Background
Psychiatry is experiencing a generalised enthusiasm surrounding the rapid-onset and marked antidepressant effects of intravenous subanaesthetic doses of ketamine in treatment-resistant non-psychotic unipolar or bipolar major depression (TRD).Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 Ketamine is a dissociative anaesthetic agent that acts as a glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) non-competitive receptor antagonist and the neurobiological mechanisms underlying its antidepressant properties have not yet been completely elucidated.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 Although many clinical trials have endorsed the efficacy of ketamine in major depression, they have also demonstrated that these antidepressant effects are short lived, disappearing by 7 days post-infusion in most studies.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1
To solve this fleeting antidepressant efficacy, current lines of research are examining the possibility of sustaining ketamine's therapeutic benefit over longer time periods through intravenous repeated infusions and maintenance strategies similar to those employed in electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 Furthermore, less invasive routes of administration than the intravenous one are also being investigated.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 However, several concerns have been raised in light of ketamine's psychotomimetic side-effects, the potential risk for abuse and the lack of long-term data on safety and efficacy.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1,2
Use of ketamine for TRD in the USA
Despite these concerns and gaps in knowledge, the off-label use of ketamine for patients with TRD has been rapidly increasing in the USA, where it is estimated that around 60–100 ketamine clinics are currently operating – many of them without meeting basic safety standards.Reference Nemeroff3 Faced with this scenario, and in spite of the fact that this treatment is not included in the current American Psychiatric Association (APA) depression guidelines, a consensus statement has recently been published by the APA Council of Research Task Force with the aim of providing some guidance and expert recommendations on the issues regarding the off-label clinical use of ketamine in the treatment of TRD.Reference Sanacora, Frye, McDonald, Mathew, Turner and Schatzberg4
Use of ketamine for TRD in Europe
From a European perspective and within the framework of national public healthcare systems, we are far from that current American scenario. To date, there are not European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommendations, nor a position statement from the European Psychiatric Association, on the use of ketamine for depression. The unresolved issues and limitations related to ketamine's long-term safety and efficacy have led to the situation where, beyond research settings, the therapeutic use of ketamine for TRD in clinical practice in Europe is generally not recommended and is restricted to cases of severe refractoriness.2 To a large extent, these differences could be as a result of the fact that, in European public health systems, the use of off-label drugs is actively controlled and limited to serious, life-threatening conditions or those that could strongly affect patients' quality of life when there are no other evidence-based therapeutic alternatives available in the established care protocols for those diseases. Such treatment protocols may vary according to the clinical guidelines that each public health system uses, with probably the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommendations as the clinical reference guidelines most widely followed in Europe.
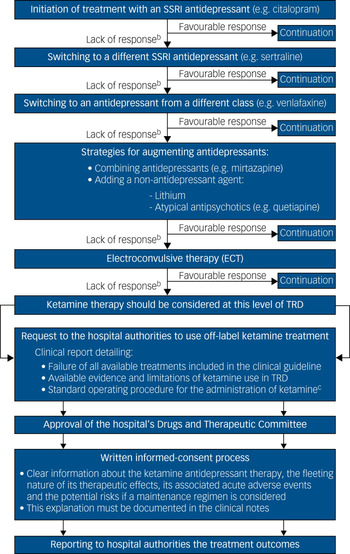
Thus, a patient with unipolar TRD who is a candidate for ketamine therapy in a European national health service should have had, following the NICE pathways for depressive disorders, an inadequate pharmacological response – in combination with high-intensity psychological interventions – to: (a) two different selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants; (b) an antidepressant from a different class (such as venlafaxine or vortioxetine); (c) augmenting strategies with a second antidepressant (such as mianserin or mirtazapine) or with a non-antidepressant agent (such as lithium or low doses of atypical antipsychotics); and (d) ECT (Fig. 1).5 It is only at this degree of severe resistance, after attempting all evidence-based antidepressant strategies outlined in the clinical guidelines, when the off-label use of ketamine should be considered as a novel or innovative therapy for TRD.

Fig. 1 Pharmacological treatment algorithm for adult non-psychotic major depressive disordersa and procedural framework for the off-label use of intravenous ketamine in TRD in a public healthcare system
At this point, the treating psychiatrist should request to the hospital the use of off-label ketamine treatment, justifying through a detailed clinical report the need for its use in that particular patient with TRD.2 Upon approval of that request by the hospital's Drugs and Therapeutic Committee, the patient and carers should be rigorously advised about the risks and benefits of ketamine therapy – documenting that explanation in the clinical notes – before they sign the written informed consent.2 Finally, the clinical outcomes, as well as any severe adverse events during the treatment course, should be periodically monitored and reported to the hospital authorities, who could suspend or withdraw the approval of the off-label use of ketamine in the case of safety or inefficacy issues (Fig. 1).2
Beyond the recommendations of the clinical guidelines and the regulatory framework for off-label prescribing, there remains a widespread reluctance among European psychiatrists to include ketamine in the armamentarium of depression pharmacotherapy. Tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and other drugs not approved by the EMA for the treatment of depression, such as thyroid hormones or pramipexole, are generally regarded as more suitable treatment options than ketamine for patients with TRD.Reference Nemeroff3
In our experience and opinion, although the enthusiasm surrounding ketamine as a breakthrough antidepressant treatment should be tempered until the database on its long-term efficacy and safety grows, its clinical off-label usage in public healthcare services may be a potential option to treat individuals with complex TRD when no further evidence-based therapies are available. However, outside the institutional supervision and procedural framework mentioned above (Fig. 1), we suggest that this practice should be avoided.
Intranasal esketamine
A quite different scenario from the one described here, will be what we are going to have when intranasal esketamine – which is a more potent inhibitor at NMDA receptors and offers an improved tolerability profile than ketamine – is commercialised.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 Intranasal esketamine has now completed phase III studies – two of them focused on long-term safety and efficacy – and will be undergoing review by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2019 for TRD.Reference Molero, Ramos-Quiroga, Martin-Santos, Calvo-Sánchez, Gutiérrez-Rojas and Meana1 If approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and if later the EMA does the same in Europe, the framework for this discussion would be substantially different, since the off-label use of ketamine for TRD might be relegated to a rather weak position. Nevertheless, although on-label intranasal esketamine could be prescribed for TRD in the near future, the same criticism should be applied to it until enough evidence on this emerging therapy has been accumulated for it to be included in the treatment algorithms of major clinical practice guidelines.



eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.