Introduction
Knowledge of a species’ potential distribution and the suitability of available habitat are fundamental for effective conservation planning and management, providing a basis for many assessment schemes (IUCN 2001). However, the quality of information on the distribution of species and their required habitats varies greatly across taxa and regions worldwide (Collen et al. Reference Collen, Ram, Zamin and McRae2008). For many species, geographical distributions mostly describe species limits based on expert knowledge, but often no information on species occurrence or density within those limits is available (Jetz et al. Reference Jetz, McPherson and Guralnick2012). This is particularly challenging for species in tropical landscapes, where difficult accessibility to unpopulated areas has limited survey efforts and prevented obtaining high-quality census data (Raxworthy et al. Reference Raxworthy, Martinez-Meyer, Horning, Nussbaum, Schneider, Ortega-Huerta and Townsend Peterson2003, Collen et al. Reference Collen, Ram, Zamin and McRae2008). When available, these data are often limited to small samples of observed localities obtained in limited recent surveys or from historical records in museum collections (Pearson et al. Reference Pearson, Raxworthy, Nakamura and Peterson2007).
These limitations hold for our knowledge of the distribution of many parrot species. Parrots (Psittaciformes) are among the most threatened bird taxa of the world, with nearly one third of total species threatened under IUCN criteria (IUCN 2016). The likelihood of parrot species being classified as threatened has been recently related to their life history traits, socio-economic factors (linked to anthropogenic threats such as logging, agriculture spread, hunting and trapping), and the historical distribution size of the species (Olah et al. Reference Olah, Butchart, Symes, Guzmán, Cunningham, Brightsmith and Heinsohn2016). Despite the fact that some parrot species have received conservation attention (Toft and Wright Reference Toft and Wright2015), the distribution of many species in remote and difficult to access habitats has prevented the collection of basic biological and distributional information (e.g. Tella et al. Reference Tella, Rojas, Carrete and Hiraldo2013).
Species distribution models (SDMs) can provide valuable predictive tools for filling information gaps and can produce continuous predictions of potential distribution for poorly surveyed species. They may thereby better depict a species’ actual distribution (Botero-Delgadillo et al. Reference Botero-Delgadillo, Páez and Sanabria-Mejía2012b) and can be helpful for effective conservation management (Peterson et al. Reference Peterson, Soberón, Pearson, Anderson, Martínez-Meyer, Nakamura and Araújo2011, Ferrer-Sánchez and Rodríguez-Estrella Reference Ferrer-Sánchez and Rodríguez-Estrella2016). Presence-only models, particularly, rely solely upon species presences and environmental data, and can provide accurate predictions of species’ distributions with reduced numbers of known occurrences (Elith et al. Reference Elith, Graham, Anderson, Dudík, Ferrier, Guisan, Hijmans, Huettmann, Leathwick, Lehmann, Li, Lohmann, Loiselle, Manion, Moritz, Nakamura, Nakazawa, Overton, Peterson, Phillips, Richardson, Scachetti-Pereira, Schapire, Soberón, Williams, Wisz and Zimmermann2006, Phillips et al. Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). However, these models should account for potential spatial biases in geographical and environmental information to be useful (Phillips et al. Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). One common bias in distributional data is the high concentration of observations along highly accessible areas such as roads and rivers (Reddy and Dávalos Reference Reddy and Dávalos2003, Kadmon et al. Reference Kadmon, Farber and Danin2004). Although widely recognised, the potential effects of this bias on modelled distributions are often not considered, including the few cases when the distribution of tropical parrots has been modelled (Marini et al. 2010, Monterrubio-Rico et al. Reference Monterrubio-Rico, Renton, Ortega-Rodríguez, Pérez-Arteaga and Cancino-Murillo2010, Botero-Delgadillo et al. Reference Botero-Delgadillo, Páez and Bayly2012a, Pidgeon et al. Reference Pidgeon, Rivera, Martinuzzi, Politi and Bateman2015).
In this study we use species distribution models to disentangle the relative importance of habitat characteristics, accessibility and the combination of these factors in the distribution of the ‘Critically Endangered’ Blue-throated Macaw Ara glaucogularis throughout its known range in the wild. Historically, this was a poorly-known species endemic to Bolivia, not discovered in the wild until 1992, and considered among the most threatened species in the world with a population size estimated between 250 and 300 individuals (BirdLife International 2015). Individuals are concentrated in three subpopulations with a maximum of 16 known breeding pairs occurring over a vast region (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014). As has been found in other ‘Endangered’ macaw species (Tella et al. Reference Tella, Rojas, Carrete and Hiraldo2013, Pacífico et al. Reference Pacífico, Barbosa, Filadelfo, Oliveira, Silveira and Tella2014), breeding individuals might constitute a small fraction of the overall population. However, due to logistical difficulties and limited accessibility to a large part of its distributional range, the population size and breeding and global distribution of the species could have been underestimated. This species exclusively inhabits an expansive region of Amazonian flooded savannahs in the Llanos de Moxos, Beni Department, Bolivia, where it occupies forest islands dominated by palms and, secondarily, gallery forests (Yamashita and De Barros Reference Yamashita and De Barros1997; BirdLife International 2015). The few geographic records available for this species impeded accurate estimates of its area of occupancy, which was previously estimated between 9,236 and 61,500 km2 (Herzog et al. Reference Herzog, Maillard Z., Embert, Caballero and Quiroga2012, BirdLife International 2015). Surveys of remote, potential areas where unknown populations of the species could persist have been highlighted as important conservation actions (BirdLife International 2015). Our modelling approach aims to identify potential spatial bias of previous surveys to more accessible areas, and to offer a better prediction of its potential (or even actual) distribution, to guide further surveys, research and management actions.
Methods
Study area and data compilation
The study area is located in the Beni department, north-eastern Bolivia and comprises approximately 200,000 km2 (Fig. 1). The region is made up of seasonally flooded savannas interspersed with a complex mosaic of forest islands, gallery forest, grasslands and cerrado (Yamashita and De Barros Reference Yamashita and De Barros1997, Mayle et al. Reference Mayle, Langstroth, Fisher and Meir2007). Forest patches are restricted to areas that are elevated just enough to avoid flooding. Most of these are eroded relicts of natural or man-made levees or terraces of abandoned river channels (Hanagarth and Beck Reference Hanagarth and Beck1996). Annual precipitation ranges from 1,300 to 2,000 mm and is mostly concentrated from November to May (Hanagarth and Beck Reference Hanagarth and Beck1996). Human settlements currently inhabit the region at low densities, but there is an extensive human use of nearly the entire region, with cattle-ranching being the primary economic activity (Mayle et al. Reference Mayle, Langstroth, Fisher and Meir2007).

Figure 1. Study area.
The breeding population of Blue-throated Macaw in the study area has been monitored intensively since 2002 (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014, J. A. Díaz unpubl. data). Each year, known breeding sites and other potentially suitable areas were searched intensively for Blue-throated Macaws from early August to January. Potentially suitable areas were considered to be fragments of gallery forest and forest islands located close (1–3 km) to areas where the species was already known to occur. Additionally, other areas with similar vegetation structure and areas where local people reported the presence of Blue-throated Macaws were also explored. Access to the surveyed areas was done by car, aeroplane, horseback, or on foot. Most records consisted of visual observations of individuals, but occasionally presence was confirmed by acoustical contacts or identification of recently moulted feathers. In total, 79 occurrences were recorded throughout the study period (33 with evidence of reproduction, i.e. active nests of breeding pairs detected).
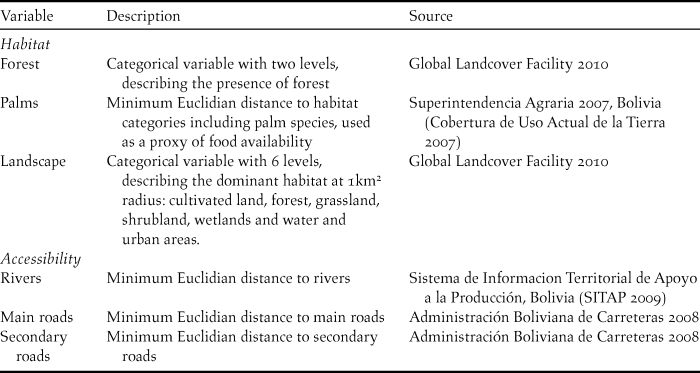
Occurrence locations were entered into a Geographic Information System at 10 arcseconds (∼30m) resolution. We compiled data on six variables to represent habitat variability and accessibility in the study area (Table 1). Climatic variability was low in the study area, and thus we preferred to focus only on the fine-grain habitat suitability and accessibility which are likely to be more important at fine spatial scales (Herzog et al. Reference Herzog, Maillard Z., Embert, Caballero and Quiroga2012). These variables were derived at 10 arcseconds to match the species occurrence data. Additionally, we used spatial statistics to derive a land-use variable related to the dominant landscape composition at 1-km radius around each ∼30m pixel. For this we used “focal statistics” in ArcMap 9.3 with the “majority” statistic.
Table 1. Variable description and information sources. All variables were derived at 10 arcseconds (∼30m) resolution.
Modelling
We built a SDM (Peterson and Soberón Reference Peterson and Soberón2012) to estimate the probability of distribution of Blue-throated Macaw using the occurrence data and environmental variables. Models were constructed using all occurrence data to maximise sample size, although similar results were obtained when only considering occurrences with evidence of reproduction (Appendix S1 in the online Supplementary Material). SDMs were implemented in Maxent 3.3.3k software (Elith et al. Reference Elith, Phillips, Hastie, Dudík, Chee and Yates2011). We selected 500 iterations for model convergence and employed the default regularization procedure to prevent overfitting (Phillips and Dudík Reference Phillips and Dudík2008). To construct the models, random samples of background pixels (10,000) within the study area were used as pseudo-absences (Phillips and Dudík Reference Phillips and Dudík2008). To address our questions, we followed a hierarchical approach and ran Maxent with three models based on different combinations of the variable sets, namely an environmental model that included only habitat variables (habitat); an accessibility model that included only variables of human accessibility (access); and a habitat and accessibility model that included both habitat variables and variables of human accessibility (habitat+access).
Model accuracy was assessed by dividing the species occurrence data into random training (70%) and test (30%) datasets. To reduce uncertainty caused by sampling artefacts of training and test data, we conducted 10 replicates for each model. Models were evaluated on the test data using the Area Under the receiver operating characteristics Curve (AUC) and test gain as threshold-independent assessment measures (Phillips et al. Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). Note that AUC values in MAXENT are used for the problem of classifying presences vs. background points (which may or may not be true absences; Phillips et al. Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). AUC values range from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates perfect model performance and 0.5 indicates predictive discrimination no better than random. We also calculated the true skill statistic (TSS). TSS ranges from −1 to +1, where +1 indicates perfect agreement and values of zero or less indicate a performance no better than random (Allouche et al. Reference Allouche, Tsoar and Kadmon2006). Additionally, model significance was tested using threshold-dependent binomial probability tests. For this, we used the 10-percentile training presence and the maximum sensitivity plus specificity values as thresholds (Liu et al. Reference Liu, Berry, Dawson and Pearson2005, Botero-Delgadillo et al. Reference Botero-Delgadillo, Bayly, Gómez, Pulgarín-R. and Páez2015). Note that specificity values defined by MAXENT use predicted area, rather than true commission (Phillips et al. Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006). We used a partitioning procedure (Maxent jackknife test) to take into account the co-linearity between spatially related variables. This allows the ‘pure’ effect of each variable/variable set to be separated from joint effects that cannot unambiguously be attributed to one variable/variable set or another due to spatial collinearity. This procedure entailed the calculation of incremental improvement in performance of a model with a particular variable/variable set compared with the equivalent model without that variable/variable set. We also calculated model performance for each variable/variable set when used in isolation. The estimated contributions were based upon the test gain.
Finally, we calculated total surface of suitable area for the species according to Maxent models in the whole study area and in the species extent of occurrence (EOO), that is, the, the area within the Minimum Convex Polygon (MCP) including all known locations of the species. For this task, model predictions were transformed into binary maps (i.e. presence/absence) using as thresholds the 10-percentile training presence and the maximum sensitivity plus specificity values (Liu et al. Reference Liu, Berry, Dawson and Pearson2005, Botero-Delgadillo et al. Reference Botero-Delgadillo, Bayly, Gómez, Pulgarín-R. and Páez2015).
Results
Occurrence patterns and accessibility
Probability of occurrence near roads and rivers was greater than that expected from a spatially random distribution (Table 2), indicating that the distribution of occurrence points was skewed towards more accessible areas (Figure 2). Among accessibility variables, distance to secondary roads showed both the highest model performance when used in isolation and the highest pure contribution in multivariate models (Figs 3a, c).
Table 2. Model performance of Maxent models based on different sets of variables using AUC, TSS and Test gain values. Note that for each set of variables, AUC, TSS and test gain (TG) values are averaged values across 10 replicate models calibrated using different randomly selected subsamples of total data (N = 79 records). Model significance was tested using threshold-dependent binomial probability tests, using the 10 percentile training presence (10p TP) and the maximum sensitivity plus specificity values (MSPS) as thresholds. The number of significant replicate models is provided.
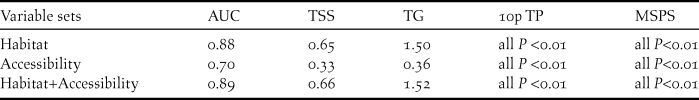
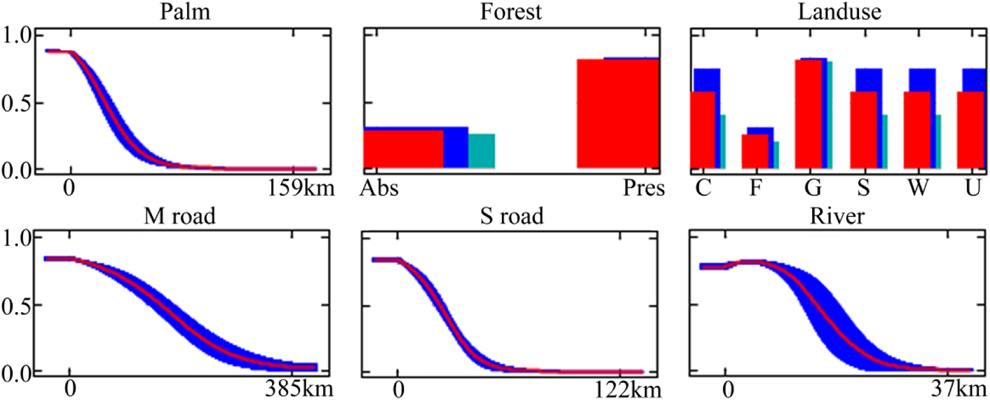
Figure 2. Partial response curves illustrating the relationships between probability of occurrence of the blue-throated macaw and our set of environmental and accessibility variables. These curves show how the shape of the response changes for a particular variable, while all other variables are held at their mean sample value. Mean response curve of the 10 replicate Maxent runs (red in the online version; black in the printed version) and standard deviation (blue in the online version; grey in the printed version; two shades for categorical variables) are shown. For forest: Abs = absence, Pres = presence. For landuse: C = cultivated land, F = forest, G = grassland, S = shrubland, W = wetlands and water and U = urban areas.

Figure 3. Performance of environmental and accessibility variables in univariate models (a) and independent contribution (b–d) of individual variables to multivariate models using different combinations of variables. Mean variable contributions and their standard deviations are calculated based on 10 replicate runs. The model contributions are based on test gain from Maxent.
Occurrence patterns and habitat
Among habitat variables, distance to palms followed by land use composition at the landscape level (∼1 km, variable “landuse”) showed the highest model performance when used in isolation (Figure 3a). Interestingly, the presence of forest at a local scale (∼30 m, variable “forest”) was a poor predictor when used in isolation. In contrast, pure contribution of this variable was high when used in combination with the other habitat variables (Figure 3b). This is because probability of occurrence increased with the presence of forest at a local scale (∼30 m resolution) only when forest patch size was low and thus surrounded by other habitat types at the landscape scale (Figure 2). That is, occurrence probability increased in forest islands dominated by palms.
Partitioning the effect of habitat and accessibility
The predictive model including both habitat and accessibility variables was more accurate than the model which only considered habitat (Table 2). However, the magnitude of these differences was low and model predictions were similar (Figure 4). Habitat variables showed the highest pure contribution to the habitat+access model (76.2%) according to Maxent jackknife test, indicating that their main effect was not related to their spatial covariation with accessibility. However, some degree of spatial covariation between both variable sets was found (joint contribution of habitat and accessibility variables: 22.3%). This was mainly related to covariation of land-uses at the landscape scale with distance to secondary roads (Appendix S2; note also the reduction in pure effect of these two variables in the habitat+access model; Figure 3d). Broadly, the presence of forest at the landscape scale (used as a measure of continuous forest) was more common with increasing distance from secondary roads (Appendix S2).
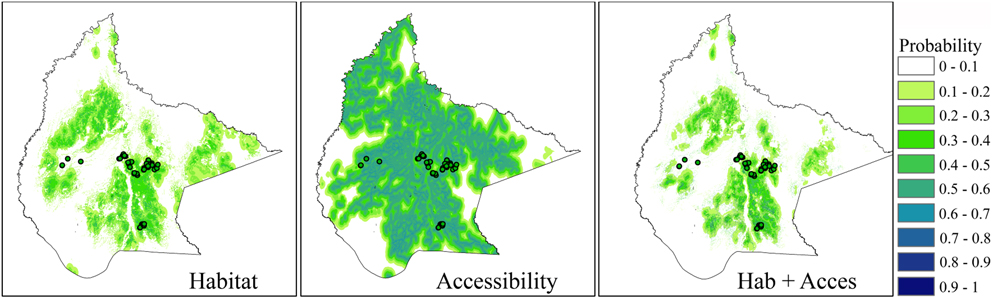
Figure 4. Predicted distributions of the Blue-throated Macaw in Bolivia. Predicted distributions are based on Maxent models using occurrence data (dots, n = 79) and different sets of variables: habitat, accessibility and habitat+accessibility. Note that models developed for each set of variables were calibrated using 10 different randomly selected subsamples of total data. Averaged predictions are shown.
According to the habitat+access model, suitable habitats occupied 29,183 km2 or 56,064 km2 in the whole study area, when using the 10-percentile training presence or the maximum sensitivity plus specificity thresholds. This value was reduced to 12,347 km2 or 19,249 (10-percentile and maximum sensitivity plus specificity thresholds, respectively) when only considering the area within the actual known distribution range of the species (i.e. that included in the MCP containing all occurrence points).
Discussion
The spatial distribution of species represents the cumulative effects of many different factors that are often difficult to separate. Sampling bias towards more accessible areas is a common phenomenon in biodiversity databases, but models based on such databases rarely take them into account in model predictions (Yackulic et al. Reference Yackulic, Chandler, Zipkin, Royle, Nichols, Campbell Grant and Veran2013). When accessibility bias allows covering enough environmental variability to disentangle the pure contribution of habitat variables on observed patterns (Ferrer-Paris et al. Reference Ferrer-Paris, Sánchez-Mercado, Rodríguez-Clark, Rodríguez and Rodríguez2014), results of SDMs could be used confidently. However, in other situations, the difficulty in determining which factors ultimately determine observed species distributions makes the usefulness of SDMs controversial. Therefore, future effort should be dedicated to quantifying the extent of different sources of sampling bias in datasets used in habitat modelling as well as exploring the consequences of such bias on model predictions. Partitioning methods, such as those present in this study, can help clarify the proportion of the total variance that might be accounted for by uncertainty due to joint effects of different variable sets.
Our study revealed the contrasting importance of habitat characteristics and habitat accessibility in the spatial distribution of a ‘Critically Endangered’ and still poorly-known species inhabiting tropical South America. As with other bird species (Reddy and Dávalos Reference Reddy and Dávalos2003, Kadmon et al. Reference Kadmon, Farber and Danin2004), occurrence probability of the Blue-throated Macaw decreased with the distance to human pathways (mostly to secondary roads). This pattern may result from different, not mutually exclusive processes. It could reflect biases in bird surveys towards more accessible areas and a poorer coverage of the most remote ones, but it could also result from ecological processes since distributions of species may respond negatively as well as positively to human development of landscape (e.g. Carrete et al. Reference Carrete, Tella, Blanco and Bertellotti2009, Cardador et al. Reference Cardador, Carrete, Gallardo and Tella2016, Ferrer-Sánchez and Rodríguez-Estrella Reference Ferrer-Sánchez and Rodríguez-Estrella2016). For this species, all known breeding sites are within private and highly managed cattle ranches, and recent occurrence models obtained at a smaller spatial scale showed that, contrary to other sympatric macaws (Blue-and-yellow Ara ararauna and Red-and-green Ara chloropterus), the Blue-throated Macaw does not appear to avoid human settlements (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Cepeda, Marinelli, Simoy, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Gandoy, Aramburú and Gilardi2016). This might suggest that Blue-throated Macaws prefer more human-altered areas and/or that they are displaced towards those areas by stronger congeneric competitors (see below). However, since all sampled locations in our study (not only presences but also absences) were skewed towards more accessible areas (Appendix S3), we could not separate the effects of habitat selection from sampling bias in observed patterns. In any case, the bias in the spatial distribution of occurrences in relation to secondary roads did not mask the independent contribution of most environmental factors on observed patterns (with the exception of forest at the landscape scale), probably because road and river networks are distributed throughout the entire study site, reaching areas in most of the sampled habitat types (Kadmon et al. Reference Kadmon, Farber and Danin2004, Leitão et al. Reference Leitão, Moreira and Osborne2011).
Although the good fit of a model does not necessarily imply causation, our explanatory models suggest that the most suitable areas for this species are forest islands containing palms, which is consistent with the previously described association of the species with these habitats (Yamashita and De Barros Reference Yamashita and De Barros1997, Herrera and Hennessey Reference Herrera and Hennessey2007). According to our models, the amount of suitable habitat for the species is predicted to be between 29,183 km2 and 56,064 km2. These estimates are closer to the upper limit of the variability range described for the species (9,236–61,500 km2) (Herzog et al. Reference Herzog, Maillard Z., Embert, Caballero and Quiroga2012). Predicted suitable habitat appears to be very large in comparison with the distribution of known records of the species. Clearly, factors beyond these measured environmental variables are currently constraining the spatial distribution of the species.
Our SDMs may inform a deeper analysis of the conservation status, threats and potential for the recovery of this species. The critical status of this bird is attributed to habitat loss and trapping for the pet trade (BirdLife International 2015). Population viability analyses suggest that further or even small annual increases in habitat loss (2%) and trapping (3%) would significantly increase its extinction risk over the next 50 years (Bouzat and Strem Reference Bouzat and Strem2012). The habitat loss hypothesis is challenged by our SDMs, which show the current extent of suitable habitat for the species could currently hold a much larger, healthier population; in fact, congeneric macaws are present in the same region at high densities (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Simoy, Cepeda, Marinelli, Kacoliris, Daniele, Cortelezzi, Díaz-Luque, Friedman and Aramburú2015, Reference Berkunsky, Cepeda, Marinelli, Simoy, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Gandoy, Aramburú and Gilardi2016). Regarding the wild-bird trade hypothesis, trade in the most attractive parrot species (including macaws) has been related to their population decline and current threatened status (Tella and Hiraldo Reference Tella and Hiraldo2014). However, legal international export of wild parrots was banned in Bolivia in 1984 (BirdLife International 2015), and trade in Blue-throated Macaws does not appear to have been any more intensive relative to other Bolivian species since that time. For example, international trade in Red-fronted Macaws Ara rubrogenys, an ‘Endangered’ species also endemic to Bolivia, was more intense than trade in Blue-throated Macaws in recent decades (www.cites.org), and current domestic trade in Blue-throated Macaws is negligible compared to the very high rates of Red-fronted Macaws annually poached and traded (Tella et al. Reference Tella, Rojas, Carrete and Hiraldo2013, Pires et al. Reference Pires, Schneider, Herrera and Tella2016). Despite that, the current population of Red-fronted Macaws (Tella et al. Reference Tella, Rojas, Carrete and Hiraldo2013) is at least three times higher than the estimated for Blue-throated Macaws, and the breeding population of Blue-throated Macaw seems not being recovering (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014). However, in contrast to birds captured for the pet trade that usually involve young individuals (but see Pires et al. Reference Pires, Schneider, Herrera and Tella2016), adult macaws were hunted in the Beni region for making traditional head-dresses. Population viability analyses indicate that the Blue-throated Macaw, as many other long-lived species, is highly sensitive to adult mortality (Bouzat and Strem Reference Bouzat and Strem2012) and thus the species could have been largely affected by this activity. However, this activity has been largely reduced nowadays and is not likely to be the main cause impeding the recovery of the species (BirdLife International 2015, M. Herrera pers. comm.).
Other less considered factors such as low breeding performance or other abiotic/biotic constraints (e.g. microhabitat selection or interspecific interactions) could be maintaining the population at low-density, thus limiting the access and use of all suitable habitats. In this regard, it is known that only an average of 4.3 nestlings per year fledged from all known nests (n = 19) despite intense management to improve breeding success (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014). The entire population may be already too small and scattered through such a large region that behavioural, demographic and/or genetic-related Allee effects (Courchamp et al. Reference Courchamp, Clutton-Brock and Grenfell1999, Tella Reference Tella2001) might currently impede the species’ recovery. On the other hand, key ecological factors acting at a smaller scale not measured in this study, such as the number of tree cavities for breeding, the size and habitat deterioration of the forest islands, or food availability (palm fruits) could also be related (Yamashita and De Barros Reference Yamashita and De Barros1997, Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Simoy, Cepeda, Marinelli, Kacoliris, Daniele, Cortelezzi, Díaz-Luque, Friedman and Aramburú2015). Additionally, other factors such as interspecific interactions might also be important. Previous studies in the region have shown that the occurrence of a rich community of parrots depends upon local abundance of tree cavities in forest patches (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Simoy, Cepeda, Marinelli, Kacoliris, Daniele, Cortelezzi, Díaz-Luque, Friedman and Aramburú2015), which suggests that interspecific competition might be high. Blue-throated Macaws share their preference for nesting in large cavities of dead palms and trees with the larger-bodied Blue-and-yellow Macaw and Red-and-green Macaw (J. A. Díaz unpubl. data). Observations conducted in another Amazonian region showed that nesting Blue-and-yellow Macaws engage in frequent intra- and inter-specific agonistic interactions in an area of up to 100 m around the nest, causing even infanticide and nesting failures (Renton Reference Renton2004). Interference competition of nesting macaws may thus exclude potential breeders, effectively limiting nest availability where palm cavities are clumped in space (Renton Reference Renton2004), as it is the case of palm forest islands where Blue-throated and Blue-and-yellow Macaws coexist (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Simoy, Cepeda, Marinelli, Kacoliris, Daniele, Cortelezzi, Díaz-Luque, Friedman and Aramburú2015). As Blue-and-yellow Macaws are larger, more aggressive, and far more abundant (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014, J. A. Díaz unpubl. data), they might limit access to reproduction sites by Blue-throated Macaws even after the provision of artificial nests (see also Renton 2014). This may explain why the breeding population has not increased after a long-term programme of nest-site provisioning within the species’ breeding areas (Berkunsky et al. Reference Berkunsky, Daniele, Kacoliris, Díaz-Luque, Silva Frias, Aramburú and Gilardi2014). More specific studies are needed to determine whether, and to what extent, microhabitat selection (including food availability across the annual cycle) and interspecific interactions may be limiting the actual abundance and distribution of this ‘Critically Endangered’ species.
Finally, population size and distribution range of the species could be actually larger than those recorded here, but limited surveys in less accessible areas limit our current knowledge. Future monitoring programs could directly benefit from results of SDMs provided in this study, which can be iteratively refined (as more observational data are collected), to conduct new surveys in the most suitable habitat patches. As a first step, new surveys should prioritise collection of empirical data in more remote (less accessible) areas and better distributed with respect to land-use composition at a landscape scale (particularly with better representation of continuous forest). Additionally, our SDMs should also help the optimal design of potential reintroduction or population reinforcement programmes that are projected for the species (BirdLife International 2015). Such programmes may benefit from validated estimates of the distribution of optimal habitats for the species (White et al. Reference White, Collazo, Dinsmore, Llerandi-Román and Devore2014), and a misunderstanding of these fundamentals may lead to inappropriate conservation management efforts. Refining SDMs with new surveys would aid in the optimal selection of release sites based both on habitat suitability and distance - connectivity - to the patches currently occupied by the species. SDM-based approaches could also help to increase the success of a number of translocation projects of parrots (White et al. Reference White, Collar, Moorhouse, Sanz, Stolen and Brightsmith2012) and many other animal taxa (Pérez et al. Reference Pérez, Anadón, Díaz, Nicola, Tella and Giménez2012). Importantly, new studies should also consider finer habitat-demographic links, since habitat-related choices made by individuals, and thus distribution patterns, may be in some situations decoupled from fitness outcomes (e.g. Cardador et al. Reference Cardador, Brotons, Mougeot, Giralt, Bota, Pomarol and Arroyo2015).
Supplementary Material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0959270917000144
Acknowledgements
We thank the previous project directors (Toa Kyle and Igor Berkunsky) and all the project´s staff and volunteers for their commitment over the past 15 years; without it this study would not have been possible. For their support of our field work and access to macaw habitat, we also thank the owners of the many cattle ranches where this study took place. Field work was supported by The World Parrot Trust while travelling (by JLT and FH) was supported by Junta de Andalucía (PAI RNM107) and Fundación Biodiversidad. JADL is coordinating the Proyecto de Conservación Paraba Barba Azul with the support of the World Parrot Trust. We also thank Dirección General de Biodiversidad y Áreas Protegidas (Viceministerio de Medio Ambiente y Aguas, Estado Plurinacional de Bolivia) and Gobernación del Beni for institutional support. The idea of this collaborative work arose from a visit of FH and JLT to the Proyecto de Conservación Paraba Barba Azul funded by the Fundación Noel Kempff Mercado.








