INTRODUCTION
The Belgian concept for the geological disposal of high-level nuclear waste, the so-called Supercontainer design, foresees disposal of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels in a cementitious environment. In carbon steel, which is the most important material of the RPV, 14C is mainly produced by the thermal neutron activation of 14N, according to the transmutation reaction 14N(n,p)14C. In the safety assessment of the geological disposal of high-level nuclear waste, 14C is a critical nuclide, because of its long half-life (5730 yr) and its high mobility in the geosphere and biosphere. The release of 14C is determined by the corrosion rate of carbon steel, which according to literature data is approximately 10–100 nm/yr (Grauer Reference Grauer, Knecht, Kreis and Simpson1991; Fujiwara Reference Fujiwara2002; Mihara Reference Mihara, Nishimura, Wada and Honda2002; Smart Reference Smart, Rance, Winsley, Fennell, Reddy and Kursten2009; Diomidis Reference Diomidis2014; Kursten Reference Kursten2014).
In order to investigate the release of carbon-14 from carbon steel in a highly alkaline environment, we performed simple immersion tests and potentiostatic corrosion tests. The simple immersion tests consisted of exposing the sample to an anaerobic cementitious environment (saturated portlandite pore water solution) for several months without applying any potential, while in the shorter potentiostatic corrosion tests an electrochemical setup was used to fix the potential at a more anodic value than the corrosion potential, in order to accelerate the corrosion process. The carbon speciation was determined by chromatographic analyses of gases produced during the corrosion tests, while the corrosion rate was calculated by the 60Co and the carbon release.
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials
The material used for our study was JRQ steel, which is an internationally accepted reference material representative for RPV steel. Its manufacturing process and general properties are described in detail elsewhere (IAEA 2001). JRQ is the IAEA designation for the ASTM A533 grade B class 1 steel. Its composition is given in Table 1. The irradiated material was representative for end-of-life conditions in the Belgian nuclear power plants and as such offered the advantage of providing realistic data on carbon-14 release and speciation. The investigated samples were irradiated in 1993 in the BR2 reactor at SCK∙CEN in the Vestale irradiation loop at a temperature of 290 ± 15°C and a pressure of 150 bar. For the accelerated tests, a sample with dimensions 10×6×4.5 mm was used with a contact dose rate of 920 µSv/h. For the static tests, three samples with dimensions of approximately 8×10×1 mm and a contact dose rate of approximately 350 µSv/h were used.
Table 1 Nominal composition of JRQ steel (ASTM A533).
Nitrogen Content Analysis and γ-Ray Spectrometry
The nitrogen content of unirradiated JRQ steel was measured by using an inert gas fusion method with a LECO TC436 analyzer. The sample was cut into a small cube of ~0.5 g and stored in acetone until the analysis. Before the sample analysis, 3 nitrogen blanks were measured and the results were normalized with the blanks. The instrument was calibrated using two certified reference materials of different nitrogen concentrations: AR668 with a nitrogen concentration of 29 µg/g (Alpha Resources) and AR660 with a nitrogen concentration of 61 µg/g (Alpha Resources). The lower limit of detection of the method was approximately 1 µg/g.
For γ-ray spectrometry, two HPGe detectors were used, one from Canberra and one from Ortec. The HPGe detectors were energy- and efficiency-calibrated over an energy range of 60–2000 keV using a γ-ray reference solution with a mixture of 10 different radionuclides.
Corrosion Experiments
Two types of corrosion experiments have been performed: simple immersion tests and potentiostatic corrosion tests. The simple immersion tests were long-term leaching experiments that allowed for the observation of a realistic corrosion behavior and associated carbon-14 release and speciation. The potentiostatic corrosion tests, which involved applying a fixed potential to a JRQ steel electrode, served mainly for preliminary speciation determination. Indeed, by enforcing a higher corrosion rate, the yield of released carbon species was increased.
Choice of the Electrolyte
For the static and accelerated test, the main electrolyte used was a saturated portlandite (Ca(OH)2) solution of pH 12.5. Portlandite is representative for the Belgian waste repository environment, which involves the use of large quantities of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC). The artificial pore water was prepared in a glove box under anaerobic conditions and degassed with nitrogen to reduce the risk of dissolving environmental 14CO2, which would cause an artifact. In the accelerated tests, a second type of electrolyte was used, by adding 0.5 M CaCl2 (this corresponds to 1 M of chloride) to a saturated portlandite solution. This increased the production of carbon species and made their detection easier.
Corrosion Setups and Sampling
Figure 1 shows the schematic of the experimental setup for the simple immersion tests. The JRQ steel sample was placed in contact with portlandite pore water inside a steel vial equipped with a PEEK liner. The internal volume of the steel vial was 50 mL. The vials were each filled with 35 mL of saturated portlandite pore water before adding the JRQ steel sample. Afterwards, the lid was screwed to the vial to make it airtight. All these manipulations took place in a glove bag under nitrogen atmosphere to ensure that conditions for the static tests were anaerobic. After the leaching tests, which lasted for approximately 7.5 months (231 days), gas and liquid samples were taken and analyzed for carbon species. The gas sampling was performed with a 500 µL gas tight syringe, which was then transferred to the gas chromatograph for analysis.
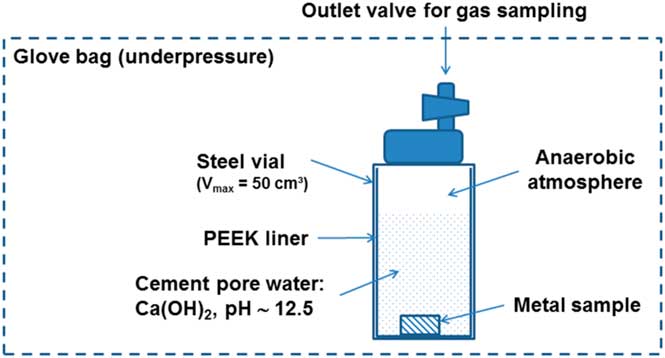
Figure 1 Schematic of the experimental setup for the simple immersion tests.
For the accelerated corrosion tests, JRQ steel specimens were embedded in an epoxy resin and mechanically wet-ground, with successively finer SiC papers, down to 500 grit, and then cleaned with double demineralized water and finally left to dry in an argon atmosphere. The electrochemical test cell consisted of a glass vial equipped with three electrodes attached to the lid: (1) the working electrode (carbon steel sample), (2) the platinum counter electrode, and (3) the in-house manufactured Ag/AgCl reference electrode. These electrodes constitute a traditional three-electrode setup described in the general literature on electrochemistry (Tait Reference Tait1994). Prior to the actual accelerated tests, a polarization curve was recorded. From this polarization curve, a potential was derived (resulting in an increased current density or corrosion rate) which was applied to the JRQ steel electrode during the accelerated test.
Determination of the Carbon Speciation
The carbon speciation was determined using a gas chromatography system type Shimadzu GC-2010 Plus, tailor-made to our needs. The carrier gas was pure Argon (N7.5, Air Products). To remove any residual impurities, this gas was passed through two gas purifiers (VICI Valco Instruments Co. Inc.) before it entered the GC column. For the analyses we used a ShinCarbon ST column composed of a high surface area carbon molecular sieve. This has been developed for the rapid separation of permanent gases, such as N2, O2, CO, and CO2, and low hydrocarbons, without cryogenic cooling. The detector was a Pulsed Discharge Helium Ionization Detector (PDHID). Table 2 shows the detection limits for common carbon compounds.
Table 2 Detection limits for common carbon compounds, measured with the Shimadzu GC-2010 Plus.

RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Estimation of the 14C Content of Irradiated JRQ Steel
The basis for the estimation of the 14C content of irradiated JRQ steel was the determination of the 14N content of an unirradiated sample, assuming that the neutron activation of 14N is the most probable production pathway of 14C in carbon steel. We obtained an average 14N concentration of 19 ± 0.4 µg/g in the unirradiated material, which is slightly lower than the range mentioned in literature (20–30 µg/g; IAEA 2009). Assuming the measured value, and taking into account the irradiation history with a total neutron fluence of 5×1019 n/cm², the theoretical concentration of 14C in irradiated samples was calculated using the “Triton” depletion sequence in the SCALE-6.1 code. This yielded a 14C concentration of 1.069×103 wt. µg/g, which corresponds to an activity of 175 Bq/g. The corrosion of 1 g of JRQ steel will lead to the release of approximately 1 ng of 14C.
Corrosion Rate Determination from 60Co Measurements
The measurement of the corrosion rate of carbon steel in a highly alkaline environment is a difficult task with traditional techniques because of the extremely low values involved. Therefore, we investigated whether the corrosion rate could be determined radiometrically by measuring the release of activation products, such as 60Co, when an irradiated steel sample is in contact with artificial portlandite pore water. This approach assumes a homogeneous distribution of 60Co in the material and the same leaching rate as Fe under alkaline conditions.
The corrosion rate of carbon steel in highly alkaline solutions is determined by the diffusion of iron through a passive film on top of the steel surface (Kursten Reference Kursten2014). This implies that the corrosion rate obeys a parabolic law, and this behavior was the basic assumption for our interpretation of the results from the 60Co determinations. Table 3 summarizes the results from γ-ray spectrometry, showing the total 60Co activity in a 20 mL test cell. The result at 50 days, being two orders of magnitude higher than the other values, is presumed to be an outlier. This might have been caused by the accidental transfer of a very small piece of irradiated metal into the measurement vial. Therefore, we omitted this data point from subsequent analyses.
Table 3 Total 60Co activity released in the 20 mL test cell (results obtained by γ-ray spectrometry).
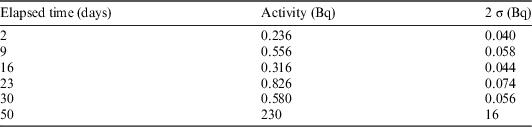
The scatter on the results is high. This might be due to the precipitation of small sized particles, which are visible in the solution. Indeed, under alkaline conditions, the released 60Co can precipitate as a hydroxide. It was difficult to completely homogenize the solution, which made it difficult to take representative samples. Another source of error might be that these precipitates adsorbed on the wall of the test cell. The third source of error may lie in the γ-ray spectrometry itself. In order to obtain a reliable measurement, a prerequisite is that 60Co is homogenously distributed throughout the solution, while in our case the precipitates may have (partially) settled on the bottom of the vial. In this case, the calibration factor can differ by a factor of two. Furthermore, the amount of precipitates in the vial may have been different for each sampling, and it is not possible to quantify this retroactively.
Figure 2 shows a linear fit of the 60Co release data as a function of the square root of the elapsed time of the experiment, with the fit line forced through the zero point. A fit with R2=0.91 is obtained. The parabolic rate law is
where R Co-60 is the total released 60Co activity in Bq at time t, and t is the elapsed time in days. This confirms that the release of 60Co is controlled by diffusion through the passive layer formed under highly alkaline conditions.
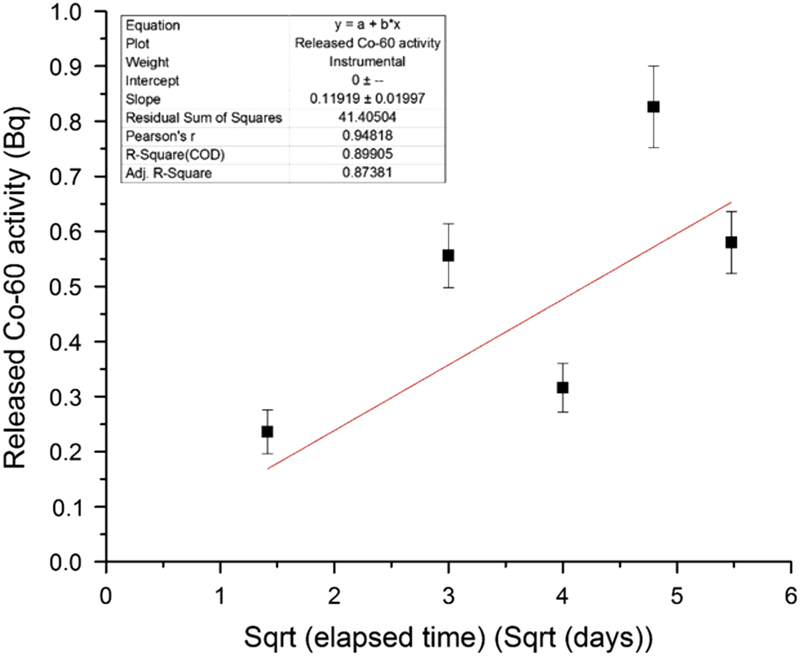
Figure 2 Linear fit of the released 60Co activity as a function of the square root of the elapsed time.
After 365 days, according to Equation (1), 2.3 Bq of 60Co will have been released. The original carbon steel specimen had dimensions of 2×2×35 mm and a total activity of 1.6 x 105 Bq. This means that the dissolved fraction of the specimen (assuming that 60Co was distributed evenly throughout the carbon steel sample) was 2.3 / 160,000=1.4×10–5. On a total initial volume of 140 mm3 this results in 2×10–3 mm3 of dissolved carbon steel. The exposed surface of the sample is 288 mm². This yields a corrosion depth, after one year of exposure, of 7 nm. A corrosion rate of 7 nm/yr is a bit lower than the reference range of 10–100 nm/yr, but this may be explained by the observed precipitation. Also, it is not proven that the diffusion behavior of cobalt through the passive film is the same as that of iron. It probably also means that in these conditions 60Co measurements are not the ideal way to determine the corrosion rate of carbon steel.
Speciation Determination
Simple Immersion Tests
After immersing an irradiated JRQ steel sample in saturated portlandite pore water, we applied a potential of 620 mV (vs. SHE) to the sample. This resulted in a current density of 5.9×10–6 A. The test lasted for 165 h and gas samples were taken after respectively 25, 64, and 165 hr. GC analysis showed the production of hydrogen gas by anaerobic corrosion of the steel and the appearance of CO2. No other gaseous carbon species were detected.
For the second test we added 0.5 M CaCl2 to the saturated portlandite pore water to induce pitting corrosion and thus to increase the yield of corrosion products. A potential of −200 mV (SHE) was applied to the sample because this corresponds to the highest current density within the stability domain of water. The test lasted for 4.5 hr. Again, the production of H2 and CO2 was detected but no other carbon species were measured.
Potentiostatic Corrosion Tests
Three irradiated samples were used for the static corrosion tests, with respective codes CS-A, CS-B, and CS-C. After 231 days, gas samples were taken. Figure 3 shows the corresponding gas chromatograms. At a retention time of approximately 1 minute, a high nitrogen/argon/oxygen peak appears. Such a high concentration of O2 could not have come from an accidental injection of air in the GC column, because its presence is recurrent in all three samples. Moreover, a leak in the vials can be excluded because the CO2 signal is comparable to the one obtained during calibration of the GC. The third and most probable explanation is that the oxygen peak originates from the radiolysis of water by the irradiated JRQ sample.
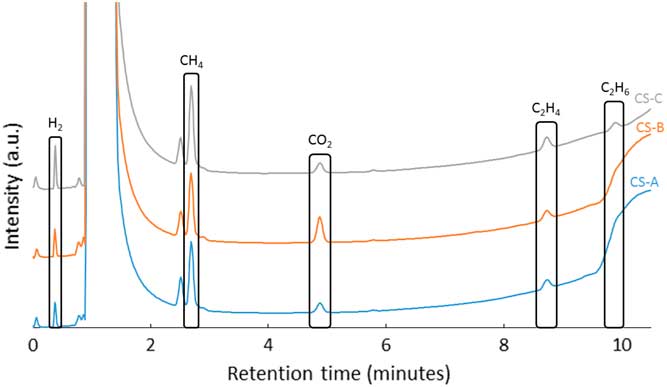
Figure 3 Gas chromatograms obtained after the simple immersion tests with irradiated JRQ carbon steel in portlandite pore water (duration 231 days).
Further peaks can clearly be distinguished for hydrogen, methane, carbon dioxide, ethene, and ethane. For two of the three chromatograms, the ethane peak is largely hidden by a large peak, which could be attributed to water. Calibration curves were used to quantify the signals for the carbon compounds. The results of this quantification are shown in Table 4. The measured concentrations are low, but well above the detection limit. On the basis of the calculated carbon-based gas production and the carbon concentration in the bulk of the JRQ steel, an approximation of the corrosion rate could be determined. Under the hypothesis that all the carbon released from the JRQ steel was transformed in carbon-based gaseous compounds, the calculated corrosion rate was 68–117 nm/yr, which is in good agreement with the 10–100 nm/yr reference range.
Table 4 Calculated concentrations of methane, ethene, and ethane in the gas phase after simple immersion tests with irradiated JRQ carbon steel in portlandite pore water (duration 231 days).

CONCLUSIONS
The carbon-14 release and speciation of irradiated carbon steel representative of the reactor pressure vessel of Belgian nuclear power plants were investigated in a cementitious environment relevant for the Supercontainer design, as perceived for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in Belgium. To achieve this, two types of corrosion tests were performed: (1) simple immersion tests to obtain information on the carbon steel behavior in real disposal conditions and (2) potentiostatic corrosion tests to obtain in a shorter reaction time an indication of the corrosion mechanism and the speciation of light carbon molecules.
In order to determine the corrosion rate of carbon steel, we measured the 60Co release by γ-spectrometry. In spite of the large scatter on the results, we could confirm a parabolic law rate for the release of 60Co, which is in accordance with literature results. This led to a corrosion rate of 7 nm/yr, which is relatively low in comparison with earlier data. The simple immersion tests showed that hydrogen, methane, carbon dioxide, ethene, and ethane were released from the carbon steel. Under the hypothesis that all the carbon released from the carbon steel was transformed into carbon-base gaseous compounds, the calculated corrosion rate was 68–117 nm/yr, which is in good agreement with literature data.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union’s European Atomic Energy Community’s (Euratom) Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-2013 under grant agreement no. 604779, the CAST project. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of this work by ONDRAF/NIRAS, the Belgian national radioactive waste management organization. The authors acknowledge also Pieter Schroeders, Steven Smets, Ben Gielen, Sabrina Lunardi and Wim Verwimp for the technical support, and Kevin Govers for his help with the computer simulation.









