Sea-ice floating in the Arctic ocean is a constantly moving, growing and melting layer. The seasonal cycle of sea-ice volume has an average amplitude of 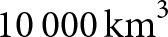 $10\,000\,\mathrm{km}^3$ or 9 trillion tonnes of sea ice. The role of dynamic redistribution of sea ice is observable during winter growth by the incorporation of satellite remote sensing of ice thickness, concentration and drift. Recent advances in the processing of CryoSat-2 radar altimetry data have allowed for the retrieval of summer sea-ice thickness. This allows for a full year of a purely remote sensing-derived ice volume budget analysis.
$10\,000\,\mathrm{km}^3$ or 9 trillion tonnes of sea ice. The role of dynamic redistribution of sea ice is observable during winter growth by the incorporation of satellite remote sensing of ice thickness, concentration and drift. Recent advances in the processing of CryoSat-2 radar altimetry data have allowed for the retrieval of summer sea-ice thickness. This allows for a full year of a purely remote sensing-derived ice volume budget analysis.
Here, we present the closed volume budget of Arctic sea ice over the period October 2010–May 2022 revealing the key contributions to summer melt and minimum sea-ice volume and extent. We show the importance of ice drift to the inter-annual variability in Arctic sea-ice volume and the regional distribution of sea ice. The estimates of specific areas of sea-ice growth and melt provide key information on sea-ice over-production, the excess volume of ice growth compared to melt. The statistical accuracy of each key region of the Arctic is presented, revealing the current accuracy of knowledge of Arctic sea-ice volume from observational sources.