, and 28 as ?fecal. Several of the Montana natural assemblages of L. commutata are shown on Figure 2. Those considered natural consist of up to 15 elements, although some elements may be hidden beneath other elements. Natural assemblages typically exhibit a recognizable recurring pattern of element positions; however, element positions may be disrupted by post-mortem changes. Those assemblages termed ?natural are probably natural, but show varying degrees of element disturbance; these two categories provide the most useful information regarding original element composition and position. Fecal assemblages are associations of two or more elements, but typically of 15 or more elements of varying maturities, sometimes including elements belonging to different conodont species, that are jumbled, show no discernible element pattern, and occur with black bituminous material. Assemblages termed ?fecal are most likely fecal, however, they typically may represent one, or sometimes two or more relatively complete individuals, that show moderate to significant disruption. They occasionally provide information regarding element composition and position in an apparatus. Conodonts in the fecal and ?fecal categories were either regurgitated, excreted, or even brought together by bottom currents.
We list the material studied by locality in the section that follows. Abbreviations for the institutions at which specimens are reposited are provided at the end of the section, and locality data are provided in the Appendix.
Locality 1 (Heath Formation, Montana)
One partial bedding-plane assemblage (CM 33965) and several isolated elements of L. commutata collected by Richard Lund.
Locality 2 (Heath Formation, Montana)
Two bedding-plane assemblages collected by Scott (Reference Scott1942), and designated by him as holotype and paratype of L. montanaensis, UI X-1318 and UI X-1319, respectively. Forty-nine bedding-plane assemblages and dozens of isolated elements on shale surfaces designated as L. montanaensis paratypes on UI slides; none assigned numbers by Scott (Reference Scott1942). Scott (Reference Scott1942) reported that he recovered 180 conodont assemblages and 3,000 individual elements from Montana, but most of these specimens could not be located at UI.
Thirty-four bedding-plane assemblages of L. commutata (L. montanaensis) and more than a thousand topotype P1, P2, M, S0, S1, S2, and S3/4 elements collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976), and reposited at the ISGS.
Locality 3 (Tyler Formation, Montana)
Eighty-one bedding-plane assemblages and several thousand P1, P2, M, S0, S1, ?S2, and S3/4 elements of L. commutata collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976), and reposited at the ISGS.
Locality 4 (Hindsville Formation, Oklahoma)
The syntype of Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) (UM C552-2) selected by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a) as the lectotype of S. commutatus, and here as the lectotype of L. commutata. Topotype L. commutata P1, P2, M, S0, and S3/4 elements collected by RDN and reposited at the ISGS.
Locality 5 (Fayette Formation, Oklahoma)
Lochriea commutata P1, M, S0, and S3/4 elements collected by RDN and reposited at the ISGS.
Locality 6 (Goddard Formation, Oklahoma)
Lochriea commutata P1 element (SUI 33624) illustrated by Lane and Straka (Reference Lane and Straka1974, fig. 37.1, 37.2).
Locality 7 (Ridenhower Formation, Illinois)
Lochriea commutata P1, P2, M, S0, and S3/4 elements collected by RDN and reposited at the ISGS.
Locality 8 (Bluestone Formation, West Virginia)
Fused clusters and P1, P2, M, S0, S1, S2, and S3/4 elements of L. commutata collected by RGS and reposited at the USNM.
Locality 9 (Upper Windsor Group, Nova Scotia)
Lochriea commutata P1, P2, and M elements collected by PvB and reposited at the ROM.
Locality 10 (Herdringen Formation, Germany)
Lochriea commutata P1, M, S0, and S3/4 elements collected by Charles Collinson and reposited at the ISGS. P1 elements from this locality were previously documented and referred to by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb).
Locality 11 (Lüsenberg Formation, Germany)
Part and counterpart of bedding-plane assemblage of Lochriea sp. (IMGP Gö 600-36) from the collection of Schmidt and Müller (Reference Schmidt and Müller1964), illustrated by Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998). Original material not examined; only photographs studied.
Notes on conodont element notation
Lochriea commutata Scott, Reference Scott1942, Lochriea sp. of Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998), and Lochriea bigsnowyensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, the latter here re-assigned to Cavusgnathus Harris and Hollingsworth, Reference Harris and Hollingsworth1933, possessed 15-element apparatuses of paired P1, P2, M, S1, S2, S3, and S4 elements, and an unpaired S0 element. Many of the illustrated elements of these taxa have a superscript notation d, ?d, s, or ?s after the element type, indicating whether that element was positioned on the right (dextral) or the left (sinistral) side of the plane of bilateral symmetry of the skeletal apparatus (Sweet, Reference Sweet, Clark, Sweet, Bergström, Klapper, Austin, Rhodes, Müller, Ziegler, Lindström, Miller and Harris1981), with the question mark indicating uncertainty (e.g., a P2d element is a dextral P2 angulate element positioned on the right side of the feeding apparatus, and a S2?s element is a questionable sinistral S2 bipennate element on the left side of the apparatus).
Repositories and institutional abbreviations
Specimens examined in this study are deposited in the following institutions: Carnegie Museum of Natural History (CM), Pittsburg, Pennsylvania, USA; University of Göttingen (IMGP Gö), Göttingen, Germany; Illinois State Geological Survey (ISGS), Champaign-Urbana, Illinois, USA; Royal Ontario Museum (ROM), Toronto, Ontario, Canada; State University of Iowa (SUI), Iowa City, Iowa, USA; University of Illinois (UI), Champaign-Urbana, Illinois, USA; University of Missouri (UM), Columbia, Missouri, USA; University of Montana (UM), Missoula, Montana, USA; U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), Reston, Virginia, USA; U.S. National Museum (USNM), Washington, D.C., USA.
Systematic paleontology
Phylum Chordata Bateson, Reference Bateson1886
Class Conodonta Pander, Reference Pander1856
Order Ozarkodinida Dzik, Reference Dzik1976
Suborder Ozarkodinina Dzik, Reference Dzik1976
Superfamily Polygnathacea Bassler, Reference Bassler1925
Genus Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942
- Reference Branson and Mehl1941
Spathognathodus Branson and Mehl; Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941a, p. 172 [nomen nudum].
- Reference Branson and Mehl1941
Spathognathodus Branson and Mehl; Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b, p. 98 [partim].
- Reference Scott1942
Lochriea Scott, p. 298.
- Reference Hass1953
Gnathodus Pander, Reference Pander1856; Hass, p. 78 [partim].
- Reference Meischner1970
Paragnathodus Meischner, p. 1173 [nomen nudum].
- non Reference Scott1973
Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942; Melton and Scott, p. 58.
- non Reference Scott1973
Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942; Scott, p. 94.
- Reference Higgins1975
Paragnathodus Higgins, p. 70.
- Reference Norby1976
Lochriea Scott, Reference Scott1942; Norby, p. 139.
- ?Reference Mizuno1997
Neolochriea Mizuno, p. 253.
Type species
Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, 1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b).
Diagnosis
A conodont genus bearing a typical 15-element ozarkodinid feeding apparatus that contains sinistral and dextral pairs of P1, P2, M, S1, S2, S3, and S4 elements, and an unpaired S0 element. P1 elements are carminiscaphate and possess a large subcircular, subquadrate, lanceolate or lachrymiform posterior basal cavity below a platform surface that is unornamented, or is ornamented with a few nodes, rows of nodes, or lateral ridges, and a free blade lacking a prominent anterior crest. P2 elements are angulate, typically with discrete denticles. M elements are makellate, with large cusps and arched posterior processes, typically with discrete denticles decreasing in height distally. S0 elements are alate. S1–4 elements are bipennate with short to medium length anterior processes of three different styles.
Etymology
Although Scott (Reference Scott1942) did not provide his source or derivation for the genus name Lochriea, and did not designate or identify the gender of Lochriea, he was almost certainly honoring Elizabeth Lochrie, a highly regarded Montanan artist who painted portraits of Native Americans and their environments, and who drew the illustrations Scott had used eight years before (Scott, Reference Scott1934, p. 449). We here specify that the genus Lochriea be considered a feminine genus. Norby (Reference Norby1976), Mapes and Rexroad (Reference Mapes and Rexroad1986), and Sweet (Reference Sweet1988), following Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), used the masculine ending, -us, when referring to the Lochriea species L. commutata. We here apply the feminine ending, -a, for all references to the type species of Lochriea, L. commutata, except in synonymies where we cite earlier work and where others have ended the species name with an -a or -us suffix. However, where the original generic name used was masculine, we use the suffix -us, such as in Gnathodus commutatus.
Procedural notes
Our generic synonymy (above) is selective and traces the generic assignments of the type species of Lochriea from its original description by Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b), until Norby (Reference Norby1976) recognized and acted on the priority of Lochriea.
Remarks
Our diagnosis has been modified from Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012), it in turn having been modified from Norby (Reference Norby1976).
Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012, p. 1287) reported that P1 elements of Lochriea species lack a prominent anterior crest, an observation with which we concur; however, we are unable to support or refute their opinion that M elements of Lochriea species lack an adaxial bulge at the base of their cusps and possess a basal cavity that is restricted to their cusps.
Sweet (Reference Sweet1988, p. 112) observed that “if future studies demonstrate that Lochriea and Vogelgnathus represent a lineage separate from the Spathognathodontidae and Gnathodontidae, it will probably be desirable to create and name a new family for them,” but recommended that this not be done until the relationships of Diplognathodus Kozur and Merrill in Kozur, Reference Kozur1975 and related genera belonging to the Sweetognathidae were considered. The relationship of the various genera in the Sweetognathidae (see Sweet, Reference Sweet1988, p. 188) to one another has not, to our knowledge, yet been clarified, and although we agree about the desirability of establishing a new family that would include Lochriea, we, like Donoghue et al. (Reference Donoghue, Purnell, Aldridge and Zhang2008), still regard it premature to do so.
We use the order Ozarkodinida Dzik, Reference Dzik1976, in the sense of Donoghue et al. (Reference Donoghue, Purnell, Aldridge and Zhang2008), who expanded on the systematic concepts for suprageneric classifications based on formal phylogenetic analyses using cladistics, rather than on general perceived relationships.
Even though cladistic analyses are being increasingly used to determine phylogenetic relationships between different conodont genera in an objective, repeatable manner (e.g., Donoghue, Reference Donoghue2001; Donoghue et al., Reference Donoghue, Purnell, Aldridge and Zhang2008; Atakul-Özdemir et al., Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012), Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012, p. 1287) recovered a clade of Lochriea + Sweetognathus + Clydagnathus, which is an identical grouping recovered by Donoghue et al. (Reference Donoghue, Purnell, Aldridge and Zhang2008). However, Atakul-Özdemir et al. (Reference Atakul-Özdemir, Purnell and Riley2012) resolved Lochriea in a sister group relationship with (Sweetognathus + Clydagnathus), whereas Donoghue et al. (Reference Donoghue, Purnell, Aldridge and Zhang2008) consistently resolved a Lochriea + Clydagnathus clade.
The P1 elements described by Mizuno (Reference Mizuno1997) as Neolochriea hisaharui and Neolochriea nagatoensis are morphologically similar to P1 elements of species currently assigned to Lochriea; those on which Neolochriea hisayoshii Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997 and Neolochriea koikei Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997 are based are not. This suggests that until the apparatuses of one or more Neolochriea species are known and can be compared with those of Lochriea commutata, it will remain uncertain whether Lochriea spp. and Neolochriea spp. are a part of the same lineage in an ancestor-descendent relationship, whether the P1 elements of species of the two genera are homeomorphs of one another, and whether Neolochriea is, in whole or in part, a junior synonym of Lochriea.
Lochriea commutata (Branson and Mehl, 1941) (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b)
Figures 1–9
- Reference Branson and Mehl1941
Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl; Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941a, p. 172, pl. 5, figs. 19–22 (= P1 elements) [nomen nudum].
- Reference Branson and Mehl1941
Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl; Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b, p. 98, pl. 19, figs. 1–4 (= P1 elements). These elements were re-illustrated by von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2.6–2.15, 3.1–3.6, 3.9–3.12), and they selected specimen UM C552-2 as the lectotype (= Fig. 3.7–3.10 of this paper).
- Reference Scott1942
Lochriea montanaensis Scott, p. 298, pl. 37, figs. 1–7, pl. 38, figs. 1–4, 6, 7, 10, 12 are bedding-plane assemblages; p. 298, pl. 39, fig. 1, subhorizontal element, is a dextral S1 element; a more vertical element may be a dextral S2 element; “hindeodells,” p. 298, pl. 39, figs. 4, 7 are a pair of sinistral and dextral S3/4 elements, respectively; “a pair of prioniods,” p. 298, pl. 39, fig. 9 are two M elements; “hindeodell,” p. 298, pl. 40, fig. 2 is an ?S1 element; “prioniodells,” p. 298, pl. 40, figs. 9, 10 are P2 elements; “prioniod,” p. 298, pl. 40, fig. 12 is an M element; “hindeodell,” p. 298, pl. 40, fig. 18 is an S3/4 element; “spathognaths,” p. 298, pl. 40, figs. 13, 15, 19 are P1 elements.
- Reference Scott1942
Lochriea bigsnowyensis Scott, “prioniod,” p. 299, pl. 40, fig. 3 is an M element [partim].
- Reference Scott1942
unidentified element, Scott, p. 299, pl. 40, fig. l6 is an S0 element.
- Reference Stanley1958
Hindeodella montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942); Stanley, p. 465, pl. 64, figs. 1–4, 5 are S3/4 elements.
- Reference Stanley1958
Prioniodina montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942); Stanley, p. 474, pl. 64, fig. 5 (vertically oriented element) and pl. 65, fig. 1 are both P2 elements.
- Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969
Neoprioniodus montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942); Rhodes et al., p. 160, pl. 22, figs. 5a–8b are M elements.
- Reference Marks and Wensink1970
Neoprioniodus montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942); Marks and Wensink, p. 266, pl. 1, figs. 9, 10 are M elements.
- Reference Igo1973
Neoprioniodus montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942); Igo, p. 195, pl. 29, fig. 32 are M elements.
Lectotype
UM C552-2 (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2.6–2.9, 3.9); paralectotypes UM C1139-9, UM C1139-10, and UM C1139-11 (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2.10–2.15, 3.1–3.6, 3.10–3.12).
Diagnosis
A species of Lochriea with a typical 15-element ozarkodinid apparatus containing sinistral and dextral pairs of P1, P2, M, S1, S2, S3, and S4 elements, and an unpaired S0 element. The carminiscaphate P1 elements have low platforms that are subcircular to subquadrate in upper view, subrectangular outline in lateral view, are unornamented, and possess cup-shaped basal cavities restricted to the posterior one-half to one-third of the element. The angulate P2 elements have slight downward-curving posterior processes and straight anterior processes, both with long typically discrete denticles. The makellate M elements have a large cusp, and an arched and flexed posterior process with typically discrete denticles that decrease in height distally. The alate S0 elements possess a posterior process of medium length and two short anterolateral processes. The bipennate S1 and S2 elements have long posterior processes, and either very short, or medium-length, inwardly flexed anterior processes. The bipennate S3 and S4 elements have prominent main cusps, long posterior, and short, inwardly curved, upswept anterior processes.
Description of elements
P1 element (Fig. 3)
The carminiscaphate P1 element has a subrectangular outline in lateral view and is ~3–5 times as long as high, typically narrowing toward the base to varying degrees at the posterior end giving it a slightly arched appearance. In upper view, the element can be nearly straight, but typically curves toward the inner side with a smooth and unornamented low platform, typically asymmetric and slightly wider on the inner side, occupying the posterior one-third to one-half of the element. The blade typically consists of 15–18 denticles with a noted maximum of 22 and <15 in immature elements; blade may extend slightly beyond posterior tip. Denticles on the anterior free blade are generally fused along most of their length with just the tips exposed, which are sharp edged in immature forms but are more rounded in mature elements. Denticles on the posterior blade (carina) above the basal cavity generally fuse completely along all their length and in some mature elements widen considerably to include microsculpture, this sometimes extending onto the anterior free blade. In lower view, the basal cavity can be semicircular, oval, or subquadrate, tapering sharply on both axial ends, but more so on the posterior end.
P2 element (Fig. 4)
The angulate P2 element is straight to nearly straight in oral view, typically thin and laterally compressed. The anterior process is nearly straight to slightly arched upwards in lateral view with a few to a dozen vertical to slightly posteriorly inclined denticles that are typically unfused but can be fused in more mature elements. The slightly to moderately downward-arched posterior process has a few to a dozen typically unfused denticles that recline at increasing angles posteriorly, and on some specimens exhibits a few small denticles interspersed between the larger denticles. The cusp is nearly vertical, slightly larger and higher than the denticles on the two processes. The basal cavity is typically small and elongate with some noticeable lateral flare in some elements.
M element (Fig. 5)
The makellate M element has a large, typically straight to slightly inwardly flexed, laterally compressed, sharp-edged and pointed cusp with a moderately short undenticulated anticusp and an arched, typically inwardly flexed, posterior process of approximately one-half the length of the cusp in inner lateral view. The denticles on the posterior process are typically unfused, begin about one-quarter the length from the cusp tip, abruptly decrease in height and gradually recline distally. The basal cavity is small to moderately large and everted in many mature elements.
S0 element (Fig. 6)
The alate S0 element is characterized by a large anterior cusp that is compressed laterally with two anterolateral processes that branch from sharp anterior costae on each side of the lower third of the cusp. These processes are relatively short, project slightly anteriorly forming an anterior angle of ~145–180° in upper view, diverge widely (~145°) aborally in anterior view, and typically recurve slightly to the posterior with typically small denticles that tend to alternate slightly in size. The short to medium-length posterior process is slightly to moderately arched upward and is ~50–60% of the length of the posterior process of S1–4 elements of similar maturities. Denticles on the posterior process gradually recline distally, alternate in size and height, and typically increase in size and height in the distal half. A very small aboral basal pit occurs at the junction of the three processes.
S1 element (Fig. 7)
The bipennate S1 element consists of a small cusp, commonly inclined inward with a moderately long anterior process that initially bends outward then inward at 90–120° and slightly downward. This process bears 8–12 denticles that alternate in size and are nearly vertical where the process projects from the cusp, but progressively recline and increase in size toward the upswept distal end. The secondary denticles on the posterior process of S1 elements may bend slightly inward, a feature observed on some of the specimens from the Bluestone Formation of West Virginia (Fig. 7.18). The moderately long posterior process is slightly to moderately arched in lateral view, bearing an alternating dentition. The basal pit is small and continues as a small basal groove under both processes.
S2 element (Fig. 8)
The bipennate S2 element consists of a moderately long, nearly straight to slightly arched posterior process with a typical alternating denticulation with a typical slight upsweep at its distal end. The cusp is subequal or slightly larger than the secondary denticles on either process, and the cusp typically bends inward. The anterior process is relatively short, projects anteriorly, with a very short bend outward, followed by a sharp bend inward, forming an inner angle of 90° or less with the posterior process, and curves slightly downward, typically exhibiting three to four secondary and about four to more tertiary denticles. The basal pit is small and continues as a small basal groove under both processes.
S3/4 element (Fig. 9)
The bipennate S3/4 element has a large, prominent, pick-like cusp, which gently inclines posteriorly. The short anterior process bears five to eight denticles, the first one to three small denticles are typically situated high on the anterior slope of the cusp followed anteriorly by an increase in denticle size to the upturned distal end, where some are one-third to one-half the height of the cusp. As the denticles increase in height, the anterior process curves smoothly inward until it forms an angle of ~90° with the posterior process, and curves upward to a noticeable degree. The bar portion of the anterior process tends to be higher than that of the S1 and S2 elements, causing it to have an elongated ovoid cross section. The denticles of the posterior processes alternate in size and are noticeably longer than are those of S1 and S2 elements. In lateral view, the posterior process is relatively straight, with gentle arching occurring only near the anterior end of some specimens.
Remarks
Our specific synonymy (above) is selective and seeks to integrate the single-element taxonomy of Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) with that based on multielement concepts used by Scott (Reference Scott1942). Also, because the Lochriea commutata P1 element, unlike the remaining elements of the Lochriea commutata apparatus, is both well known from the literature and uncontroversial, we have avoided providing a long, exhaustive list of previous identifications and illustrations.
We have applied the morphological descriptors of Sweet (Reference Sweet, Clark, Sweet, Bergström, Klapper, Austin, Rhodes, Müller, Ziegler, Lindström, Miller and Harris1981, Reference Sweet1988) to describe the shape, orientation, and morphology of individual elements in the feeding apparatus of L. commutata, and the biological terminology of Purnell et al. (Reference Purnell, Donoghue and Aldridge2000) to describe the orientation and position of elements within the feeding apparatus of L. commutata (Fig. 12).
Stanley (Reference Stanley1958) was apparently the first to apply nomenclatural priority of a Carboniferous conodont species name, based on conodont elements in bedding-plane assemblages, to subsequently studied discrete Carboniferous conodonts. He did this when he identified S3/4 elements as Hindeodella montanaensis, and P2 elements as Prioniodina montanaensis, designating lectotypes for these two species from the illustrations of Scott (Reference Scott1942). Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 123, 160, pl. 22, figs. 5–8, pl. 28, figs. 21, 26), and subsequently Marks and Wensink (Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 266, pl. 1, figs. 9, 10) and Igo (Reference Igo1973, p. 195, pl. 29, fig. 32), identified particular S and M elements as the species montanaensis. Remarkably, none of these authors applied this taxonomic procedure to the Lochriea montanaensis P1 element that was abundant as discrete elements in their collections. For example, although Stanley (Reference Stanley1958, p. 465), synonymized Spathognathodus commutatus Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941 (Branson and Mehl, Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) with, and apparently incorrectly assigned priority to, the later-named Gnathodus inornatus Hass, Reference Hass1953, he did not recognize these P1 elements as montanaensis, which is something he was able to do for the P2 and S3/4 elements he regarded as identical to those present in the bedding-plane assemblages of L. montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942. Similarly, although Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 95, 96), Marks and Wensink (Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 258), and Igo (Reference Igo1973, p. 193) recognized and acknowledged that particular discrete M elements were identical to those in the bedding-plane assemblages of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942, they continued to identify abundant P1 elements as Gnathodus commutatus.
The final remaining step in this evolving, and now accepted, taxonomic procedure was to apply a Carboniferous conodont genus name having priority, but based on bedding-plane assemblages, to discrete Carboniferous conodonts. Varker and Sevastopulo (Reference Varker, Sevastopulo, Higgins and Austin1985, p. 183) apparently took this step when they reported Lochriea singularis (Hass), an M element, from the Michelinia grandis beds of the Cloghergnathus Zone at Ravenstonedale, Cumbria, England.
The lower surface of some elements, primarily of the M and S elements, of Lochriea commutata have a moderately strong to strong tendency toward eversion of the basal cavity, resulting in a well-developed attachment scar (see von Bitter and Merrill, Reference von Bitter and Merrill1983, text-fig. 1A, 1B, for a representation of how this feature develops in the ontogeny of this and other conodont species). An everted basal cavity is well developed and common on the basal surface of M elements (Fig. 5.16–5.18, 5.20), is present in some mature S0 elements (Fig. 6.11), and is common in S3/4 elements (Fig. 9.15–9.21); the basal surfaces of P1, P2, S1, and S2 elements show less of a tendency toward eversion. The denticulation of S elements is characterized by the alternation of prominent long, single denticles that are separated by two or three denticles of reduced length. Denticles of elements other than the P1 elements exhibit striae 2–5 μm apart; these are somewhat finer on the cusp of M elements (Norby, Reference Norby1976).
Discussion
P1 element (Fig. 3)
Having previously (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, Reference von Bitter and Norbyb) correlated the changes in the width of carinal nodes and their microsculpture fields with an increase in element size, we agree with Rhodes et al. (Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 96) and Metcalfe (Reference Metcalfe1981, p. 21) that the morphology of the Lochriea commutata P1 element is variable. The length to height ratio typically increases with ontogeny by becoming more elongated (greater length to height), as noted in the lectotype and paralectotypes of the species (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2.6–2.15, 3.1–3.6), but particularly for specimens from the Heath and Tyler formations of Montana (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 6, 7), and reaches a maximum length to height ratio in specimens from the Heath Formation (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 7).
Blade denticulation of P1 elements is also variable, with the lectotypes and paralectotypes of the species, for example, not being particularly denticulate (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, figs. 2, 3), which Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b, p. 98) described as having a tendency “to fuse.” Microsculpture is absent on the denticles of these specimens, with the upper denticle surface being covered by secondary crystal overgrowths (von Bitter and Norby, Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a, fig. 3.9–3.12). We conclude that Lochriea commutata P1 elements vary from being relatively short with stubby, commonly fused blade denticles and carinal nodes to more elongate with better-defined blade denticles and carinal nodes (Fig. 3).
Variation in P1 element morphology has been the most frequently applied criterion for recognizing and defining conodont species. Among Lochriea species with unornamented P1 elements, recognition of such variation has led to the definition of species such as Spathognathodus pellaensis Youngquist and Miller, Reference Youngquist and Miller1949, Gnathodus inornatus Hass, Reference Hass1953, G. commutatus nagatoensis Igo and Koike, Reference Igo and Koike1965 (the latter included by Mizuno, Reference Mizuno1997, in Neolochriea), G. scotiaensis Globensky, Reference Globensky1967, and G. simplicatus Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, the latter species recently placed in Pseudognathodus by Sanz-López et al., Reference Sanz-López, Blanco-Ferrera and Giles2018. Confirmation that these species with unornamented P1 elements are valid species related, or unrelated, to Lochriea commutata must await monographic and biometric study. Increasingly, it will also be necessary to determine the element composition of their apparatuses to confirm or refute these relationships.
P2 element (Fig. 4)
We recognize three main morphotypes of Lochriea commutata P2 elements in North America, two of which appear to intergrade, based on the degree of arching of the posterior process, on the degree of denticle separation or fusion, and on the overall length/height ratio. The first, the montanaensis morphotype, is the classic one illustrated by Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 40, figs. 9, 10), and is often found in bedding-plane assemblages from Montana (Fig. 4.1, 4.2, 4.5, 4.7, 4.19, 4.22). It is recognized as possessing a strong upward-arching posterior process and generally distinct denticle separation, particularly on the posterior process.
Some montanaensis morphotype P2 elements illustrated in the literature are Prioniodina montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942), Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 474, pl. 64, fig. 5 (lower left specimen), pl. 65, fig. 1; ?Prioniodina sp. A Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 474, pl. 65, fig. 3; Prioniodina sp. B Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 474, pl. 65, fig. 7; ?Prioniodina sp. C Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 474, pl. 65, fig. 2; and ?Ozarkodina deflecta Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 472, pl. 65, figs. 4, 5.
The second, the recta morphotype, is characterized by Ozarkodina recta of Rexroad, (Reference Rexroad1957, pl. 2, figs. 5, 6) and is recognized by its less-pronounced arching of the posterior process and denticles that tend to be somewhat shorter and fused along part of their length (Fig. ?4.3, 4.21, 4.23). Intergradations between the montanaensis and recta morphotypes are shown in Figure 4.18 and 4.20. Those shown in Figure 4.4 and 4.6 do not fit either of the two end-member morphotypes precisely; however, the specimen illustrated in Figure 4.4 is probably closer to the montanaensis morphotype. Both examples show some downward arching of the tip of the anterior process, which is seen in only a few examples of the recta morphotype (e.g., Fig. 4.22).
Some recta morphotype P2 elements illustrated in the literature are Ozarkodina recta Rexroad, Reference Rexroad1957, p. 36, pl. 2, figs. 5, 6; ?Rexroad and Furnish, Reference Rexroad and Furnish1964, p. 674, pl. 111, fig. 8; Thompson and Goebel, Reference Thompson and Goebel1969, p. 41, pl. 3, fig. 22; and Ozarkodina cf. O. recta Rexroad, Dunn, Reference Dunn1970, p. 338, pl. 62, figs. 25, 26.
The Bluestone morphotype (Fig. 4.9–4.17), based on P2 elements from the Bluestone Formation of West Virginia, is recognized as a third morphotype; it is similar to the montanaensis morphotype, but the length/height ratios differentiate the Bluestone and montanaensis morphotypes. The Bluestone morphotype P2 elements show shorter anterior and posterior processes that possess exceptionally long, non-fused, comb-like denticles whose lengths are commonly two to three times that of the supporting process bar. Further study of the Bluestone morphotype may lead to the recognition and definition of a new subspecies of Lochriea commutata. Bluestone morphotype P2 elements have not been described previously and are illustrated in Figure 4.9–4.17.
The fourth morphotype, the subaequalis morphotype, is based on Subbryantodus subaequalis of Higgins (Reference Higgins1961, pl. 12, fig. 15), and is likely the Lochriea commutata P2 element most common in Europe. It shows similarities to both the montanaensis and recta morphotypes, exhibits some arching of the posterior process, and often shows alternation of slightly smaller denticles with larger denticles on the anterior process. Although we did not recover or recognize the subaequalis morphotype in North American collections, Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 40, figs. 4, 5) illustrated examples that are similar.
Some subaequalis morphotype P2 elements in the literature are Subbryantodus subaequalis Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, p. 218, pl. 12, fig. 15, text-fig. 6; Higgins and Bouckaert, Reference Higgins and Bouckaert1968, p. 47, pl. 3, figs. 1, 2; Higgins, Reference Higgins1975, p. 74, pl. 5, fig. 17; Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981, pl. 19, fig. 17; Prioniodina subaequalis (Higgins), Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 198, pl. 28, figs. 1a–4; Ozarkodina subaequalis (Higgins), Marks and Wensink, Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 267, pl. 1, fig. 13 only; ?Subbryantodus stipans Rexroad, Reference Rexroad1957, Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, p. 219, pl. 12, fig. 14, text-fig. 6; Higgins, Reference Higgins1962a, p. 13, pl. 1, fig. 9, text-fig. 2; ?Prioniodina stipans (Rexroad), Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 198, pl. 28, figs. 7a–10c; Ozarkodina plana (Huddle), Reynolds, Reference Reynolds1970, p. 2, pl. 2, fig. 12; Lochriea commutata Pb element, Stone, Reference Stone1991, p. 34, pl. 4, fig.14; Lochriea sp. Pb element, Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 4, figs. 11, 12.
Most Montana P2 elements are of the montanaensis morphotype, although some mature elements from the Tyler Formation of Montana that tend to be larger and have more completely fused denticles are of the recta morphotype. Most Illinois P2 elements are of the recta morphotype; however, they are generally smaller than Montana specimens, and conversely, a few Illinois P2 elements are of the montanaensis morphotype. The Bluestone morphotype has been recovered from only a single locality in West Virginia and presently appears to be restricted to eastern North America.
Although all elements exhibit breakage, many more elements, particularly the P1, M, and S3/4 elements, can be recognized from fragmented or smaller remains than can the P2 elements. The thin, blade-like nature of the anterior and posterior processes of P2 morphotypes and the fragility of their discrete denticles lead to breakage, which makes it difficult to identify discrete P2 elements.
The co-occurrence of L. commutata P1 elements and P2 recta morphotypes in the Renault and Ridenhower formations of Illinois (Rexroad, Reference Rexroad1957, table 1), as well as in our own collections from the Ridenhower Formation of Illinois, suggests that they were part of the same apparatus. However, the cluster analysis applied by Horowitz and Rexroad (Reference Horowitz and Rexroad1982, p. 966, text-fig. 3) to Chesterian conodont collections from the Beech Creek, Haney, and Glen Dean formations of Indiana failed to group the recta element with the P1, M, and S elements they hypothesized to be parts of the Lochriea commutata apparatus. The authors nevertheless included the recta element in the statistical reconstruction of the species (text-fig.10), attributing the failure of the clustering procedure to low element occurrences and difficulties in identifying broken elements, also noting that current sorting and breakage also affects the presence and abundance of conodonts. Subsequently, Rexroad and Horowitz (Reference Rexroad and Horowitz1990, p. 509) did include Ozarkodina recta and O. subaequalis in their extensive synonymy of the Pb (= P2) element of Lochriea commutata.
M element (Fig. 5)
This large pick-shaped element is, along with the P1 element and perhaps the S3/4 elements, the most distinctive element of the L. commutata apparatus. Variation in this element includes differences in denticle spacing, the angle of the posterior bar to the apical denticle, and the length of the anticusp. Many mature specimens from the Heath and Tyler formations of Montana and the Bluestone Formation of West Virginia show well-developed attachment scars (Fig. 5.7, 5.8, 5.12, 5.14), whereas this feature is less well developed in immature specimens, such as in those from the Ridenhower Formation of Illinois (Fig. 5.21, 5.22). Examination of the two associated M elements illustrated by Scott (Reference Scott1942, p. 298, pl. 39, fig. 9) show them to be outer lateral views of sinistral and dextral M elements of similar maturity. This is probably a fortuitous association because no other elements occur in the vicinity of these two elements, and we know of no other L. commutata M elements in such direct association with each other.
Some M elements of Lochriea commutata, or of related Lochriea spp., illustrated in the literature are Prioniodus singularis Hass, Reference Hass1953, p. 88, pl. 16, fig. 4; Prioniodus roundyi var. dividen Elias, Reference Elias, Hicks, Westheimer, Tomlinson, Putman and Selk1956, p. 110, pl. 2, figs. 39–41; Prioniodus cf. P. singularis, Elias, Reference Elias, Hicks, Westheimer, Tomlinson, Putman and Selk1956, p. 112, pl. 2, fig. 45; Prioniodus roundyi var. parviden Elias, Reference Elias, Hicks, Westheimer, Tomlinson, Putman and Selk1956, p. 112, pl. 2, figs. 42, 43; Prioniodina alatoidea (Cooper), Bischoff, Reference Bischoff1957, p. 45, pl. 5, figs. 33, 34, 36; Prioniodus sp. A Ziegler in Flügel and Ziegler, Reference Flügel and Ziegler1957, p. 50, pl. 4, fig. 3; Neoprioniodus singularis (Hass), Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 471, pl. 66, figs. 2, 3; Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, pl. 11, fig. 5; Higgins, Reference Higgins1962a, pl. 1, fig. 8; Higgins, Reference Higgins1962b, p. 68, pl. 3, fig.11; Rexroad and Furnish, Reference Rexroad and Furnish1964, p. 674, pl. 111, fig. 32 (listed as fig. 33 in text); Higgins and Bouckaert, Reference Higgins and Bouckaert1968, p. 45, pl. 1, fig. 8; Webster, Reference Webster1969, p. 40, pl. 7, fig. 14; Dunn, Reference Dunn1970, p. 337, pl. 64, figs. 32, 33; Thompson, Reference Thompson1972, p. 37, pl. 1, figs. 21, 22; Lane and Straka, Reference Lane and Straka1974, fig. 34.1; Higgins, Reference Higgins1975, p. 68, pl. 3, fig. 11 (not Higgins and Varker, Reference Higgins and Varker1982, pl. 19, fig. 15); Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981, pl. 18, figs. 1–3; Neoprioniodus sp. A Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 472, pl. 66, figs. 4, 5; ?Neoprioniodus miser Elias, Reference Elias, Cline, Hilseweck and Feray1959, p. 154, pl. 2, figs. 23, 24; Elias, Reference Elias1966, p. 26, pl. 2, figs. 23, 24; Neoprioniodus aff. N. alatoideus Elias, Reference Elias, Cline, Hilseweck and Feray1959, p. 155, pl. 2, fig. 3 (only); Elias, Reference Elias1966, p. 27, pl. 2, fig. 3 (only); ?Neoprioniodus singularis (Hass), Globensky, Reference Globensky1967, p. 444, pl. 55, figs. 23, 24; Koike, Reference Koike1967, p. 307, pl. 4, fig. 30; Neoprioniodus montanaensis (Scott), Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 160, pl. 22, figs. 5a–8b; Marks and Wensink, Reference Marks and Wensink1970, p. 266, pl. 1, figs. 9, 10; Igo, Reference Igo1973, p. 195, pl. 29, fig. 32; Lochriea commutata M element, Stone, Reference Stone1991, p. 34, pl. 4, fig. 13; Lochriea sp. element, Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 1, fig. 5, 6 (both clusters contain the characteristic Lochriea commutata M element); Lochriea sp. M element, Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 4, figs. 13, 14.
S0 element (Fig. 6)
The S0 element of L. commutata is rare because it is only one of 15 elements in the apparatus and because of its susceptibility to breakage, being exceeded in rarity only by the S1 and S2 elements. This alate element is, like most elements of this general morphology, particularly susceptible to breakage when compressed laterally, the result being that its two anterolateral processes, and or its posterior process, are generally broken. The posterior process (Fig. 6.3–6.5, 6.14) has prominent terminating denticles at its posterior end, making it unlikely to be confused with those of any of the other S elements. Although an uncommon feature, a few specimens exhibit an everted lower surface (Fig. 6.11).
Although Scott (Reference Scott1942) did not recognize an S0 element to have been a part of the L. commutata apparatus, he illustrated (Scott, Reference Scott1942, pl. 40, fig. 16) and recognized (p. 299 in pl. 40 explanation) an S0 element as “the only specimen of its kind found in the Heath shales.” Some S0 elements of Lochriea commutata, or of related Lochriea spp., illustrated in the literature are Hibbardella pennata Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, p. 213, pl. 12, figs. 5, 6; Reynolds, Reference Reynolds1970, p. 2, pl. 2, figs. 8, 9; Higgins, Reference Higgins1975, p. 36, pl. 1, fig. 6 (only); Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981, pl. 14, figs. 1a, 1b, 4a, 4b; Riley et al., Reference Riley, Varker, Owens, Higgins and Ramsbottom1987, pl. 2, fig. 15; ?Higgins and Bouckaert, Reference Higgins and Bouckaert1968, p. 36, pl. 1, fig. 10; ?Hibbardella (Hibbardella) parva Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 114, pl. 25, fig. 21a, 21b.
Other than Norby (Reference Norby1976, p. 157, pl. 11, figs. 15a, 15b, 17a–18), who described this as the A3 element of L. commutatus, only Mapes and Rexroad (Reference Mapes and Rexroad1986, p. 115, pl. 1, fig. 21) and Rexroad and Horowitz (Reference Rexroad and Horowitz1990, p. 510, pl. 2, fig. 25) referred to this element, describing it as the Sa element of this species. Varker (Reference Varker1994, pl. 4, fig. 7) referred a well-preserved S0 element to Lochriea sp., which we would include in L. commutata.
This element can be confused with S0 elements belonging to species of other genera, particularly those of Gnathodus. S0 elements of G. bilineatus have a much more acute angle, <60°, between the lower edges of the two anterolateral processes (e.g., Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 3, fig. 8), whereas that same angle is 145° or greater in Lochriea commutata S0 elements (cf., Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 4, fig. 7).
S1 element (Fig. 7)
Scott (Reference Scott1942) illustrated an S1 element as a “hindeodell” element of Lochriea montanaensis (Scott, Reference Scott1942, pl. 39, fig. 1, subhorizontal element). The S1 element has a characteristic scythe-shaped or shepherd's crook morphology, with an angle of ~70° (Fig. 7.8–7.10, 7.13–7.17) to 90° (Fig. 7.3, 7.12, 7.18) between the anterior and posterior processes. The S1 element (Fig. 7.1, 7.2) was described and figured by Norby (Reference Norby1976, text-fig. 21, pl. 12, fig. 5c, 5d) as the Lochriea commutatus A1c element, and by Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig. 11A) as the Sb1 element of Lochriea sp.
The juncture between the anterior and the posterior processes of Lochriea commutata S1 elements is broadly curved and expanded laterally (Fig. 7), resulting in the characteristic shepherd's crook shape of their anterior ends. Discrete S1 elements are generally broken (e.g., those from bleach-processed residues from the Heath Formation), and are reported and illustrated only infrequently. Similarly, S1 elements are rarely identified in bedding-plane assemblages, and the anterior ends needed to identify them are generally preserved only as short broken stubs, (e.g., in bedding-plane assemblages from Montana; Fig. 7.1–7.4). The best-preserved, complete, discrete S1 elements (Fig. 7.9–7.18) and S1 element pairs (Fig. 7.5–7.8) were those recovered with, or in, fused clusters from West Virginia. One remarkable S1 element pair (Fig. 7.7) shows the anterior process of the dextral S1 element closely interlocked with the anterior process of the sinistral S1 element, and preserving the two elements in a tight embrace with their anterior processes facing one another (Figs. 4.8, 5.4, 7.5–7.7), and in another (Fig. 7.5, 7.6) the element embrace not being as tight (i.e., the elements having moved relative to one another). The interlocked S1 elements of Lochriea commutata (Figs. 4.8, 5.4, 7.5–7.7), like those illustrated by Varker (Reference Varker1994, pl. 1.4) in a fused cluster of Gnathodus bilineatus from England, are positioned over the posterior ends of the long posterior process of the central S0 element (Figs. 4.8, 5.5, 7.7), S1d and S2d are preserved farther posteriorly than the other S elements. Because S elements were located and functioned at the anterior end of the feeding apparatus (Aldridge et al., Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987; Purnell and Donoghue, Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998, text-fig.1e) (Fig. 12), and are not known to have functioned in apposition to one another, both the position and the interlocking nature of the S1 elements in fused clusters of both species are presently best accounted for by post-mortem contraction.
Ramiform elements with a scythe or shepherd's crook shape, similar to those of Lochriea commutata S1 elements, have been illustrated in the Carboniferous conodont literature. These include upper views of Hindeodina uncata Hass, Reference Hass1959, p. 383, pl. 47, fig. 6; Hindeodella uncata (Hass), Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981, pl. 15, ?fig. 2; Hindeodella brevis Branson and Mehl, Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, pl. 10, fig. 14; and Hindeodella croka Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 121, pl. 28, figs. 15, 17. Hindeodina uncata occurs in early Carboniferous strata and is probably the S1 element of a species of Gnathodus or of a related gnathodontid, a likelihood Varker (Reference Varker1994, p. 309) recognized when he identified this element, Hindeodella uncata (Hass), as the Gnathodus bilineatus Sd element. Higgins (Reference Higgins1975, p. 44, pl. 4, figs. 1–3) illustrated upper and lateral views of Hindeodella uncata that possesses a gently downward-arching anterior process.
S1 elements of gnathodontids, particularly those of Gnathodus bilineatus, as illustrated in Norby, Reference Norby1976, pl. 7, figs. 6, 8, 9, 11 (A1c element), Aldridge et al., Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987, fig. 4.1 (Sd element), polygnathacean apparatuses and reconstructions, Aldridge et al., Reference Aldridge, Smith, Norby, Briggs and Aldridge1987, fig. 4.7–4.12 (unlabeled Sd elements), Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 1, figs. 3, 4, 7, pl. 2, fig. 1 in fused clusters of G. bilineatus and in pl. 3, figs. 13, 15 as discrete G. bilineatus Sd elements, and of Streptognathodus/Idiognathodus von Bitter, Reference von Bitter1972, pl. 11, fig. 4a–d (Hindeodella parva), are similar to Lochriea commutata S1 elements; however, they can generally be differentiated from Lochriea spp. S1 elements by the characteristic sharp downturn, or anticusp-like extension, of the distal end of their anterior process, their more robust denticles, and the robustness and arching of their posterior process.
S2 element (Fig. 8)
The S2 element is approximately the same length as an S1 element of similar maturity, and slightly shorter than S3/4 elements. Like S1 elements, the S2 element is very rarely preserved intact, and has been difficult to recognize and characterize in bedding-plane assemblages from the Heath and Tyler formations (Fig. 8.1–8.4). The exceptionally preserved specimens associated with fused clusters in the Bluestone Formation of West Virginia (Fig. 8.5–8.12) have provided the basis for much of the foregoing description.
Because S2 elements lack strong morphological features and tend to break easily during compaction, it has been difficult to recognize them among the thousands of pieces of disjunct S elements recovered from Montana. Similarly, we have been able to identify and illustrate only a few S2 elements in bedding-plane assemblages of Lochriea commutata, generally only with a question mark (Fig. 8.4; Table 1). As with the other exceptionally preserved S elements in the Bluestone Formation of West Virginia, the S2 elements recovered with fused clusters (Fig. 8.5–8.12) have provided the basis for most of our understanding and description of S2 elements.
Scott (Reference Scott1942, pl. 39, fig. 1, nearly vertical element) illustrated a possible S2d element that crosses an S1d element and is the only such element that we identified among his illustrated material of Lochriea montanaensis. Higgins (Reference Higgins1975, p. 43, pl. 6, figs. 1–3, 5) named Hindeodella sinuosa on the basis of elements from Great Britain that are morphologically similar to Lochriea commutata S2 elements (Fig. 8). Hindeodella sinuosa Higgins has the same range as P1 elements of Lochriea commutata and other Lochriea species illustrated by Higgins (Reference Higgins1975, p. 70–72) as species of Paragnathodus: P. commutatus (pl. 7, figs. 7–9, 11, 13, 16, 20, 21), P. cruciformis (pl. 7, fig. 10), P. mononodosus (pl. 7, fig. 14), and P. nodosus (pl. 7, figs. 12, 15, 17–19, 22, 23). More recently, Varker (Reference Varker1994, p. 310, pl. 1, fig. 6) illustrated Hindeodella sinuosa in a fused cluster of Lochriea sp., and two discrete S elements, as the “probable” Sb elements of Lochriea sp. (Varker, Reference Varker1994, p. 310, pl. 4, figs. 16, 18), here regarded as S2 elements.
S3/4 element (Fig. 9)
The S3/4 element is the most commonly recognized S element of the Lochriea commutata apparatus, and is abundant in collections of discrete elements, bedding-plane assemblages, and fused clusters of the species. This abundance is primarily due to the relative robustness of the anterior process, which is a structure that does not appear to break as easily as that of S1 and S2 elements, making it easier to recognize the element. S3/4 elements are the only elements in the L. commutata apparatus that we are unable to distinguish from one another on purely morphological grounds (i.e., we are able to differentiate them only by their position within the apparatus). Thus, the S elements in the dextral nested S3/4d element pair (Figs. 8.12, 9.11) and the sinistral S3/4s element pair (Fig. 9.1, 9.5) exhibit no morphologic differences that presently allow us to distinguish them from one another in discrete element collections. The S3/4 elements are among the three most morphologically diagnostic elements of the species. One prominent feature is the large cusp with its anterior process, which is about one-third the height of the cusp and two or three times the height of the posterior process. The anterior denticles increase in height anteriorly giving the process an upswept appearance, which is an atypical feature in ozarkodinid S3/4 elements.
Some examples of S3/4 elements of Lochriea commutata, or of related Lochriea species, illustrated in the literature are ?Hindeodella bigeniculata Elias, Reference Elias, Hicks, Westheimer, Tomlinson, Putman and Selk1956, p. 106, pl. 1, figs. 20, 21, (non pl. 1, fig. 16), line drawings only; Hindeodella mehli Elias, Reference Elias, Hicks, Westheimer, Tomlinson, Putman and Selk1956, p. 108, pl. 1, fig. 24 (?figs. 22, 23), line drawings only; Metcalfe, Reference Metcalfe1981, p. 29, pl. 15, fig. 3; Hindeodella germana Holmes, Reference Holmes1928; Bischoff, Reference Bischoff1957, p. 27, pl. 6, fig. 32 (non pl. 6, fig. 34); Higgins, Reference Higgins1961, pl. 10, fig. 12 (?fig. 13); Higgins and Bouckaert, Reference Higgins and Bouckaert1968, p. 36, pl. 1, fig. 12; Higgins, Reference Higgins1975, p. 38, pl. 5, fig. 6; Hindeodella montanaensis (Scott), Stanley, Reference Stanley1958, p. 465, pl. 64, figs. 1–4, 5 (upper specimen); Rhodes et al., Reference Rhodes, Austin and Druce1969, p. 123, pl. 28, figs. 21, 26; Lochriea commutata Sc element, Rexroad and Horowitz, Reference Rexroad and Horowitz1990, p. 510, pl. 2, fig. 24; Lochriea commutata Sc1 element, Stone, Reference Stone1991, p. 34, pl. 4, fig. 12; Lochriea sp. Sc element, Varker, Reference Varker1994, p. 310, pl. 4, figs. 15, 17; possibly present as an S element in a fused cluster identified as Lochriea sp. (Varker, Reference Varker1994, pl. 1, fig. 5).
Acknowledgments
We thank R. Ethington (University of Missouri), D. Blake (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign), and J. Carter (Carnegie Museum of Natural History) for permitting us to study type and other conodont collections in their care; S.-W. Norby (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign) and G. Gomulka (University of Toronto) for scanning electron microscopy; K. David and the late J. Burke (Royal Ontario Museum) for much capable assistance during the preparation of early versions of this paper; H. Choong (formerly Royal Ontario Museum, now Royal British Columbia Museum), D. Byers, M. Knapp, and S. Krusemark (Illinois State Geological Survey) for providing vital technical expertise during the later stages of preparing figures and tables and for editing the manuscript prior to submission; J. Repetski (United States Geological Survey) for reviewing the manuscript; D. Korn (Museum für Naturkunde Berlin) for sharing information and updates on the German Carboniferous; the Palaeontological Association for its permission to reproduce plate 2 and text-figure 11 of Purnell and Donoghue (Reference Purnell and Donoghue1998) as Figures 13 and 14, respectively, and M. Purnell (Leicester University) for supplying originals of these illustrations, and subsequently providing, and allowing us to publish, an updated version of their text-figure 11A, as Fig. 14.1.
We thank Journal of Paleontology Managing Editor J. Kastigar for her encouragement and helpful technical advice, Journal of Paleontology Associate Editor S. Leslie (James Madison University), and reviewers M. Purnell and J. Over (State University of New York at Geneseo) for their helpful comments and suggestions. The reviewers’ comments, particularly those of M. Purnell, led to a stronger paper, and are very much appreciated; any shortcomings that remain are, of course, ours.
Appendix: Locality Data
Localities in Montana (1–3) and Oklahoma (4, 5), USA, correspond to localities 1–5 in von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a). Locality 8 in Mercer County, West Virginia, USA, is newly described here, but was sampled by Weems and Windolph (Reference Weems and Windolph1986) for fossil fish. Locality 9, drill hole SB-1 at Stewiacke, Colchester County, Nova Scotia, Canada, may be found in Utting (Reference Utting1980) and in von Bitter et al. (Reference von Bitter, Giles, Utting and Wong2007). Locality 10, Am Schälk, near Letmathe, Germany, is more specific than was provided for localities 1A and 1B in von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994b).
Locality 1 (Montana)
Heath Formation, sec. 27, T14N R20E, Fergus County (Loco Ridge 7.5′ Quadrangle), Montana, USA. Carnegie Museum no. 33965 was collected by Richard Lund at an unknown level in the formation at this locality. Scott (Reference Scott1942, Reference Scott1969) and Easton (Reference Easton1962) probably sampled the Heath Formation at this locality as USGS locality 13366.
Locality 2 (Montana)
Heath Formation, NE SW SW sec. 26, T14N R19E, Fergus County (Heath 7.5′ Quadrangle), Montana, USA; ~8.3 km S of Heath on E side of road. Red Hill Road section of Norby (Reference Norby1976). Samples H-A-1-1 and H-A-2-2, plus subsample H-A-2-7-1, were collected by Norby (Reference Norby1976) in brownish black fissile shale at two exposures, ~91 m (~100 yards) apart, from the northern outcrop and southern outcrop, respectively, of the upper Heath Formation. This is likely the topotype locality of Lochriea montanaensis Scott, Reference Scott1942.
Locality 3 (Montana)
Tyler Formation, Stonehouse Canyon Member on line between SE NW SE sec. 23 and SW NE SE sec. 23, T14N R20E, Fergus County (Loco Ridge 7.5′ Quadrangle), Montana, USA. Locality consists of two short roadcut exposures, each ~2 m (6.5 ft) thick and ~5 m (15 ft) apart. H-B-1-A was a bulk sample representing the entire 15 cm (6 in.) bed of brownish-black fissile shale at the top of the exposure. Sample H-B-1-B was a bulk sample of the entire 50 cm (20 in.) thick bed of fissile black shale at the top of the exposure; sample H-B-1-B-1 was taken in the lowest 10 cm (4 in.) of the previous 50 cm (20 in.) thick sampling unit. Tyler Creek section of Norby (Reference Norby1976) and Norby and Rexroad (Reference Norby and Rexroad1985).
Locality 4 (Oklahoma)
Hindsville Formation in SW SE SE sec. 22, T25N R21E, Craig County (Vinita NE 7.5′ Quadrangle), Oklahoma, USA; 13.2 km SW of Afton in road ditch on the N side of combined U.S. Highway 60, 66, and 69. Only a few cm of exposed limestone of the upper Hindsville Formation were sampled by Norby in 1987; von Bitter and Norby (Reference von Bitter and Norby1994a) listed this as sample 4, the only sample taken at field stop 3 in 1987. Corresponds to locality 1299 of Branson and Mehl (Reference Branson and Mehl1941b) and is the type locality for Lochriea commutata. See Branson et al. (Reference Branson, Huffman and Strong1965) for the identification of the Hindsville Formation at this locality.
Locality 5 (Oklahoma)
Fayetteville Formation near center sec. 28, T25N R21E, Craig County (Ketchum 7.5′ Quadrangle), Oklahoma, USA; 15.9 km SW of Afton, along Oklahoma Route 82. At stop 2, Norby sampled a 2.1 m exposure of alternating shale and limestone of the upper Fayetteville Formation as samples 5 (upper 1.83 m of limestone) and 6 (0–20 cm of shale near base of exposure) in 1987.
Locality 6 (Oklahoma)
Goddard Formation, Tiff Member, center NW NE NE, sec. 2, T3S R1E, Carter County (Springer 7.5′ Quadrangle), Oklahoma, USA (locality data from Lane and Straka, Reference Lane and Straka1974). Locality 65 of Tomlinson (Reference Tomlinson, Mayes, Westheimer, Tomlinson and Putman1959, p. 322).
Locality 7 (Illinois)
Ridenhower Formation, partial stratigraphic section sampled midpoint of section line between geographic secs. 3 and 10 (i.e., SW SW SE sec. 3, T2S R9W), St. Clair County (Millstadt 7.5′ Quadrangle), Illinois, USA. Outcrop on NE bank of Prairie du Long Creek, just above (N) of old bridge, 1.1 km (0.7 mi) NE of the still-standing (in 1974) old Vogel School. Samples VS-1 (0–0.5 m [0–1.5 ft] above creek level), VS-4 (1.1–1.4 m [3.5–4.5 ft] above creek level), VS-5 (1.4–1.7 m [4.5–5.5 ft]), VS-7 (2.0–2.3 m [6.5–7.5 ft]), and VS-12 (3.5–3.8 m [11.5–12.5 ft]), top of Ridenhower Formation, produced the Lochriea commutata elements studied and illustrated in this paper. Vogel School section of Norby (Reference Norby1976) and Norby and Rexroad (Reference Norby and Rexroad1985).
Locality 8 (West Virginia)
Bluestone Formation, Pride Shale Member, Mercer County, West Virginia, USA, at northwest end of Camp Creek Interchange (Exit 20) of the West Virginia Turnpike, 37°29.417′N and 81°06.417′W. Acid residue-derived, fused conodont clusters and discrete conodont elements recovered by Robert Stamm (USGS collection 34004-PC) from a calcareous concretion near the base of the Pride Shale Member. Geographic locality data after Weems and Windolph (Reference Weems and Windolph1986), who described Tanypterichthys pridensis, a paleoniscid fish, from a calcareous concretion from this locality; these authors also provided information regarding the geological setting of the Bluestone and underlying Princeton Sandstone formations.
Locality 9 (Nova Scotia, Canada)
Upper Windsor Group, Herbert River and Kennetcook members, Stewiacke, Colchester County, Nova Scotia, Canada. Samples HerbR-7-7 and Kenk-2-1 are from core from drill hole SB-1 at Stewiacke and processed for conodonts by Weston (Reference Weston1985). Stratigraphic terminology as per Moore (Reference Moore1967), Moore and Ryan (Reference Moore and Ryan1976), Geldsetzer et al. (Reference Geldsetzer, Giles, Moore and Palmer1980), and von Bitter and Moore (Reference von Bitter and Moore1992). Further information regarding drill hole SB-1 may be found in Utting (Reference Utting1980) and von Bitter et al. (Reference von Bitter, Giles, Utting and Wong2007).
Locality 10 (Schälk, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany)
Platy limestone (Plattenkalk of Ruprecht, Reference Ruprecht1937; Horn, Reference Horn1960; Herdringen Formation of Korn, Reference Korn2006), previously exposed but now completely covered because of landfill in two abandoned quarries at 51°22.614′N, 7°35.410′E, at Am Schälk, ~1.5 km N of Letmathe, northern margin of the Rhenish Mountains, Germany. Samples Schälk 42 and 50 were collected by Charles Collinson (Illinois State Geological Survey) in June 1964, accompanied by Willi Ziegler and Eva Paproth (Geological Survey of North-Rhine Westphalia at Krefeld). Sample Schälk 42 was collected from a 20 cm dark-gray, fine-grained limestone bed in a trenched interval between the northern quarry and southern quarry, ~12 m stratigraphically above the base of the southern quarry. Sample Schälk 50 was collected from a 50 cm thick medium-dark gray, fine-grained limestone bed at or near the base of the northern quarry, that is ~20.5 m stratigraphically above the base of the southern quarry. Viséan-Namurian boundary beds (according to the traditional definition) were present in these quarries, and both samples are apparently of latest Viséan age. Depending on their position in the stratigraphic column and the ammonoids they may have contained, the samples were taken in the Lyrogoniatites eisenbergensis Zone or the Lyrogoniatites liethensis Zone of the current ammonoid biozonation (Korn, Reference Korn1996).
Locality 11 (Hemer, North-Rhine Westphalia, Germany)
The so-called Arnsberger Grauwacke of Serpukhovian age, sampled by Schmidt (Reference Schmidt1934a, Reference Schmidtb), was exposed in the now completely landfilled Bröffel brickpit (Ziegeleigrube Bröffel) at 51°24.066′N, 7°45.114′E, 1 km N of Hemer at the northern margin of the Rhenish Mountains (Schmidt, Reference Schmidt1934a; Horn, Reference Horn1960). According to Schmidt (Reference Schmidt1934b, p. 77), the best of the conodont bedding-plane assemblages he studied were collected in the ‘bisulcatum-Kieselschiefer’ (siliceous shales with Eumorphoceras bisulcatum Girty, Reference Girty1909) that rest on the first prominent graywacke unit. Most or all of his study material was destroyed during World War II, but the 30 cm thick siliceous shale unit was re-collected by Hermann Schmidt and his students in 1956, which formed the basis of a new study by Schmidt and Müller (Reference Schmidt and Müller1964). The Arnsberger Grauwacke of Schmidt (Reference Schmidt1934a, Reference Schmidtb) and subsequent authors was like the Plattenkalk of locality 10 (above), a concept used before the introduction of a lithostratigraphic framework based on formations and members, after ca. 1970; thus, Korn (Reference Korn2006) placed the “Arnsberger Schichten,” the Arnsberg Layers or Beds, in the Lüsenberg Formation.

















