Introduction
Habitat loss and fragmentation, mainly because of land-cover change driven by agricultural intensification and urbanization, are major threats to biodiversity (Hilton-Taylor, Reference Hilton-Taylor2000; Lambin et al., Reference Lambin, Turner, Geist, Agbola, Angelsen and Bruce2001; Arroyo-Rodríguez et al., Reference Arroyo-Rodríguez, Cuesta-del Moral, Mandujano, Chapman, Reyna-Hurtado, Fahrig, Marsh and Chapman2013). Over 75% of non-human primate species are declining in numbers and range because of human activities, and c. 60% are threatened with extinction (Rylands et al., Reference Rylands, Williamson, Hoffmann and Mittermeier2008; Estrada et al., Reference Estrada, Garber, Rylands, Roos, Fernandez-duque and Di Fiore2017). Urgent action is needed (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Bicca-Marques, Dunham, Fan, Fashing and Gogarten2020), including the examination of population trends and threats to survival, to design effective management plans (Rylands et al., Reference Rylands, Williamson, Hoffmann and Mittermeier2008; Estrada et al., Reference Estrada, Garber, Rylands, Roos, Fernandez-duque and Di Fiore2017).
Many forest primate populations now live in isolated forest patches surrounded by human-dominated landscapes and high density of human settlements (Marsh & Chapman, Reference Marsh and Chapman2013; Estrada et al., Reference Estrada, Garber, Rylands, Roos, Fernandez-duque and Di Fiore2017). Forest habitat loss and fragmentation have resulted in a rapid decline of primate populations (Cowlishaw, Reference Cowlishaw1999). Guenons (genus Cercopithecus) are endemic to Africa, and of the 20 extant species, eight are threatened with extinction, mainly as a result of habitat loss (IUCN, 2021). The blue monkey Cercopithecus mitis is the most widely distributed guenon, occupying a variety of forested habitats. It is experiencing population and habitat decline primarily because of habitat loss and fragmentation (Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020a; IUCN, 2021). There are 17 subspecies of the blue monkey, one of which is categorized as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, four as Endangered and three as Vulnerable (IUCN, 2021).
Primates often respond to changes in their habitat by adapting their range and foraging behaviour to follow resource availability (Eppley et al., Reference Eppley, Verjans and Donati2011; Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Ghai, Jacob, Mugume Koojo, Reyna-Hurtado, Rothman, Marsh and Chapman2013). Blue monkeys are omnivorous, with a preference for fruit, which enables them to cope with fluctuating resource availability in fragmented habitats (Butynski, Reference Butynski1990; Lawes et al., Reference Lawes, Cords, Lehn, Butynski, Kingdon and Kalina2013). For example, the group size and density of Boutourlini's blue monkey Cercopithecus mitis boutourlinii and Stuhlmann's blue monkey Cercopithecus mitis stuhlmanni vary depending on the habitat quality in the forest fragments they inhabit (Mammides et al., Reference Mammides, Cords and Peters2008; Tesfaye et al., Reference Tesfaye, Fashing, Bekele, Mekonnen and Atickem2013).
The golden monkey Cercopithecus mitis kandti is a forest-dwelling subspecies occurring in the centre of the Albertine Rift, in Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda (Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020b). Although currently classified as a subspecies of the blue monkey, taxonomists have argued that it could be a separate species (Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020b). It is categorized as Endangered on the IUCN Red List because of its small population size, shrinking habitat, and threats posed by poaching and diseases (Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020b). Its distribution is restricted to two isolated forest fragments surrounded by areas with high human population densities (up to 1,000 people/km2; NISR, 2012). One of these forests is the 450-km2 Virunga massif, comprising three contiguous national parks: Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda, Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Mgahinga Gorilla National Park in Uganda. The second is the c. 16-km2 Gishwati Forest remnant (hereafter, Gishwati Forest), part of Gishwati–Mukura National Park in Rwanda (Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020b).
Within this limited geographical range, golden monkeys occur at an altitude of 2,100–3,550 m (Tuyisingize, Reference Tuyisingize, Rowe and Myers2016; Butynski & de Jong, Reference Butynski and de Jong2020b). Previous studies in Uganda showed they prefer bamboo Yushania alpina and mixed tropical montane forest (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006). Golden monkeys share their habitats with other primates, including mountain gorillas Gorilla beringei beringei in Volcanoes National Park, and L'Hoest's monkeys Allochrocebus lhoesti, eastern chimpanzees Pan troglodytes schweinfurthi and bushbabies Galago sp. in Gishwati Forest (Chancellor et al., Reference Chancellor, Langergraber, Ramirez, Rundus and Vigilant2012).
Estimates from Mgahinga Gorilla National Park showed a 41% decline in the golden monkey population during 1998–2003, probably linked to habitat loss resulting from bamboo harvesting (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006). A recent survey conducted in Gishwati Forest resulted in approximate population estimates without confidence intervals, because of low sampling effort (Siegel et al., Reference Siegel, George, Ellisor, Summerville and Renner2020). Here we report results of population surveys in both Volcanoes National Park and Gishwati Forest conducted during 2007–2018, and provide individual density, group density, distribution and population size estimates for golden monkeys in Rwanda. We also examine the relationship between golden monkey distribution and the spatial-temporal distribution of human disturbances. Our findings provide baseline information for future studies.
Study area
Volcanoes National Park and Gishwati Forest were connected until the 1950s by continuous forest habitat. Volcanoes National Park spans altitudes of 2,400–4,507 m. During 1958–1973 the total area of the Park was reduced by c. 50%, from 328 to 160 km2, as a result of agricultural expansion (Spinage, Reference Spinage1972). The Park comprises eight vegetation zones: mixed tropical montane, bamboo and Hagenia–Hypericum forest, brush ridge, meadows, and herbaceous, subalpine and alpine zones (McNeilage, Reference McNeilage1995). The majority of habitat loss occurred in the mixed tropical montane forest zone, the only vegetation zone in Volcanoes National Park containing a significant number of fruiting trees (Spinage, Reference Spinage1972). Only c. 5 km2 of mixed tropical montane forest remain.
Gishwati Forest lies at 2,100–2,500 m altitude and has also been subject to land conversion and habitat loss. Forest cover dropped from 280 km2 in the 1970s to < 10 km2 in 2003 (Nyandwi & Mukashema, Reference Nyandwi and Mukashema2011). Restoration efforts have led to a 5.6 km2 increase in forest cover since 2016. The current tropical montane forest is dominated by fruiting trees (e.g. Symphonia globulifera and Syzygium guineense) and a few bamboo stands, and the restored montane forest patch is dominated by bamboo, Xymalos monospora and Hagenia abyssinica. The two forest patches are connected by a narrow corridor. In 2016, the government of Rwanda gazetted Gishwati Forest and Mukura Forest, 16 km apart, to form Gishwati–Mukura National Park (Fig. 1). Illegal activities such as bamboo and firewood harvesting, grazing and presence of feral domestic dogs are common in both Volcanoes National Park and Gishwati Forest (Hickey et al., Reference Hickey, Granjon, Vigilant, Eckardt, Gilardi and Cranfield2019).

Fig. 1 The study sites in Rwanda where we carried out surveys of the golden monkey Cercopithecus mitis kandti during 2007–2018.
Methods
Data collection
Line transect and recce trail surveys
We used both line transects and reconnaissance trails (hereafter recce trails) to survey golden monkey populations at both study sites and across four time periods (Table 1). Line transect surveys provide accurate animal density estimates but can be time consuming and costly to implement, whereas walks along recce trails facilitate quick monitoring of large areas, without the need to cut new trails, as is necessary for line transect surveys (Fashing & Cords, Reference Fashing and Cords2000; Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006). We determined line transect starting points, lengths and orientations based on the terrain (e.g. to avoid inaccessible ravines). Daily observations from Park staff and findings from previous biomonitoring surveys in the Virunga massif showed that golden monkeys were almost exclusively found in the bamboo zone in the Virungas (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006; Tuyisingize, Reference Tuyisingize, Rowe and Myers2016; Hickey et al., Reference Hickey, Granjon, Vigilant, Eckardt, Gilardi and Cranfield2019). We surveyed a total of 22 line transects in 2007, 20 in 2011 and 20 in 2017–2018, all in areas dominated by bamboo (Fig. 2). We also collected data outside the bamboo zone along four transects (in 2007 only) and five recce trails (during all study periods) to document presence of golden monkeys there (Fig. 2). We visited each line transect and recce trail repeatedly (twice in 2007, three times in 2011 and seven times in 2017–2018) to increase the number of detections and thus the accuracy of density estimates (Buckland et al., Reference Buckland, Anderson, Burnham, Laake, Borchers and Thomas2004). The cumulative lengths of these 244 transect surveys and 15 recce trails were 420.7 km and 299.2 km, respectively.
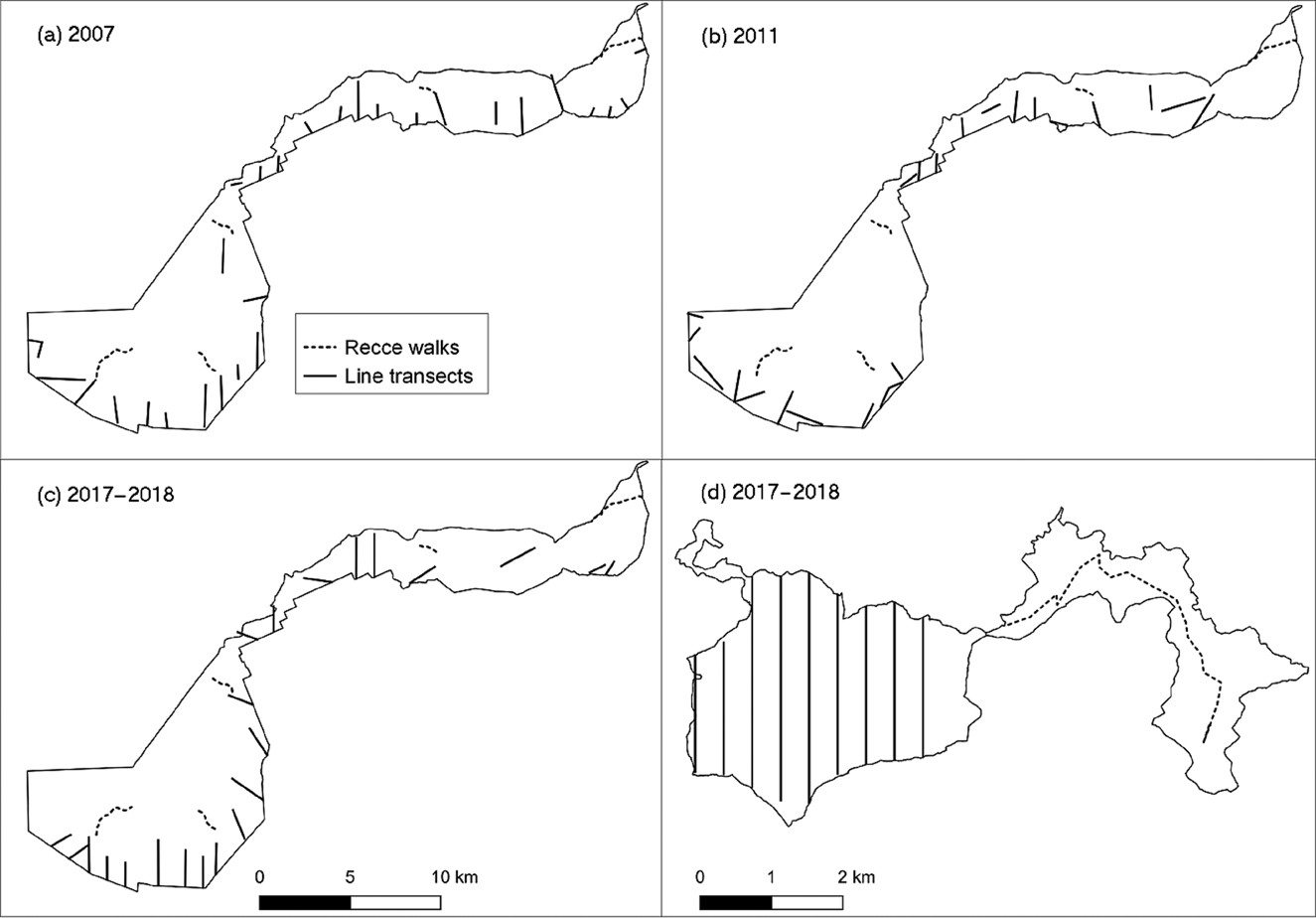
Fig. 2 Location of line transects and recce trails at both study sites: in Volcanoes National Park in (a) 2007, (b) 2011 and (c) 2017–2018 and (d) in Gishwati Forest in 2017–2018.
Table 1 Summary of golden monkey Cercopithecus mitis kandti survey efforts (km) in Rwanda, by study period and site (VNP, Volcanoes National Park; GMNP, Gishwati–Mukura National Park).

Given the small size of the Gishwati Forest, we placed nine parallel line transects systematically across the entire remnant, with gaps of 400 m between transects. We also placed a single recce trail across the corridor and restored forest patch to assess the presence of golden monkeys in these areas. We collected data along these transects and recce trail 1–3 times per month for a total of 22 times in 2017 and 2018 (Fig. 2). The cumulative lengths of transect and recce trail surveys were 473 km and 55 km, respectively.
We collected data along transects and recce trails between 7.00 and 13.00 in Volcanoes National Park and between 7.00 and 16.00 in Gishwati Forest. During line transect surveys, a single observer walked at an average speed of c. 1 km/h and stopped every 100 m to listen and look for monkeys ahead of the rest of the survey team, which comprised two people: a park ranger and an observer collecting data on illegal activities (Peres, Reference Peres1994; Plumptre & Cox, Reference Plumptre and Cox2006). Monkeys were detected from their movements, feeding signs, noise and vocalizations, but we recorded only confirmed direct sightings. Upon visual detection of one or more monkeys, the observer recorded the geographical location of detection on the transect (using a GPS), the compass bearing of the individual or centroid of the group, the number of sighted individuals and the distance from the transect to the individual or centroid of the group (using a Bushnell Elite 1,500 Golf Laser Rangefinder; Bushnell, Northbrook, USA). Teams of three observers conducted recce walks, recording the location of each monkey group and the number of individuals. We did not collect data during rainy weather, to prevent biases resulting from the lower detectability of monkeys (Peres, Reference Peres1999).
Illegal activities
We used maps of illegal activities (bamboo cuts, snares, honey and water collection, feral dogs, beehives) produced by Volcanoes National Park rangers. These data were collected during regular law enforcement and monitoring patrols along recce trails over 220 days during October 2017–September 2018. As there was no systematic monitoring by rangers in Gishwati Forest at the time of our study, we collected data on illegal activities (such as bamboo cuts, snares, cattle grazing inside the forest, collection of honey or firewood) along recce trails in areas where we suspected illegal activities may occur. The goal of this biased search was to establish a list of illegal activities taking place in the forest. These searches took place 3–4 times per month for 12 months, starting in June 2017. We used ArcGIS 3.6 (Esri, Redlands, USA) to create maps of frequently occurring (mean frequency > 7 records per month) illegal activities in both study areas.
Data analysis
Population density and size
We estimated golden monkey group densities using point process models with the spatstat package in R 3.6.1 (Niemi & Fernández, Reference Niemi and Fernández2010; Baddeley et al., Reference Baddeley, Rubak and Turner2015; R Core Team, 2019). Inhomogeneous Poisson point process models can be fitted to spatial distributions of points to investigate the link between point density and point attributes (e.g. species, sex, group size) or environmental covariates (e.g. vegetation type, terrain, distance to transects). This approach is less commonly used than the distance sampling method but provides more flexibility in handling fine-scale spatial variation in animal density and nested sampling designs (Borchers & Marques, Reference Borchers and Marques2017). In the spatstat package, the design of inhomogeneous Poisson point process models is similar to the design of generalized linear models; the main difference is that the dependent variable in point process models is a spatial point pattern object as opposed to a numerical variable in generalized linear models. We modelled the natural log of the point density as a linear function of the squared distance to the transect line (denoted as x). This implies that the expected sighting density ![]() $\hat{D}$ is:
$\hat{D}$ is:
where A is the sighting density on the transect line (i.e. for x = 0), and b the negative coefficient denoting the spread of the detection function. This model assumes the detection function has the shape of a half-normal distribution. Visual inspection of the distribution of distances to the transect line confirmed this was a good approximation. Our point process models also included transect identity as a random-effects variable influencing the intercept, to consider our nested design, with each transect repeated 2–7 times in Volcanoes National Park, and 22 times in Gishwati Forest. Models were fit using the mppm() function from spatstat (Baddeley et al., Reference Baddeley, Rubak and Turner2015).
Most sighted individuals were within 80 m of a transect line. The few observations that were beyond 80 m were considered outliers and were not used in our statistical analysis. We also excluded the four Volcanoes National Park transects outside the bamboo forest from the analyses, as no golden monkeys were observed there. We fitted mixed-effects point process models to each of the four datasets described in Table 1. We estimated the group density for each dataset as the exponential of the model intercept, and calculated the 95% confidence interval as exp(intercept ± SE × 1.96).
The overall individual density ![]() $\hat{D}$ is the product of the mean group density and the mean group size. Both quantities were estimated from our data, together with associated standard errors. We used the delta method (Powell, Reference Powell2007) to estimate the standard errors of individual densities and to calculate the associated confidence intervals. The coefficient of variation (CV) of the individual density was approximated using:
$\hat{D}$ is the product of the mean group density and the mean group size. Both quantities were estimated from our data, together with associated standard errors. We used the delta method (Powell, Reference Powell2007) to estimate the standard errors of individual densities and to calculate the associated confidence intervals. The coefficient of variation (CV) of the individual density was approximated using:
where D, G and S are the individual density, group density and mean group size, respectively. The standard error of the individual density was derived as:
Confidence intervals for individual densities were then calculated for each of the four estimates as ![]() $\hat{D}$ ± 1.96 SE(D).
$\hat{D}$ ± 1.96 SE(D).
We estimated total population size for both areas by multiplying density estimates for Volcanoes National Park and Gishwati Forest with the area of the bamboo zone in Volcanoes National Park (c. 51.2 km2; McNeilage, Reference McNeilage1995) and the area of the remnant tropical montane forest of Gishwati (c. 10 km2), the only habitats where golden monkeys were found. We extrapolated the confidence intervals for abundance estimates by multiplying the confidence intervals for individual density estimates by total areas.
Results
Golden monkey distribution and population size
In Volcanoes National Park golden monkeys were exclusively observed in the bamboo zone (Fig. 3a–c), and in Gishwati Forest they were restricted to the remnant tropical montane forest (Fig. 3d). Population sizes were therefore estimated based on the size of these areas.

Fig. 3 Sightings of golden monkey social units in Volcanoes National Park in (a) 2007, (b) 2011 and (c) 2017–2018, and (d) in Gishwati Forest in 2017–2018.
Social groups sighted in Volcanoes National Park (up to 68 individuals) were larger than those in Gishwati Forest (up to 24 individuals). The percentage of observations of solitary males was smaller in Volcanoes National Park (14–17%) than in Gishwati Forest (35%; Table 2). The sighting rates in Volcanoes National Park varied little across survey periods (0.47–0.54 sightings/km) and were significantly higher than in Gishwati (0.16 sightings/km). The estimated mean group densities were also greater in Volcanoes National Park's bamboo forest than in Gishwati–Mukura National Park's tropical montane forest (Table 2).
Table 2 Summary of the results of golden monkey transect surveys conducted during 2007–2018 in the bamboo zone of Volcanoes National Park and in the tropical montane forest of Gishwati, part of Gishwati–Mukura National Park, Rwanda.

The 95% confidence intervals of group density in the bamboo forest of Volcanoes National Park overlapped considerably across the three survey periods. The most recent survey (2017–2018) yielded the most precise density estimate: 90.4 individuals/km2 (95% CI 81.4–99.4), corresponding to a population size of 4,626 individuals (95% CI 4,165–5,088). In the remnant tropical montane forest of Gishwati, individual density was significantly lower (mean 17.90 individuals/km2, 95% CI 15.48–20.32) and the estimated population size was 172 individuals (95% CI 154–190).
Illegal activities in golden monkey habitats
In Volcanoes National Park, the major illegal activities recorded during ranger patrols, and believed to significantly affect the monkeys, were bamboo cutting, water collection, feral dogs and snares. Snares primarily target the black-fronted duiker Cephalophus nigrifrons and bushbuck Tragelaphus scriptus but golden monkeys are occasionally caught, as we have personally observed (DT, pers. obs., 2017). During the most recent survey period (2017–2018), most of the illegal activities recorded were in the bamboo zone, in particular in the south-western sector of the Park (Fig. 4).

Fig. 4 Locations of illegal activities recorded in Volcanoes National Park during October 2017–September 2018: (a) bamboo cutting, (b) feral dogs, (c) snares and (d) water collection.
Gishwati Forest is surrounded by farmland with livestock, pastures and houses. Cattle grazing, bamboo cutting and firewood collection were the most common types of human activity recorded in both the remnant and the restored patch (Fig. 5). Bamboo is used by local communities for agriculture (e.g. as bean poles) and weaving material.

Fig. 5 Locations of illegal activities recorded in Gishwati Forest during June 2017–May 2018: (a) bamboo cutting, (b) grazing and (c) firewood collection.
Discussion
Population density estimates
In Volcanoes National Park, golden monkeys are restricted to the bamboo zone, although anecdotally Park staff report observations, particularly of solitary males, outside this zone. This population included c. 4,600 individuals in 2017–2018 and did not change significantly over the 12-year study period. In comparison, a previous study from Mgahinga Gorilla National Park, Uganda, suggested a 59% decline in the golden monkey population size during 1998–2003, from 2,438 ± SD 1,463 to 989 ± SD 521.5 (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006).
In Gishwati Forest, an estimated 172 golden monkeys persist in the remnant tropical montane forest, but not in the corridor or the restored forest patch. A brief study conducted in 2019 (Siegel et al., Reference Siegel, George, Ellisor, Summerville and Renner2020) in Gishwati Forest estimated the population size to be 70–211 individuals, but the authors did not provide confidence intervals for their estimates because of methodological limitations.
The Gishwati remnant tropical montane forest includes mature fruit trees such as S. globulifera, Maesa lanceolata, S. guineense and Ilex mitis, potentially providing a more suitable habitat for golden monkeys than the restored montane forest patch dominated by bamboo stands, young X. monospora, H. abyssinica and exotic plant species such as Acacia mearnsii and Alnus spp. The trees present in the narrow corridor connecting the patches form an open canopy forest with low bamboo stands and X. monospora, limiting arboreal movement between the two patches.
The mean estimates of golden monkey group density in Volcanoes National Park (5.41–7.89 groups/km2) are close to previous estimates from the subpopulation in Mgahinga Gorilla National Park, which were 6.03 and 4.28 groups/km2 in 1998 and 2003, respectively (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006). They are also similar to density estimates (4.3–6.0 groups/km2) for Stuhlmann's blue monkey in the intact forest of Kakamega, Kenya (Fashing & Cords, Reference Fashing and Cords2000). The group density estimate from Gishwati Forest is similar to that of Stuhlmann's blue monkey (1.71–2.06 groups/km2) in the logged parts of Kibale National Park, Uganda (Chapman et al., Reference Chapman, Balcomb, Gillespie, Skorupa and Struhsaker2000), and to that of the Samango monkey Cercopithecus mitis labiatus (1.58–3.46 groups/km2) in a fragmented Afromontane forest in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa (Lawes, Reference Lawes1992).
Group sizes and densities in each study population probably reflect differences in resource availability at the different sites. The Gishwati population is mainly frugivorous, whereas the Volcanoes National Park population is mainly folivorous (Tuyisingize et al., Reference Tuyisingize, Eckardt, Caillaud and Kaplin2021). Differences in the spatial and temporal distribution of key food types may drive the differences in group sizes and densities between the sites (Clutton-Brock & Harvey, Reference Clutton-Brock and Harvey1977; Twinomugisha et al., Reference Twinomugisha, Chapman, Lawes, O'Driscoll Worman, Danish, Chapman, Lawes and Danish2007). Leaves are abundant and available year-round in the bamboo forest of Volcanoes National Park (Twinomugisha et al., Reference Twinomugisha, Chapman, Lawes, O'Driscoll Worman, Danish, Chapman, Lawes and Danish2007; Tuyisingize, Reference Tuyisingize, Rowe and Myers2016), supporting larger group sizes and higher group densities. In contrast, frugivorous primates rely on smaller, scattered, seasonal food patches, which may lead to smaller group sizes and lower densities (Snaith & Chapman, Reference Snaith and Chapman2007).
The percentage of solitary males was higher in Gishwati than in Volcanoes National Park, which reflects differences in the social organization of the two populations. Golden monkeys in Volcanoes National Park are observed in groups with one male and multiple females or in large multimale–multifemale groups (DT, pers. obs., 2017; Tuyisingize, Reference Tuyisingize, Rowe and Myers2016), whereas in Gishwati Forest they only form groups with one male and multiple females (DT, pers. obs., 2017).
Effect of human activities
We observed potential threats to the golden monkey, such as bamboo cutting, collection of firewood and water, cattle grazing inside the forest and presence of feral domestic dogs, during this study. The occurrence of illegal activities in their habitat may limit golden monkey population growth, especially in unmonitored populations, as documented for Virunga mountain gorillas (Granjon et al., Reference Granjon, Robbins, Arinaitwe, Cranfield, Eckardt and Mburanumwe2020). Illegal activities such as bamboo and firewood harvesting are suspected to have contributed to a sharp population decline in the golden monkey population in Mgahinga Gorilla National Park during 1998–2003 (Twinomugisha & Chapman, Reference Twinomugisha and Chapman2006). Intense bamboo and firewood collection can affect vegetation dynamics and nutrient availability, leading to forest degradation (Sheil et al., Reference Sheil, Ducey, Ssali, Ngubwagye, van Heist and Ezuma2012; Sassen et al., Reference Sassen, Sheil and Giller2015). Furthermore, cattle grazing and water collection inside golden monkey habitats may also increase the risk of disease transmission between livestock, people and golden monkeys, as reported for mountain gorillas (Hogan et al., Reference Hogan, Miller, Cranfield, Ramer, Hassell and Noheri2014). Feral dogs can predate native mammals, including arboreal primates, and should be controlled (Galetti & Sazima, Reference Galetti and Sazima2006; Soto & Palomares, Reference Soto, Palomares and .2015).
Golden monkeys may also be negatively affected by climate change. A study in Volcanoes National Park reported a decline in bamboo regeneration, possibly the result of an overall decrease in rainfall in the Virunga region (van der Hoek et al., Reference van der Hoek, Faida, Eckardt, Kwizera, Derhé and Caillaud2019). A simulation study focusing on the Albertine Rift predicted a decrease in the extent of habitats preferred by endemic species, including golden monkeys, because of climate change in the coming 6 decades (Ayebare et al., Reference Ayebare, Plumptre, Kujirakwinja and Segan2018).
Future research and conservation perspectives
The density of golden monkeys in the bamboo forest in Volcanoes National Park is more than four times higher than in Gishwati tropical montane forest. More research is needed to determine the roles of ecological (e.g. food resource availability and quality) and other factors (e.g. population history and current anthropogenic pressures) on golden monkey demography. People, livestock and feral dogs often use golden monkey habitats and may introduce parasites and other pathogens potentially harmful to the primates. Research is needed to identify pathogens that are likely to be introduced by people and domestic animals, and whether golden monkeys are exposed and susceptible to these pathogens. To examine population trends, regular surveys are needed as part of a long-term conservation management plan for this subspecies.
Given that the Gishwati population is particularly small (172 individuals, 95% CI 154–190) and totally isolated, genetic studies are needed to measure the effects of genetic drift and inbreeding, and to predict possible impacts on population health. If this population shows low genetic diversity, the possibility of translocating animals from Volcanoes National Park to Gishwati Forest could be explored.
Our latest survey, from 2017–2018, provides recent and accurate estimates of golden monkey population sizes in Volcanoes National Park and Gishwati Forest, and will serve as a baseline to estimate future population trends. Surveys are urgently needed in Mgahinga National Park, Uganda, and in Virunga National Park, Democratic Republic of the Congo, to assess the size and demographic trend of golden monkey populations outside Rwanda. Despite ongoing protection efforts, including the recent creation of Gishwati–Mukura National Park, illegal activities are ongoing throughout the range of the golden monkey in Rwanda. We recommend the development of a comprehensive conservation action plan for the subspecies that incorporates a long-term monitoring programme in all three range countries. This plan should address threats to golden monkeys and their habitats using a participatory approach with local communities, to explore ways to reduce the reliance on forest resources that threatens forest biodiversity.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund, Cleveland Metroparks Zoo and Conservation International for funding the preliminary golden monkey survey in 2007; Primates Conservation for funding the 2011 survey; National Geographic (grant number WW-003C-17), Critical Ecosystem Partnership Funds (grant number S16-442-RWA-DFGFI) and Margot Marsh Biodiversity Fund for funding the 2017 and 2018 surveys; and the field teams from the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund for their support during fieldwork.
Author contributions
Study conception and design: DT, DC, WE, BK; data collection: DT, AM; data analysis: DT, DC; writing and revision: all authors.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical standards
This research abided by the Oryx guidelines on ethical standards. No samples of animals were obtained during this study and all field efforts took place with permission of the Rwanda Development Board.









