Carbohydrate is an important source of energy for most physiological processes in vertebrates and has been widely used in practical feed as the lowest cost energy source(Reference Ye, Tan and Chen1). The intestinal tract is the predominant region of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates and also plays principal roles in glucose transport and metabolism(Reference Sanders2). Generally, glucose from the diet directly or from hydrolysis of other carbohydrates was taken up into the epithelial cells through specific GLUT, such as sodium/glucose co-transporters (SGLT)(Reference Sanders2–Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5). Among these SGLT, SGLT1 and SGLT2 function as glucose sensors in the intestine and they transport glucose from the intestinal lumen to the cytosols of enterocytes(Reference Röder, Geillinger and Zietek3–Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5). But, the underlying mechanisms regulating intestinal SGLT-mediated glucose absorption remain unknown.
Dietary carbohydrate played important roles in lipid metabolism because they provided substrates for de novo lipogenesis(Reference Uyeda and Repa6,Reference Crescenzo, Bianco and Falcone7) . Up to now, several studies have focused on the effects of dietary carbohydrate on growth performance, digestibility, hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism(Reference Li, Sang and Wang8,Reference Ren, Habte-Tsion and Xie9) , but there was little research on intestinal glucose absorption and lipid metabolism. Meanwhile, the intestine also plays an important role in lipid absorption and metabolism(Reference Ling, Wu and Zhang10). However, at present, the underlying signalling events of dietary carbohydrate leading to intestinal lipid deposition have not been fully elucidated.
Phospholipase C (PLC) is involved in many signalling events in eukaryotic cells, including lipid metabolism and glucose transport(Reference Rupwate, Rupwate and Rajasekharan11). On the one hand, PLC hydrolyses phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) to generate inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and diacylglycerol, which can subsequently be acylated to form TAG. On the other hand, studies showed that PLC mediated intestinal glucose absorption by regulating the expression of glucose transport-related proteins under ghrelin treatment, such as SGLT1/2 and GLUT2(Reference Blanco, Bertucci and Ramesh4). Although studies have explored the mechanisms by which PLC influenced glucose absorption and lipid metabolism in animals(Reference Blanco, Bertucci and Ramesh4,Reference Rupwate, Rupwate and Rajasekharan11,Reference Bae, Cantley and Chen12) , the crosstalk among PLC, intestinal glucose transport and downstream lipid metabolism remains unclear.
Lipid metabolism in vertebrates is very complicated and involves multiple regulatory mechanisms. Carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) was a glucose-activated transcription factor(Reference Iizuka13,Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14) and mediated the glucose-induced lipogenesis(Reference Postic, Dentin and Denechaud15,Reference Filhoulaud, Guilmeau and Dentin16) . Many studies have suggested that the function of ChREBP is regulated by translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus and multiple post-translational modifications(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5,Reference Kawaguchi, Takenoshita and Kabashima17–Reference Marmier, Dentin and Daujat-Chavanieu20) . Importantly, ChREBP is modified by acetylation, and acetylated ChREBP increases ChREBP transcriptional activity. Bricambert et al.(Reference Bricambert, Miranda and Benhamed18) pointed out that high glucose increased the acetylation level of ChREBP and that decreasing ChREBP acetylation level prevented hepatic steatosis onset in mouse. Meanwhile, our recent study showed that histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-mediated deacetylation of ChREBP was involved in the glucose-induced intestinal lipid synthesis of yellow catfish(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5).
Therefore, given the importance of understanding the mechanisms of changes in intestinal glucose absorption and glucose-induced lipid metabolism and lipid deposition, we hypothesise that these molecular signals mediated glucose-induced glucose absorption and changes of lipid metabolism in the intestine. So, the purpose of this study was to explore the role and the mechanism of PLC in glucose influencing intestinal glucose absorption and lipid metabolism.
Materials and methods
Ethical statement
The protocols for all experiments were approved by the Committee of Huazhong Agricultural University (HZAU) on the Ethics of Laboratory Animal and Cell Experiments (identification code: Fish-2016-0420, Date: 20 April 2016).
Isolation and culture of intestinal epithelial cells from the yellow catfish
Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) were isolated from yellow catfish intestine and cultured, based on the method described in our recent publications(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5,Reference Ling, Wu and Zhang10) . The primary IEC were incubated in the control (5 mm glucose) or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h to explore the mechanisms by which glucose influences glucose absorption and lipid metabolism. In order to identify the role of the PLC pathway mediating the glucose-induced changes in glucose transport and lipid metabolism, we used the pharmacological PLC inhibitor U-73122 (HY-13419; MCE) to incubate the IEC.
Human embryonic kidney 293T cells culture and treatment
Human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293T cells) have high transfection efficiency and have been widely used to explore genetic function in fish(Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14,Reference Wei, Luo and Hogstrand21) . So, in the present study, HEK293T cells were incubated in the control (5 mm glucose) or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h to explore the mechanism by which glucose influenced ChREBP acetylation. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-ChREBP plasmids with Lipofectamine 2000 (11668019; Invitrogen). Here, we performed four treatments: a control, U-73122, glucose and U-73122 + glucose. The method of transfection experiment was based on our recent study(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5). After 24 h, the cells were harvested for immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation assays.
Cell viability, TAG, glucose contents and lipogenic enzyme activities determinations
Cell viability was measured with the use of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (V13154; Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to our previous publication(Reference Wang, Feng and Li22). The contents of TAG and glucose were determined by commercial kits (A110-1-1 and F006-1-1, respectively; Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Lipogenic enzyme activities were evaluated based on previously described(Reference Ling, Wu and Zhang10,Reference Barroso, Peragón and García-Salguero23,Reference Hisar, Sonmez and Beydemir24) . Soluble protein concentrations were measured with a Bradford based on the method described by Zhao et al.(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5).
BODIPY 493/503 staining of the isolated intestinal epithelial cells
BODIPY 493/503 staining for the lipid droplets of IEC was carried out according to the protocols described in our previous publications(Reference Ling, Wu and Zhang10,Reference Wei, Luo and Hogstrand21) . Briefly, IEC were cultured in twelve-well plates, treated with the corresponding treatments for 24 h, washed twice with PBS and incubated with 5 μg/ml BODIPY 493/503 (D3922; Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 30 min, followed by thrice PBS washes. The IEC were observed with a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica DMI8) to visualise the intensity of fluorescence. The green dots were defined as lipid droplets, which were quantified with a CytoFlex flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter). The data analysis was conducted using FlowJo v.10 software.
mRNA expression analysis (quantitative real-time PCR) of the isolated intestinal epithelial cells
Quantitative real-time PCR assays were conducted according to our recent studies(Reference Ling, Wu and Zhang10,Reference Wu, Zhao and Hogstrand25) . Total RNA was isolated with Trizol reagent (TaKaRa) and transcribed into the cDNA with a Reverse Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The gene-specific primers are shown in online Supplementary Table S1. Ten housekeeping genes (rpl7, β-actin, hprt, tuba, b2m, ubce, tbp, gapdh, 18s rRNA and elfa) were selected to examine their transcriptional stability. The 2−ΔΔCt method was used when normalising to the geometric mean of the best combination of two genes as analysed by geNorm to calculate the relative expression of genes(Reference Pfaffl26).
Flag-carbohydrate response element-binding protein plasmids construction
The Flag-ChREBP expression plasmid was constructed according to our published protocol(Reference Xu, Tan and Xu27). In brief, total RNA was extracted from the intestine samples of yellow catfish using TRIzol reagent (Takara) and reverse-transcribed to cDNA, which was used as a template for the construction of ChREBP expression plasmid. The open reading frame sequence encoding ChREBP was amplified from cDNA using PCR. They were subcloned into pcDNA3.1 (+) vector with FLAG-tag sequence inserted at the N-terminus of ChREBP sequence using the ClonExpress™ II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme) and named Flag-ChREBP plasmid. All the primers were synthesised in a commercial company (Tsingke) and are shown in online Supplementary Table S1.
Immunoblotting analysis
According to the methods described in our recent publications(Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14,Reference Xu, Xu and Zhao28) , we used Western blot analysis to test protein expression, such as SGLT1, SGLT2, Flag-ChREBP and Ac-Lys of ChREBP. Briefly, cell lysates were prepared with cell lysis buffer for Western blot and immunoprecipitation (BL509A; Biosharp). Proteins (40 μg from each sample) were separated on SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to PVDF membranes (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and blocked with 8 % (w/v) skimmed milk in Tris buffered saline + Tween 20 (TBST) buffer (20 mm Tris–HCl, pH 7·5, 150 mm sodium chloride, 0·1 % Tween 20) at room temperature for 2 h and then washed thrice with TBST buffer for 5 min each, followed by incubation with specific primary antibodies including rabbit anti-SGLT1 (1:1000, ab14686; Abcam), anti-SGLT2 (1:1000, ab37296; Abcam), mouse anti-Flag-tag (1:5000, no. 2064), rabbit anti-GAPDH (1:10000, 10494-1-AP; WUHAN SANYING), overnight at 4°C, followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit or mouse IgG antibody (1:10000, no. 7074; Cell Signaling Technology). The protein bands were visualised by a Vilber FUSION FX6 Spectra imaging system (Vilber Lourmat) and quantified them using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software. Three independent replications were conducted, and the representative bands were presented in the text.
Immunofluorescence analysis
Immunofluorescence was used to analyse the expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 in the IEC, according to our recent publications(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5,Reference Xu, Xu and Zhao28) . Briefly, cells were cultured in twenty-four-well plates and incubated with the corresponding treatments for 24 h, washed thrice with PBS and fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 10 min. Then, they were blocked in 5 % BSA for 2 h and followed by incubation with specific primary antibodies including rabbit anti-SGLT1 (1:500, ab14686; Abcam) and anti-SGLT2 (1:500, ab37296; Abcam) overnight at 4°C. The cells were washed thrice with PBST for 5 min each time, followed by incubation with a Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 647, 1:500, ab150079; Abcam) secondary antibody for 60 min at room temperature in the darkness. Hoechst 33342 was used to stain the nucleus of the IEC. The images were obtained with a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica).
Immunoprecipitation analysis
Immunoprecipitation was used to determine the acetylation level of ChREBP in HEK293T cells based on the recent studies(Reference Wu, Zhao and Hogstrand25,Reference Xu, Xu and Zhao28,Reference Yang, Zhao and Wu29) . In brief, we transfected the Flag-ChREBP plasmid into HEK 293 T cells by using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in 60 mm plates and then followed corresponding treatment. We prepared cell lysates with cell lysis buffer for Western blot and immunoprecipitation (BL509A; Biosharp) on ice for 30 min. Flag-tag was immunoprecipitated with specific antibodies and protein A/G agarose (P2012; Beyotime Biotechnology). Then, we used the immunoprecipitated complexes to Western blot analysis. Target proteins were immunoprecipitated or determined using antibodies against Flag-tag (no. 2064; Dia-an) or Ac-Lys (ab80178; Abcam). IgG (A7016; Beyotime Biotechnology) was used as loading controls.
Statistical analysis
All the results are expressed as means with their standard errors. The statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS 19.0 (IBM). First, the normality of the different treatments was evaluated with the Shapiro–Wilk test. Then, all data were evaluated by one-way ANOVA and further analysed by post hoc Duncan’s multiple range testing to determine statistical significance. The statistical significance level was considered to be P < 0·05.
Results
Effects of different glucose concentrations on lipid accumulation in intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish
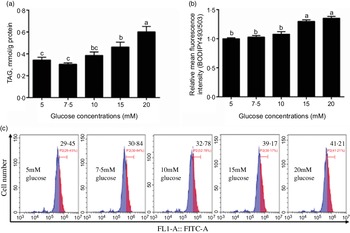
In this study, the content of TAG increased with the increase of glucose concentration (Fig. 1a) and the BODIPY 493/503 fluorescence intensity of 15 mm and 20 mm groups was higher than those of the other three groups (Fig. 1b and c). Because 15 mm glucose not only induced TAG deposition of IEC but also was a physiologically relevant amount in the plasma of yellow catfish. Therefore, we chose 15 mm glucose for the subsequent experiment to explore the mechanisms of glucose transport and lipid deposition in the IEC of yellow catfish.

Fig. 1 Effects of glucose concentrations on the TAG content and BODIPY 493/503 fluorescence intensity in IEC of yellow catfish. Primary IEC were incubated in different glucose solutions for 24 h in the DMEM medium. (a) TAG content. (b) The lipid content was quantified by flow cytometric analysis of FL1 (green fluorescence) mean fluorescence intensity with BODIPY 493/503 staining. (c) The presence of BODIPY 493/503-stained LD was demonstrated by flow cytometry. Values are mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test).
Effects of U-73122 on the phospholipase C signal in intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish
We used U-73122 (a PLC inhibitor) to investigate the role of PLC in mediating glucose-induced changes in glucose transport and lipid metabolism. First, U-73122 was selected for the subsequent experiments at a concentration of 10 μm because it had no significant effect on cell viability (Fig. 2a). Meanwhile, pre-incubation with U-73122 alleviated the glucose-induced increase of plcb2, plce1 and plcg1 mRNA expression (Fig. 2b), suggesting that U-73122 had an inhibitory effect on PLC. However, some studies found that U-73122 may inhibit human 5-lipoxygenase by covalently binding with cysteine 416(Reference Feisst, Albert and Steinhilber30,Reference Hörnig, Markoutsa and Häfner31) . We found that although U-73122 alone can reduce the mRNA expression of alox5, glucose treatment had no significant effect on the mRNA level of alox5 (Fig. 2b). Thus, the influence of 5-lipoxygenase on subsequent experimental results can be excluded.
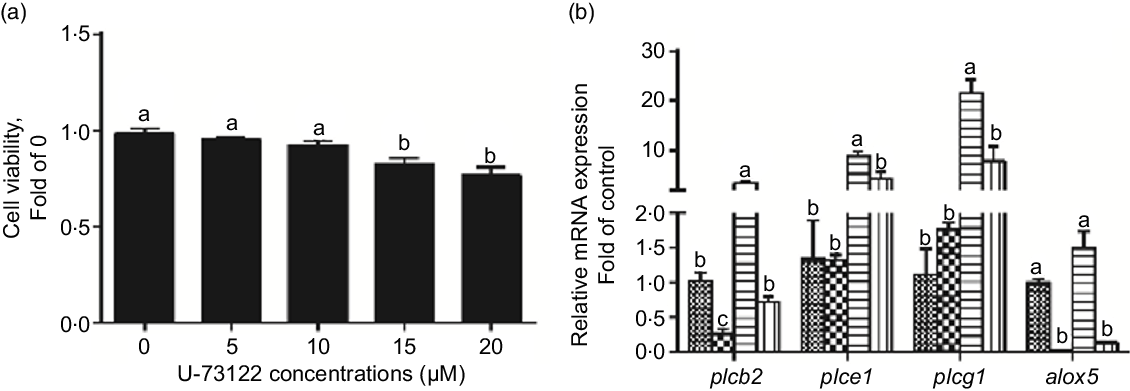
Fig. 2 Effects of U-73122 on the cell viability and the mRNA levels of the plc and alox5 of IEC in yellow catfish. Primary IEC were incubated in different U-73122 solutions or incubated in control or glucose (10 mm glucose) for 24 h with or without 2-h pre-treatment with 10 μm U-73122 (PLC inhibitor) in the DMEM medium. (a) Cell viability. (b) mRNA expression of plc and alox5. Values are mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test). plc, Phospholipase C; alox5, arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase. ![]() , control;
, control; ![]() , glucose;
, glucose; ![]() , U-73122;
, U-73122; ![]() , glucose + U-73122.
, glucose + U-73122.
Phospholipase C mediated the glucose-induced glucose transport in intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish
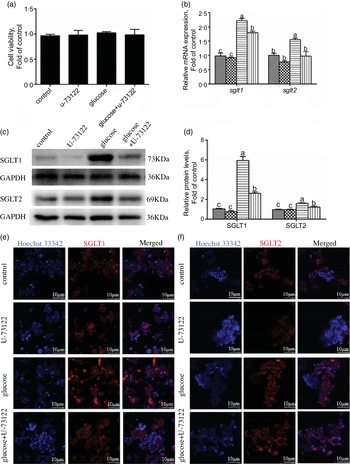
In the present study, pre-treatment with U-73122 did not significantly affect the viability of the IEC in yellow catfish (Fig. 3a). Pre-incubation with U-73122 alleviated the glucose-induced increase in sglt1 and sglt2 mRNA and SGLT1/2 protein expressions (Fig. 3b–d), which was further confirmed by the immunofluorescence (Fig. 3e and f). Furthermore, U-73122 pre-treatment alleviated the glucose-induced increase in glucose content in the IEC of the yellow catfish (Fig. 4a). Overall, these results support the supposition that PLC was involved in the glucose-induced changes in glucose transport and glucose content in IEC of yellow catfish.
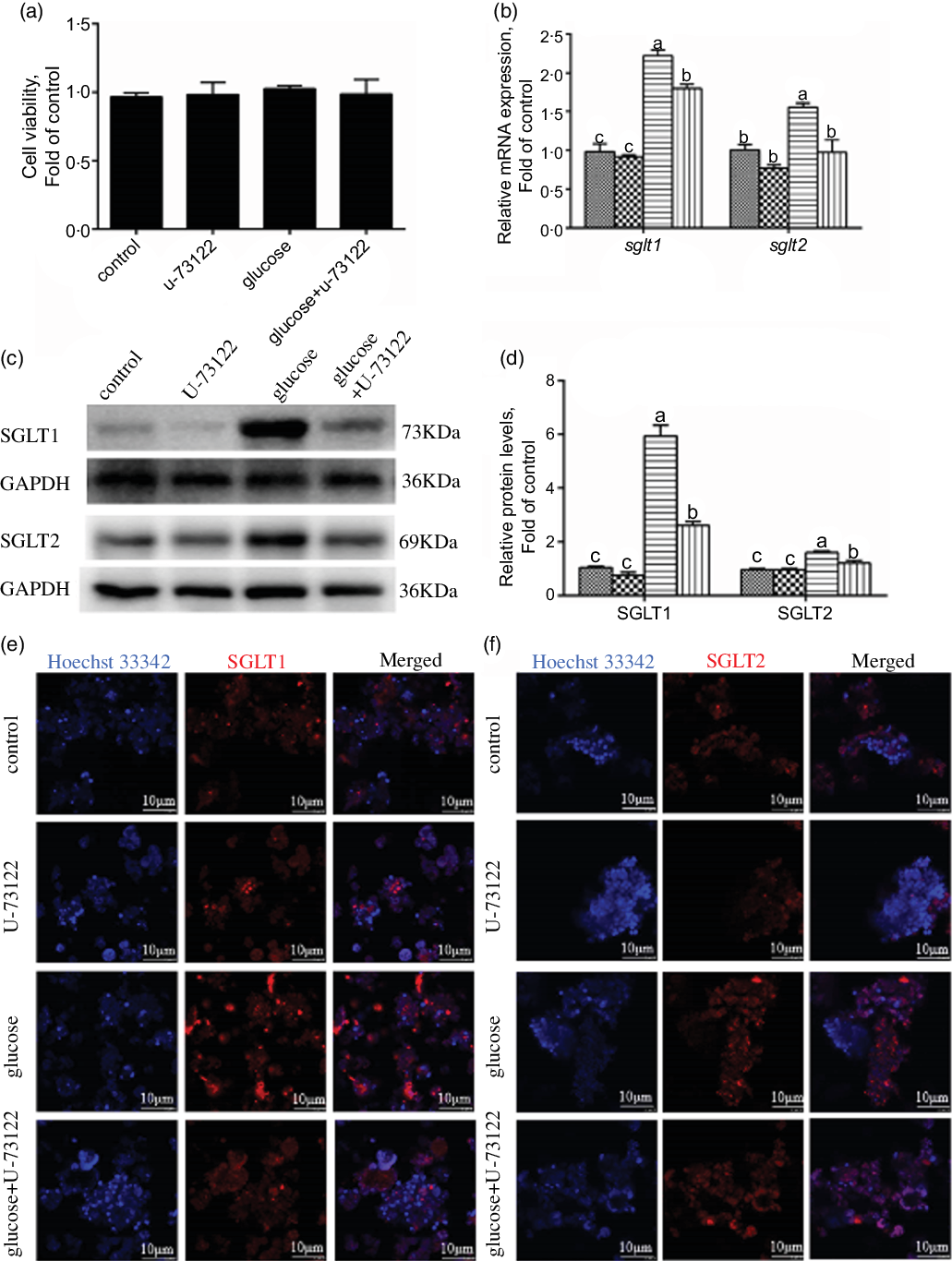
Fig. 3 PLC signal mediated glucose-induced glucose transport in IEC of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Primary IEC were incubated in the control or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h with or without 2-h pre-treatment with an PLC inhibitor (10 μm U-73122). (a) Cell viability. (b) mRNA expression of sglt1 and sglt2. (c) Western blot analysis of SGLT1 and SGLT2 expression. (d) Protein levels of SGLT1 and SGLT2. (e) and (f) Representative confocal images showing SGLT1 and SGLT2 protein by immunofluorescence staining. Values are mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SGLT, sodium-dependent glucose transporter. ![]() , control;
, control; ![]() , glucose;
, glucose; ![]() , U-73122;
, U-73122; ![]() , glucose + U-73122.
, glucose + U-73122.

Fig. 4 PLC signal mediated glucose-induced glucose and lipid accumulation in IEC of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Primary IEC were incubated in control (5 mm glucose) or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h with or without 2-h pre-treatment with an PLC inhibitor (10 μm U-73122). (a) Glucose content. (b) TAG content. (c) The lipid content was quantified by flow cytometric analysis of FL1 (green) mean fluorescence intensity with BODIPY 493/503 staining. (d) The presence of BODIPY 493/503-stained LD was demonstrated by flow cytometry. (e) Representative confocal microscopy image of enterocytes with 5 μg/ml BODIPY 493/503 staining. Values are mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test), FL1, green fluorescence.
Phospholipase C mediated the glucose-induced changes of lipid metabolism in intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish
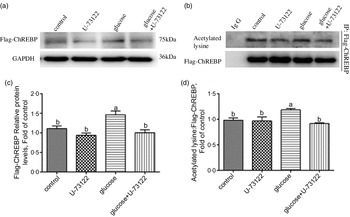
Next, we explored whether PLC was involved in glucose-induced lipid deposition and metabolism in IEC of yellow catfish. The results showed that U-73122 pre-treatment alleviated the glucose-induced increase in TAG content and BODIPY 493/503 fluorescence intensity, as well as the number and size of lipid droplet (Fig. 4b–e). Meanwhile, U-73122 pre-treatment attenuated the glucose-induced increase in the lipogenic enzymes (glucose 6-phospate dehydrogenase (G6PD), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD), malic enzyme and fatty acid synthase (FAS)) activity, and the mRNA expressions of lipogenic genes and related transcription factors (g6pd, 6pgd, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (acca), fas, srebp1, pparg and chrebp) in IEC of yellow catfish (Fig. 5a and b). Furthermore, U-73122 pre-treatment mitigated the glucose-induced increase of the protein expression and the acetylation level of ChREBP in HEK293T cells (Fig. 6a–d), which indicated that the PLC signal affects not only the protein expression of ChREBP but also the acetylation of ChREBP at the post-transcriptional modification to promote lipid accumulation. Taken together, these data further demonstrated that the PLC played a major role in the glucose-induced changes in lipid metabolism.
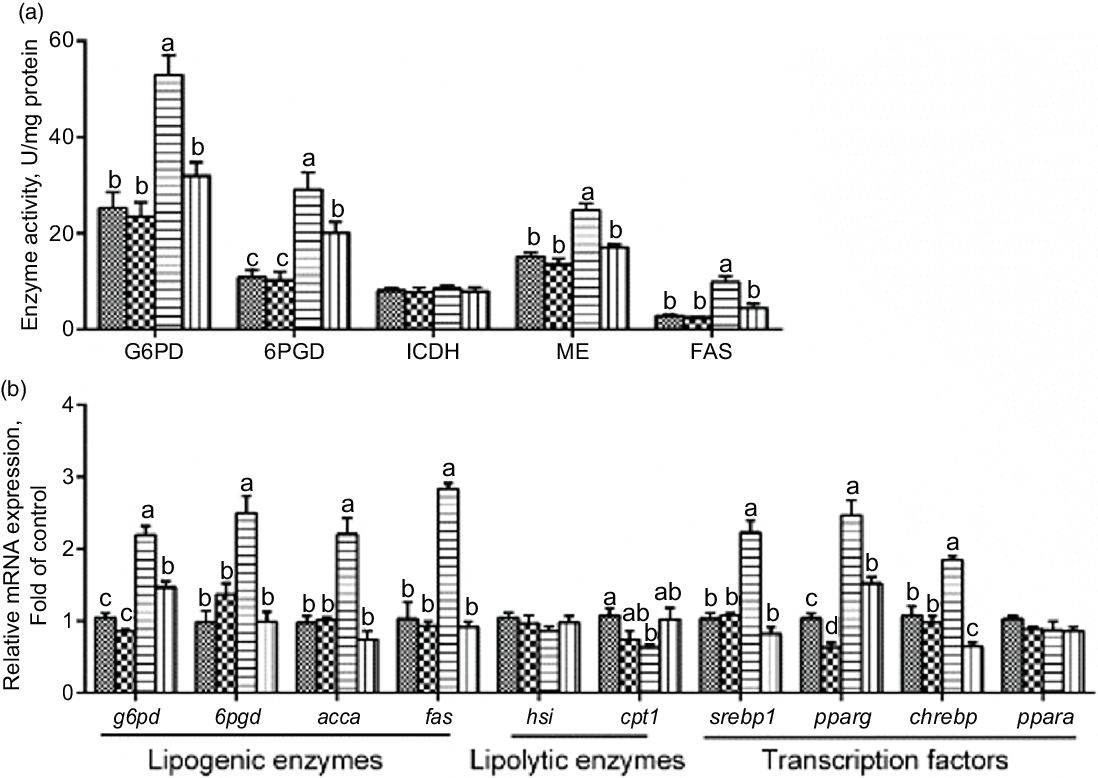
Fig. 5 mRNA levels of the lipid metabolism-related enzymes activity (a) and the key genes of the lipid metabolism (b) in IEC from Pelteobagrus fulvidraco were incubated in control or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h with or without 2-h pre-treatment with 10 μm U-73122 (PLC inhibitor). Values are mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test). acca, acetyl-CoA carboxylase a; chrebp, carbohydrate response element-binding protein; cpt 1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; FAS, fatty acid synthase; G6PD, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase; hsl, hormone-sensitive lipase; ICDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; ME, malic enzyme; ppar, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; srebp1, sterol-regulator element-binding protein-1; 6PGD, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. ![]() , control;
, control; ![]() , glucose;
, glucose; ![]() , U-73122;
, U-73122; ![]() , glucose + U-73122.
, glucose + U-73122.

Fig. 6 PLC signal mediated glucose-induced ChREBP expression and ChREBP acetylation in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-ChREBP plasmid and then incubated in control or glucose (15 mm glucose) for 24 h with or without 2-h pre-treatment with PLC inhibitor (10 μm U-73122). (a) Western blot analysis of Flag-ChREBP. (b) Relative quantification of protein levels of Flag-ChREBP. (c) Immunoprecipitation of Flag-ChREBP and immunoblotting for acetylated lysine. (d) Relative quantification of ChREBP acetylation levels. All data are expressed as mean with their standard errors (n 3). Labelled means without a common letter differ, P < 0·05 (one-way ANOVA, Duncan’s post hoc test). ChREBP, carbohydrate response element-binding protein; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Discussion
Only several studies found that U-73122 could inhibit human 5-lipoxygenase(Reference Feisst, Albert and Steinhilber30,Reference Hörnig, Markoutsa and Häfner31) , but most of the studies showed that U-73122 exerted time-dependent and dose-dependent inhibition effects on PLC in human oesophageal cancer cells(Reference Chen, Xin and Peng32) or other cells(Reference Zhang, Wang and Bai33–Reference Jin, Qian and Zhou35). In this study, we selected U-73122 to explore the role of PLC in mediating glucose-induced changes in glucose transport and lipid metabolism in IEC of yellow catfish. We found that glucose significantly increased the mRNA levels of plcb1, plce1 and plcg1, but reversed by U-73122 pre-incubation. Although U-73122 alone reduced the mRNA expression of alox5, glucose treatment had no significant effect on the mRNA level of alox5 in this study. Thus, the interference of 5-lipoxygenase on experimental results can be excluded.
SGLT1/2 are active GLUT, and they use the energy generated by the Na gradient to absorb glucose in a concentration gradient(Reference Wright36). Several studies pointed out that dietary glucose significantly up-regulated SGLT1 and SGLT2 expressions to accelerate glucose absorption and lipid synthesis(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5,Reference Dong, Wang and Song37,Reference Qin, Yang and Zheng38) , but the underlying factors that mediate SGLT1/2 expression remain poorly understood. In the present study, in agreement with the reports by Yamazaki et al.(Reference Yamazaki, Philbrick and Zawalich39), our study indicated that glucose significantly increased PLC activation. Therefore, next, we explored the mechanism of the PLC signal mediating glucose-induced changes in glucose transport and lipid metabolism in IEC of yellow catfish. We found that U-73122 (a PLC inhibitor) pre-treatment alleviated the glucose-induced increase in SGLT1 and SGLT2 mRNA and protein expression and glucose content, which indicated that the PLC mediated glucose transport by regulating the expression of SGLT1/2 in IEC of yellow catfish. Similarly, Epps-Fung et al.(Reference Epps-Fung, Gupta and Hardy40) demonstrated that U-73122 inhibited PLC activity which in turn alleviated stimulation of glucose transport by insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Wright et al.(Reference Wright, Craig and Fick41) found that U-73122 caused a dose-dependent inhibition of insulin-promoted glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle. Meantime, PLC inhibited by U-73122 attenuated insulin-increased glucose transport in rat soleus muscle(Reference Wright, Fick and Olesen42). Blanco et al.(Reference Blanco, Bertucci and Ramesh4) pointed out that PLC activated SGLT1/2 expression to facilitate glucose transport in goldfish. Thus, we concluded that glucose activated PLC signals and increased SGLT1/2 expression, which in turn increased glucose transport. These observations linked the PLC to glucose transport and suggested that it was a target of the glucose signals responsible for the stimulation of glucose transport.
Moreover, several studies have suggested that PLC participated in the regulation of lipid biosynthesis(Reference Bae, Cantley and Chen12) and contributed to diacylglycerol production(Reference Coccetti, Tisi and Martegani43). A similar phenomenon was also observed in the present study. Our study indicated that the inhibition of PLC expression by U-73122 alleviated the glucose-induced increase in TAG content and lipogenesis, suggesting that PLC was involved in the glucose-induced changes in lipid accumulation. The transcription factor ChREBP is primarily a glucose response factor, which has become the main mediator for intracellular glucose sensing(Reference Filhoulaud, Guilmeau and Dentin16), and to control the de novo fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis) under physiological conditions(Reference Filhoulaud, Guilmeau and Dentin16). The present study showed that glucose increased the mRNA and protein expressions of ChREBP, in agreement with our recent study(Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14) and other report(Reference Wang and Wollheim44). Studies pointed out that activated ChREBP regulated the lipogenesis and up-regulated the expression of lipogenic genes, such as acca, fas and pparg (Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14,Reference Filhoulaud, Guilmeau and Dentin16,Reference Iizuka, Bruick and Liang45,Reference Dentin, Pégorier and Benhamed46) , and then resulted in the increase of lipid deposition(Reference Zhao, Wu and Hogstrand14). Interestingly, ChREBP activation was regulated by acetylation and deacetylation(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5,Reference Bricambert, Miranda and Benhamed18) . Bricambert et al. (Reference Bricambert, Miranda and Benhamed18) pointed out that ChREBP acetylation was required for its capacity to interact with its target genes. Thus, in order to elucidate the mechanism of translational modification of ChREBP by glucose, we explored the glucose-induced changes of ChREBP acetylation levels. Our study indicated that glucose increased the acetylation level of ChREBP, FAS activity and mRNA expression of acca and fas, but all of them were reversed by U-73122, which revealed that the PLC mediated lipid accumulation by regulating ChREBP acetylation. However, the direct effect of PLC and ChREBP needs to be further studied. In addition, in the recent study, we found that glucose-induced increase in ChREBP acetylation was mediated by HDAC6, which is a well-known cytoplasmic deacetylase(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5). Meanwhile, we also demonstrated that the enhancement of ChREBP acetylation by inhibiting HDAC6 further increased the TAG content and lipogenic gene expression(Reference Zhao, Yang and Chen5). Overall, these evidences confirmed that PLC signal mediated the acetylation of ChREBP to further regulate lipid metabolism in IEC of yellow catfish.
Conclusions
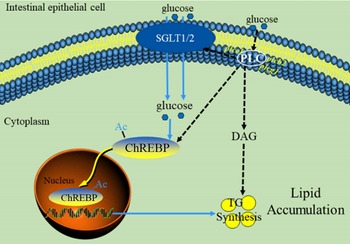
In summary, our data indicated that PLC signal played a vital role in glucose transport and lipid accumulation of IEC. A proposed model for this crosstalk is summarised in Fig. 7. These findings are particularly noteworthy because it is possibly recognised as potential targets for the treatment of excessive fat deposition in the intestine.

Fig. 7 The model of glucose-induced changes of glucose absorption and lipid accumulation in the intestinal epithelial cells of yellow catfish through PLC signal. Ac, Acetylation; ChREBP, carbohydrate response element-binding protein; DAG, diacylglycerol; PLC, Phospholipase C; SGLT1/2, sodium/glucose co-transporters 1/2.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0900400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31422056) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (2662018PY089).
Z. L. and T. Z. designed the experiments. T. Z. carried out experiments and sample analysis with the help of S.-B. Y., Y.-C. X., G.-H. C. and Y.-H. X.; T. Z. and Z. L. analysed data; T. Z. wrote the manuscript, and Z. L. revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material referred to in this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521000350