Zn is an essential micronutrient, which may exert an antioxidant activity as demonstrated in defined chemical and cell culture systems, as well as in vivo (Reference Cortese, Suschek and Wetzel1). Therefore, the maintenance of discrete subcellular pools of Zn is critical for the functional and structural integrity of cells and contributes to a number of important biological processes(Reference Truong-Tran, Ruffin and Zalewski2). Due to its antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and membrane-stabilising activities, it has been hypothesised that Zn protects the endothelium against oxidative stress by maintaining the integrity of endothelial cells(Reference Beattie and Kwun3).
On the other hand, lung epithelial cells (pneumocytes) are responsible for the gas exchange in lungs. Chronic injury induces damage and subsequent loss of parenchymal cells(Reference Kisseleva and Brenner4). Damage to lung epithelium is associated with interstitial oedema, leucocyte invasion and decreased gas exchange. This situation has been demonstrated in Zn-deficient (ZD) rats, with a significant oxidative and nitrosative stress(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5). In addition, these recruited inflammatory cells increase local concentration of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, which causes the re-organisation and activation of pulmonary fibroblasts. Besides, the increase in reactive oxygen species production is associated with the direct activation of pro-fibrogenic genes that produce collagen and with the decrease in endogenous antioxidants that have a protective role(Reference Kisseleva and Brenner4). Previously, we analysed the expression of antioxidant enzymes in ZD lung(Reference Biaggio, Pérez Chaca and Valdéz6).
Resolution of alveolar epithelial/capillary membrane damage after lung injury requires coordinated and effective tissue reconstruction to re-establish a functional barrier. Several lines of investigation suggest that the mechanisms of resolution and lung repair are controlled in part by regulatory pathways that are important in lung morphogenesis and development(Reference Willis, Liebler and Luby-Phelps7). One of them is cell–cell interactions, which play the most important role during differentiation and tissue architecture regulation. The main members of cell–cell adhesion are cadherins, which form cell–cell adherens junctions associated with actin microfilaments via the cytoplasmic plaque proteins(Reference Gloushankova8). Cadherins provide mechanical cell–cell adhesion and regulate cell shape, segregation, migration, proliferation and cellular differentiation(Reference Gloushankova8). The interactions between cadherins and filaments of the cytoskeleton are dynamic(Reference Drees, Pokutta and Yamada9). Another mechanism of resolution are cytokeratins (CK), intermediate filaments (IF) of the cytoskeleton, which are expressed in tissue-specific patterns and reflect differentiation, functional specialisation and pathological alterations of the cell(Reference Iyonaga, Miyajima and Suga10). Desmin and vimentin also represent also IF proteins, which are related to tumour proliferation(Reference Hockfield and McKay11); however, there are few studies about the expression of these IF in the lung parenchyma.
In addition, while epithelial cell damage is largely due to the sustained effects of inflammatory mediators localised to the airways, the subsequent process of epithelial cell differentiation is attributed to members of the transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase family called epidermal growth factor (ErbB) receptors(Reference Damera, Xia and Ancha12). Activation of the ErbB receptors induces activation and phosphorylation in cascade in cytoplasmic kinases, which results in the activation of nuclear transcription proteins, and cellular growth(Reference Hamilton and Piccart13).
Previously, numerous results have shown that ZD produces important changes in the expression of antioxidant enzymes and several pro-inflammatory parameters in the lung parenchyma. We think that is quite relevant to analyse it, as ZD could lead to the fibrotic process and pulmonary dysfunction. For this purpose, we set out to investigate whether the expression of these proteins during ZD is modified and if their expressions could reach the level of the control (CO) group during the period of supplementation.
Materials and methods
Diet and experimental design
Male Wistar rats (200 ± 10 g) were fed two diets with different Zn concentrations. During the pre-test, rats with similar intake profiles were matched and randomly assigned to the CO or the ZD groups (n 14). For that purpose, rats were divided into three groups and fed, respectively: (1) a ZD diet containing 5 mg Zn/kg and (2) a Zn-adequate CO diet containing 30 mg Zn/kg (as ZnCl2). (3) A group of deficient animals was fed with the CO diet 10 d before killing (ZD refed group) in order to supply these animals with Zn ion. All the other components of the diet remained constant, and were supplemented with the recommended amounts of vitamins and minerals, according to the American Institute of Nutrition (AIN) 93-M diet(Reference Reeves, Nielsen and Fahey14). Both diets had the following composition (g/kg): 466 maize starch, 140 casein (785 % protein), 155 dextrinised maize starch, 100 sucrose, 50 fibre/cellulose, 40 soyabean oil (containing liposoluble vitamins), 35 mineral mix AIN-93M-MX (Zn was not incorporated into the mineral mix of the ZD diet), 10 vitamin mix (AIN-93-VX), 1·8 l-cystine, 0·008 ascorbic acid, 2·5 choline bitartrate (41 % choline).
All dietary ingredients were monitored for Zn concentration using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Animals were housed individually in a controlled environment with a 12 h light–12 h dark cycle and temperature maintained at 21 ± 2°C. Fresh diets were given and the leftover food discarded on a daily basis (20 g/d were enough to ensure ‘ad libitum’ feeding). All experiments were conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health Publication no. 80-23) and the National University of San Luis Committee's Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals (ordinance CD 006/02)(15). Diet acclimatisation lasted 1 week, during which time the CO diet was provided to all rats and intake was measured. During the experiment, body weights were registered weekly.
Serum and tissue collection
At the second month of the treatment and 12 h after the last feeding, the animals were killed. Previously, they were anaesthetised intraperitoneally with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg), and blood samples for the determination of Zn serum were collected in tubes previously washed and rinsed with nitric acid. The lungs were quickly removed, washed with ice-cold 0·9 % saline solution and weighed. Serum and pieces of lobes of each lung were frozen in liquid N2, and then kept at − 80°C until analysis. For immunochemistry, the tissue samples were fixed in 10 % buffered formalin during 6 h at room temperature and washed in PBS. For light microscopy, the fixed tissues were dehydrated in an ascending series of ethanol, cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffin. Then, 5 μm-thick sections were mounted in slides previously treated with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and stained with haematoxylin–eosin for preliminary observation.
Zinc analysis
Aliquots of the diet, serum and lung were collected without allowing any contact with the metal. Each sample was wet-ashed with 16 m-nitric acid, as described by Clegg et al. (Reference Clegg, Keen and Lonnerdal16). Zn concentrations of the pre-treated samples and serum were quantified by an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (model 5100, HGA-600 Graphite Furnace; Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk, CT, USA). A linear calibration curve was created using certified standard National Institute and Standards and Technology solutions. All specimens were diluted by double-distilled, deionised water, and analysed in duplicate. Before sample digestion, different amounts of the standard solution of each element were added. Recovery was between 98 and 99·2 % for different elements.
Western blot analysis for transforming growth factor-β1
Lungs were homogenised with 50 mm-Tris–HCl (pH 7·8) containing 0·01 % Triton X-100 and protease inhibitor cocktail, and centrifuged at 4°C. Protein concentrations of the resulting supernatants were determined according to the method of Wang & Smith(Reference Wang and Smith17), using bovine serum albumin as the standard. Then, 40 μg of proteins were mixed with 10 μl of the sample buffer (125 mm-Tris–HCl, pH 6·8, 4 % SDS, 3·5 mm-dithiothreitol, 0·02 % bromophenol blue and 20 % glycerol), boiled for 2–3 min and loaded into a 10 % SDS–PAGE gel. Protein molecular mass markers were always loaded on each gel. Separated proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Polyscreen NEF 1000; NEN Life Science Products, Cologne, Germany) using a blot transfer system (BioRad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). After being blocked with 5 % bovine serum albumin–Tris-buffered saline solution (20 mm-Tris, 500 mm-NaCl, pH 7·5) overnight, at 4°C with gentle agitation, membranes were incubated with a primary rabbit anti-TGF-β1 polyclonal antibody solution (1:1000 dilution; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. After washing them three times with Tween-Tris-buffered saline (0·1 % Tween 20, 100 mm-Tris–HCl, pH 7·5, 150 mm-NaCl), membranes were incubated with a secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody linked to biotin for 1 h at room temperature (1:2000 dilution). β-Actin was chosen as the reference protein, over glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, for the better linearity of expression (data not shown). Membranes were washed again and the colour was developed using a Vectastain ABC detection system (Vector Laboratories, Youngstown, OH, USA). The intensity of the bands was scanned densitometrically with the image processing and analysis software Scion Image, and is expressed as arbitrary units.
Immunohistochemistry
Details of the antibodies used are provided in Table 1. Each antibody was assayed in at least three sections of each lung from each individual. A streptavidin–biotin immunoperoxidase method was performed as described previously(Reference Salvetti, Gimeno and Lorente18, Reference Ortega, Lorente and Mira19). After deparaffinisation, microwave pre-treatment (antigen retrieval) was performed. Endogen peroxidase activity was inhibited with 1 % (v/v) H2O2, and non-specific binding was blocked with 10 % (v/v) normal goat serum. All sections were incubated with primary antibodies for 18 h at 4°C and then for 30 min at room temperature with rat pre-absorbed, biotinylated secondary antibodies selected specifically for each of the two types of primary antibodies used (mono- or polyclonal). The visualisation of antigens was achieved by the streptavidin–peroxidase method (BioGenex, San Ramon, CA, USA), and 3,3-diaminobenzidine (Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA) was used as chromogen. Finally, the slides were washed in distilled water, counterstained with Mayer's haematoxylin, dehydrated and mounted. To test the specificity of immunoreactions, adjacent control sections were subjected to the same immunohistochemical method, replacing primary antibodies by rabbit and mouse non-immune serum.
Table 1 Antibodies used in the present study
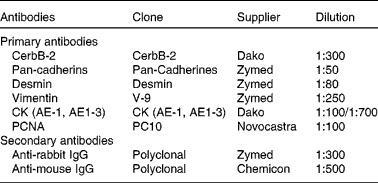
CK, cytokeratins; CK AE-1, monoclonal antibody anti-cytokeratins of high molecular weight; CK AE-3, monoclonal antibody anti-cytokeratins of low molecular weight; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
Image analysis
Image analysis was performed using an Image Pro-Plus 3.0.1 system (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MA, USA). For the immunohistochemistry technique, images were digitised by a colour charge-coupled device (CCD) video camera (Sony, Montvale, NJ, USA) mounted on a conventional light microscope (Olympus BH-2; Olympus Company, Tokyo, Japan), using an objective magnification of 40 × . The microscope was prepared for Koehler illumination. This was achieved by recording a reference image of an empty field for the correction of unequal illumination (shading correction) and by calibrating the measurement system with a reference slide to determine background threshold values. The reference slides contained a series of tissue sections stained in the absence of a primary antibody. The positive controls were used as inter-assay controls to maximise the levels of accuracy and robustness of the method(Reference Ranefall, Wester and Bengtsson20–Reference Salvetti, Muller and Acosta22). The methodological details of image analysis have been described earlier(Reference Wang, Masironi and Eriksson23, Reference Wang, Eriksson and Sahlin24). Using a colour segmentation analysis tool, the total intense positively stained nuclear area (brown reaction product) was measured and is expressed as a ratio (%) of the total area of cell nuclei (brown reaction product+blue haematoxylin). The image analysis score was calculated separately by using AutoPro macro language, an automated sequence operation created to measure the immunohistochemical-stained area (IHCSA). The IHCSA was calculated as a percentage of the total area evaluated through colour segmentation analysis, which extracts objects by locating all objects of a specific colour (brown stain). The brown stain was selected with a sensibility of 4 (maximum 5), and a mask was then applied to separate the colours permanently. The images were then transformed to a bi-level scale Tagged Image File Format (TIFF). The IHCSA (black area) was calculated from at least fifty images of each area of the lungs in each slide being studied.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the ANOVA test when only three groups were compared(Reference Denenberg25). When variances were not homogeneous, we performed log transformation of the data. Differences between means were considered significant at the P < 0·05 level.
Results
Weight gain and zinc status of rats
Table 2 shows the body weight of rats fed with a ZD diet. After 2 months of treatment, body weight was significantly lower in the ZD group than in the CO group, while body weight was significantly higher in the ZD refed group when compared with the CO group. Zn concentrations in serum and lung were significantly decreased in the ZD group; in the ZD refed group, the level of Zn overtook the control values. The results of Zn levels are in concordance with those from the literature, i.e. El Hendy et al. (Reference El Hendy, Yousef and Abo El-Naga26). In our experimental model, clinical signs such as dermatitis or alopecia were not observed.
Table 2 Body and lung weight and zinc concentrations in the serum and lung of male rats
(Mean values with their standard errors; n 14 per group)

CO, control group; ZD, Zn-deficient group; ZD refed, Zn supplementation group; ppm, parts per millon.
Mean value was significantly different from that of the CO group: *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01 (ANOVA).
Expression of transforming growth factor-β1
TGF-β1 is the most important cytokine promoting the development of fibrosis in the lung. It has multiple functions in repair, wound healing, during organogenesis and development; for this reason, we measured this factor. Fig. 1 shows the increased expression of TGF-β1 in the ZD group when compared with the CO group.

Fig. 1 Immunoblot analysis of tumour growth factor β (TGF-β1) expression in the lung. (A) Representative experiment of Western blot is shown. (a) TGF-β1 expression was detected with an anti-TGF-β1 antibody. (b) β-Actin was used as a reference protein. (B) Quantification of the protein band corresponding to TGF-β1 was performed by densitometry. Results show the intensity of the TGF-β1 band in relation to the intensity of a reference protein band (n 14 per dietary group). * Mean value was significantly different from that of the control group (P < 0·05).
Immunohistochemistry
Factor CerbB-2 immunostaining
Factor CerbB-2 was observed in the cytoplasm of cells in all groups treated. In the CO group, moderate staining was observed. Immunoreactivity in the ZD and ZD refed groups was significantly higher (P < 0·05) compared with the CO group (Table 3). The data also revealed the presence of weak cytoplasmic staining in the cells and alveolar spaces in the pulmonary parenchyma; this staining was considered as part of the background, and it was not included in the analysis (Fig. 2(A)–(C)).
Table 3 Percentage of the immunostaining area in the lung with different antibodies used in immunohistochemistry
(Mean values with their standard erros; n 14 per group)

CO, control group; ZD, Zn-deficient group; ZD refed, Zn supplementation group; CerbB-2, epidermal growth factor receptor; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.
** Mean value was significantly different from that of the CO group (P < 0·01; ANOVA).

Fig. 2 Immunohistochemical findings of CerbB-2, pan-cadherins and cytokeratins (CK) in the lung parenchyma of the control (CO), zinc deficiency (ZD) and ZD refed groups. (A)–(C) CerbB-2 expression in the cytoplasmic regions (arrows). (D)–(F) Pan-cadherin expression is present in the alveolar cells and capillary wall (arrows). (G)–(I) Positive immunostaining for CK (arrows), 40 × .
Pan-cadherin immunostaining
The results of the quantitative image analysis of pan-cadherin immunostaining (IHCSA) are shown in Table 3. Immunostaining did not show significant differences between all treated groups (Fig. 2(D)–(F)).
Cytokeratin immunostaining
CK showed a low expression in ZD lungs, while in the ZD refed group, the expression of CK was significantly increased (P < 0·05) compared with the CO group (Table 3; Fig. 2(G)–(I)).
Desmin immunostaining
Desmin was observed in the cytoplasm of all cells in each treated group. Immunoreactivity did not show significant differences between all groups (Table 3; Fig. 3(D)–(F)).

Fig. 3 Immunohistochemical findings of vimentin, desmin and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in the lung parenchyma of the control (CO), zinc deficiency (ZD) and ZD refed groups. (A)–(C) Positive cytoplasmic immunostaining of vimentin (arrows). (D)–(F) Desmin immunostaining in the cytoplasmic cell regions (arrows). (G)–(I) Nuclear expression of PCNA protein (arrows), 40 × .
Vimentin immunostaining
The results of the quantitative image analysis of vimentin immunostaining are shown in Table 3. Vimentin was detected in the cytoplasm of cells in all groups. In the ZD refed group, immunostaining was significantly higher (P < 0·05) compared with the CO group (Fig. 3(A)–(C)).
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunostaining
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) was observed in the cytoplasm of cells in all groups treated. In the CO group, moderate staining was observed. Immunoreactivity in the ZD and ZD refed groups was significantly higher (P < 0·05) compared with the CO group (Table 3; Fig. 3(G)–(I)).
Discussion
Zn is known to exert antioxidant effects in vitro and in vivo, although Zn itself is redox inert(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Krezel, Hao and Maret27). On the other hand, Zn deficiency as well as Zn overload may induce oxidative stress and may be cytotoxic(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Krezel, Hao and Maret27). While Zn supplementation protects from oxidative stress in many different cell types, as well as in animal models(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Sahin, Smith and Onderci28, Reference Bediz, Baltaci and Mogulkoc29), Zn deprivation has been found to increase intracellular oxidative stress and to induce apoptotic cell death(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Ho, Courtemanche and Ames30). We have previously showed that ZD induce an important oxidative and nitrosative stress in the lung parenchyma(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Biaggio, Pérez Chaca and Valdéz6) and demonstrated that NO-related species are accumulated in the lung during the course of Zn deficiency(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5).
Taking into account studies previously undertaken by different groups as a result of a Zn deficiency, we decided to investigate what was happening in the cytoskeleton under these conditions. In addition, a group of animals with the CO diet was refed for 10 d in order to determine whether there was a recovery of some of the studied parameters.
We used an experimental model that has the advantage of being used for a long time to obtain more relevant physiological results(Reference Gomez, Fernandez and Zirulnik31, Reference Cunnane and Yang32). In our experimental design, Zn deprivation for 8 weeks induces a decrease in body weight in the ZD group. Zn is known to play a role in protein metabolism(Reference Gómez, Ojeda and Gimenez33–Reference Ying, Shu and Gu35) and has been identified that Zn deficiency produces deficient protein digestion and absorption. Yu et al. (Reference Yu, Yan and Yu36) also proposed that Zn deficiency affects the growth and development of bones, which could be another factor in the final body weight of the animals. Zn refeeding restores body weight in the ZD refed group (Table 1).
A decrease in serum Zn increased the risk for developing metabolic and clinical signs of Zn deficiency(Reference King37) and confirmed previous data(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Gómez, Ojeda and Gimenez33). During the supplementation period, serum Zn concentration increased in relation to ZD. Some authors have shown the fact that, when Zn is added back to the diet, growth is promptly resumed, and it initially proceeds even faster than in the controls(Reference Dorup and Clausen38); the time of refeeding used in the present study was enough to overtake the normal level of Zn.
The alveolar epithelium serves as a major source of TGF-β1 and many other cytokines including TNF-α, during lung injury and fibrosis(Reference Dorup and Clausen38). The alveolar epithelium also regulates an intrinsic capacity to respond to TGF-β1 stimulation through the differential expression of TGF-β1 receptor subtypes(Reference Xu, Hua and Mui39). Taken together, these data suggest that the alveolar epithelium plays a major role in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis, with the capacity to produce and respond to TGF-β1, and modify cell morphology and gene expression in response to injury, all independent of the degree of inflammation. On the other hand, Moustakas & Heldin(Reference Moustakas and Heldin40) demonstrated that TGF-β members have a strong and complex impact on the organisation of the cytoskeleton architecture. This primarily involves the actin cytoskeleton and, secondarily, certain systems of IF(Reference Khalil, Parekh and O'Connor41). TGF-β signalling seems to aim at least two different physiological outcomes that are interlinked: first, it changes the overall cellular architecture that has an impact on differentiation and, second, facilitates cell motility, prerequisites of which are altered architectural arrangement and the remodelling of the extracellular matrix. Considering these facts, the increased expression of TGF-β1 during ZD may lead to remodelling process activation in the lung parenchyma. However, the relationship between the production of growth factors by the airway epithelium and the subsequent remodelling remains poorly understood.
We have previously demonstrated an increase in the gene transcription of many inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α during Zn deficiency. In agreement with this, an important infiltration of inflammatory cells, principally, neutrophils (data not shown) was observed in our experimental model(Reference Biaggio, Pérez Chaca and Valdéz6). Besides, some authors have shown the relationship between TNF-α and other fibrogenic molecules with a fibrotic sequel, in particular TGF-β1. TGF-β1 is up-regulated in pathologies in which TNF-α is associated with fibrosis(Reference Moustakas and Heldin40, Reference Phan and Kunkel42). Recent evidence indicates that some matrix metalloproteinases are implicated in the cancer process, with infiltration of inflammatory cells and metastasis(Reference Kapanci, Desmouliere and Pache43).
In our model, the immunostaining of the CerbB-2 factor (Table 3), an epithelial protein that induces the proliferation and differentiation of cells(Reference Egeblad and Werb44), was increased in the ZD and ZD refed groups. According to the evidence, we can suggest that the increased expression of CerbB-2 during Zn deficiency and ZD refeeding is associated with cell proliferation processes, perhaps in order to promote the remodelling of the respiratory epithelium.
Chilosi et al. (Reference Chilosi, Poletti and Murer45) and Willis et al. (Reference Willis, duBois and Borok46) indicated that there are several pathways of remodelling during lung morphogenesis, including the action of these proteins; however, during a state of injury, the repair process may be altered, leading to fibrosis(Reference Hynes and Lane47). Within the pan-cadherins, β-catenin is one of the most important proteins because of its role in cell migration and adhesion by direct interaction with the cytoskeleton(Reference Willis, duBois and Borok46). Several experiments have shown that this protein is expressed in epithelial cells type II when it induces a state of hypoxia in rats(Reference Douglas, Diaz del Valle and Winn48). The present findings show a slight increase in pan-cadherins in the ZD refed group; this situation could be attributed to increased cell proliferation by promoting cell–cell adhesion. However, the expression of these proteins during Zn deficiency was not altered, which would suggest that this deficiency does not affect the integrity of cell–cell junctions.
Furthermore, the expression of CK in ZD remained unchanged; however, we showed evidence for lung epithelial damage during Zn deficiency. In the ZD refed group, the expression of these proteins increased when compared with the CO group (Table 3); this situation suggested a possible reactivation of mesothelial cells, presumably in order to repair the damaged epithelium.
On the other hand, desmin (a member of the cytoskeleton) is present in smooth muscle cells, skeletal cardiac cells, as well as in myoepithelial cells(Reference Reddy, Buckley and Doerken49, Reference Osborn, Hession and Tizard50). Most of the background found in the literature relates the presence of vimentin and desmin in the development of the carcinogenic process, where these proteins would be used as markers of proliferation. In our experimental model, desmin expression did not change in all treated groups (Table 3), which could suggest that cells with myoepithelial origin would not be affected during Zn deficiency.
The present study also showed that the immunostaining of PCNA-positive cells in the ZD and ZD refed groups was higher compared with the CO group (Table 3). Interestingly, it has been found that the PCNA expression level correspondingly increased in regions of the high expression of inducible NO synthase(Reference Yang and Makita51). In fact, our previous study has shown an increase in inducible NO synthase and endothelial NO synthase expression in ZD lung during Zn deficiency. Inducible NO synthase immunostaining was detected in alveolar type II cells and polymorphonuclear neutrophils (data not shown). Besides, recently, evidence has shown that PCNA and E-cadherin (pan-cadherin family) play an important role in the invasion and metastasis of cancer(Reference Sang, Chen and Shao52).
There is evidence that helps us to understand even more the effect of Zn deficiency on the epithelium. Nickolson & Veldstra(Reference Nickolson and Veldstra53) demonstrated the effect of Zn deficiency and oxidative stress on the microtubules; they demonstrated the deregulation of the normal functions of the cytoskeleton(Reference Weng, Wu and Yang54). It has also been observed that mesothelial cells are stimulated with high concentrations of glucose or pro-inflammatory cytokine that induces the expression of TGF-β and decreases the expression of E-cadherin(Reference Nickolson and Veldstra53), which plays a key role in the control of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition(Reference Yang, Kim and Lee55, Reference Perl, Wilgenbus and Dahl56). Additionally, MacKenzie et al. (Reference Mackenzie, Keen and Oteiza57) showed that in cultured neuronal cells with Zn deficiency, there was an alteration of the processes of neuronal differentiation and proliferation, which was reflected in the cytoskeleton, and a decrease in translocation NF-κB(Reference Takeichi58). Moreover, the excessive production of reactive oxygen species is associated with the activation of pro-fibrogenic genes in cells producing collagen(Reference Kisseleva and Brenner4). The production of reactive oxygen species has previously been shown in our experimental model(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5, Reference Biaggio, Pérez Chaca and Valdéz6). In addition, damage to respiratory epithelial cells is related to interstitial oedema, PMN invasion and decreased lung capacity(Reference Mackenzie, Keen and Oteiza57, Reference Kuwano, Hagimoto and Nakanishi59); the inflammatory status factor causes the activation of TGF-β, which in turn induces the activation of fibroblasts.
Bringardner et al. (Reference Bringardner, Baran and Eubank60) demonstrated that the inflammatory process affects the structure of the extracellular matrix, the secretion of receptors for growth factors and cellular plasticity; therefore, an increase in the degree of cellular plasticity is associated with the presence of fibrosis(Reference Strieter, Gomperts and Keane61). In fact, in our experimental model, we have shown that Zn deficiency would generate a severe inflammatory condition, which would lead to a deterioration of the respiratory epithelium, a situation which is characterised by the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the pulmonary stroma(Reference Gomez, Davicino and Biaggio5), and an increased expression of pro-inflammatory parameters(Reference Biaggio, Pérez Chaca and Valdéz6). Taken together, this evidence suggests that Zn deficiency provokes a critical damage to the alveolar epithelium, which, at least in part, could be recovered by connective tissue during the refeeding time.
In conclusion, the changes observed are probably due to structural and functional alterations that occur during Zn deficiency and may be associated with important modifications in the expression of cytoskeleton proteins and cellular adhesion molecules. Besides, the presence of fibrosis significantly increases the risk of the development of tumour foci in the lung. Finally, when this situation occurs together with other pathologies, it could lead to a worse prognosis.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET)-22Q614 and the Secretary of Science and Technology (SECyT)-Project 8104-National University of San Luis, Argentina. All authors declare that they have no commercial/financial conflict of interest. The authors would like to thank Dr A. Acosta for valuable atomic absorption spectrophotometer contribution; Dr J. Chediak for his excellent assistance in the Western blotting technique and Dr R. Dominguez for her technical assistance. The specific collaboration of each contributing author was as follows: V. S. B. and N. N. G. contributed to the experimental design and manuscript writing. V. S. B. and M. V. P. C. performed all the molecular biology experiments. S. R. V. was involved in the histological preparation of tissues. V. S. B., N. R. S. and H. H. O. collaborated on the immunohistochemistry technique. M. S. G. was the Project Director.








