Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2017
U60 ([UO2(O2)(OH)]60
60− in water) is a uranyl peroxide nanocluster with a fullerene topology and O
h symmetry. U60 clusters can exist in crystalline solids or in liquids; however, little is known of their behavior at high pressures. We compressed the U60-bearing material: Li68K12(OH)20[UO2(O2)(OH)]60(H2O)310 (
 $Fm\bar 3$
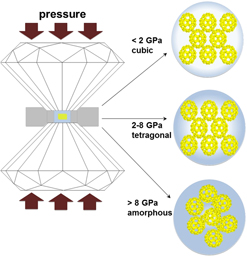
; a = 37.884 Å) in a diamond anvil cell to determine its response to increasing pressure. Three length scales and corresponding structural features contribute to the compression response: uranyl peroxide bonds (<0.5 nm), isolated single nanoclusters (2.5 nm), and the long-range periodicity of nanoclusters within the solid (>3.7 nm). Li68K12(OH)20[UO2(O2)(OH)]60(H2O)310 transformed to a tetragonal structure below 2 GPa and irreversibly amorphized between 9.6 and 13 GPa. The bulk modulus of the tetragonal U60-bearing material was 25 ± 2 GPa. The pressure-induced amorphous phase contained intact U60 clusters, which were preserved beyond the loss of long-range periodicity. The persistence of U60 clusters at high pressure may have been enhanced by the interaction between U60 nanoclusters and the alcohol pressure medium. Once formed, U60 nanoclusters persist regardless of their associated long-range ordering—in crystals, amorphous solids, or solutions.
$Fm\bar 3$
; a = 37.884 Å) in a diamond anvil cell to determine its response to increasing pressure. Three length scales and corresponding structural features contribute to the compression response: uranyl peroxide bonds (<0.5 nm), isolated single nanoclusters (2.5 nm), and the long-range periodicity of nanoclusters within the solid (>3.7 nm). Li68K12(OH)20[UO2(O2)(OH)]60(H2O)310 transformed to a tetragonal structure below 2 GPa and irreversibly amorphized between 9.6 and 13 GPa. The bulk modulus of the tetragonal U60-bearing material was 25 ± 2 GPa. The pressure-induced amorphous phase contained intact U60 clusters, which were preserved beyond the loss of long-range periodicity. The persistence of U60 clusters at high pressure may have been enhanced by the interaction between U60 nanoclusters and the alcohol pressure medium. Once formed, U60 nanoclusters persist regardless of their associated long-range ordering—in crystals, amorphous solids, or solutions.
Contributing Editor: William J. Weber
Please note a has been issued for this article.