It is essential to understand for whom and in what circumstances behaviour change interventions are effective in order to increase the understanding of behavioural change processes, identify underserved populations and be able to optimize interventions( Reference Kremers, de Bruijn and Droomers 1 – Reference Baranowski, Cullen and Nicklas 3 ). Studies investigating potential moderators of intervention effects are needed to provide such information( Reference Kremers, de Bruijn and Droomers 1 , Reference Kraemer, Wilson and Fairburn 2 ). A moderator is a variable that can influence the magnitude of this effect across different sub-populations or circumstances( Reference Rothman and Greenland 4 ). To contribute to the evidence regarding moderators of computer-tailored interventions, moderation of the effects of the computer-tailored FATaintPHAT intervention on dietary behaviours by sociodemographic, cognitive and home environmental factors was investigated.
FATaintPHAT is a school-based intervention that consists of eight modules on energy balance-related behaviours( Reference Ezendam, Oenema and van de Looij-Jansen 5 ). The dietary behaviours addressed in separate modules include the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, high-energy snacks, fruits and vegetables. Each intervention module consists of a brief introduction to the topic with information about the behaviour–health link, an assessment of behaviour and determinants, individually tailored feedback on behaviour and determinants, and an option to formulate an implementation intention to prompt specific goal setting and action planning. The intervention was found to be effective in improving sugar-sweetened beverage (OR = 0·54 for drinking >400 ml/d), snack (regression coefficient b = −0·81 snacks/d) and vegetable (b = 0·39 g/d) consumption among adolescents( Reference Ezendam, Brug and Oenema 6 ). The intervention also targeted physical activity and sedentary behaviours, but was not successful in promoting these behaviours. Computer tailoring is a technique that provides individualized feedback and behaviour change information adapted to unique characteristics of a person( Reference Hawkins, Kreuter and Resnicow 7 ). Although such interventions are tailored to personal characteristics, this does not necessarily mean that these interventions are equally effective across subgroups with different characteristics. Subgroups that differ in motivation, abilities or opportunities to engage in the recommended behaviour changes may respond differently to computer-tailored education( Reference Brug and van Assema 8 ). However, little research has been conducted to test potential moderators of computer-tailored intervention effects( Reference Brug and van Assema 8 – Reference Gans, Risica and Strolla 10 ), and to our knowledge there are no studies that have investigated this among adolescents.
In the present study three types of potentially moderating factors were examined: sociodemographic, cognitive and home environmental factors. First of all, effects of interventions like FATaintPHAT may vary according to sociodemographic factors like level of education, gender and ethnicity. If so, there might be sociodemographic subgroups for whom computer tailoring algorithms should be developed that incorporate more specific characteristics of these subgroups. Three studies on differences in effectiveness of computer tailoring according to education level of adults have been published( Reference Brug and van Assema 8 – Reference Gans, Risica and Strolla 10 ). Results showed no differential effects on fat intake( Reference Brug and van Assema 8 ) and physical activity( Reference van Stralen, de Vries and Bolman 9 ), but more effect in improving fruit and vegetable intake among lower educated compared with higher educated participants( Reference Gans, Risica and Strolla 10 ).
Furthermore, with regard to cognitive factors, awareness of dietary intake and intention are possibly important moderating factors. An important aim of the FATaintPHAT programme was to improve adolescents’ awareness about their dietary intake. The Precaution Adoption Process Model states that awareness of one's own behaviour is an important first step in the behaviour change process( Reference Weinstein, Rothman and Sutton 11 ). Adolescents who are already aware of their unhealthy dietary intake or who are already motivated to change may have higher attention to and may be more receptive to feedback messages fostering motivation and self-efficacy, and hence be more likely to move into the action phase, than adolescents who are unaware or not yet motivated to change( Reference Gollwitzer and Sheeran 12 ).
Finally, home environmental factors are expected to act as moderators since behaviour change is expected to be more likely in a facilitating environment, i.e. where the healthy behavioural options are more and unhealthy options are less easily available and accessible( Reference Kremers, de Bruijn and Visscher 13 – Reference Van der Horst, Oenema and Ferreira 15 ). For adolescents a supportive and facilitating home environment is likely to be of crucial importance where dietary behaviour is concerned( Reference Ritchie, Welk and Styne 16 ).
The current paper aimed to study whether the effects of FATaintPHAT on sugar-sweetened beverage, snack, fruit and vegetable consumption were moderated by sociodemographic, personal or environmental factors (Fig. 1). The study hypotheses were that:
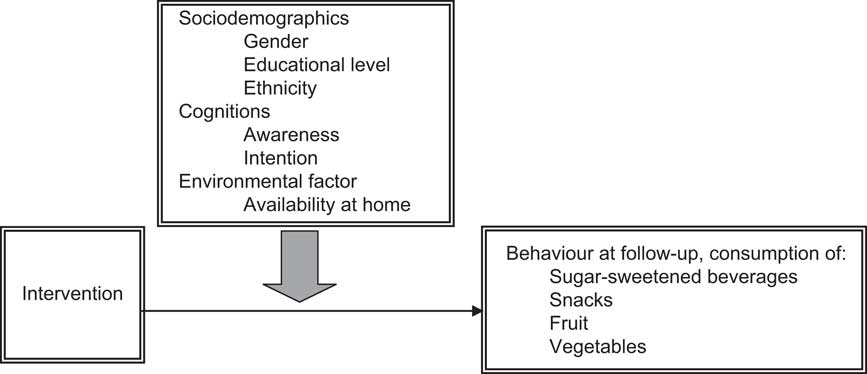
Fig. 1 Hypothetical model of potential moderators of the FATaintPHAT intervention effects on dietary behaviours
-
1. Gender, level of education and ethnicity will not significantly moderate the intervention effects, because by using the technique of computer tailoring differences according to sociodemographic factors have been taken into account.
-
2. Awareness and motivation will significantly moderate the intervention effects, because students with higher awareness and more positive intentions are expected to be more ready to change.
-
3. Perceived home availability will significantly moderate the intervention effects, because high availability of healthful and low availability of less healthful dietary products is expected to facilitate making behavioural changes.
Methods
Study design
The FATaintPHAT intervention was evaluated in a two-group cluster randomized trial (n 883)( Reference Ezendam, Oenema and van de Looij-Jansen 5 ) with assessments at baseline and 4-month follow-up (school year 2006–2007). The present study draws on data from this trial. Schools were randomly assigned to the intervention group or no-intervention control group after stratification according to educational level (vocational; higher than vocational). The outcome measures were the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages, high-energy snacks, fruit and vegetables. The study was conducted in collaboration with the Municipal Health Services in the Rotterdam area. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Erasmus University Medical Centre and registered in the Netherlands Trial Registry (ISRCTN15743786).
Participants and recruitment
Participants were recruited in a two-step procedure. First, eighty-eight schools for secondary education in Rotterdam and surrounding municipalities were invited to participate. The Rotterdam area is characterized by its large diversity in ethnic groups, with particularly large groups of Moroccan, Turkish and Cape-Verdean origin( Reference van de Looij-Jansen and de Wilde 17 ). Twenty-three schools were eligible and willing to participate. Second, adolescents of one to five classes in each school were invited to participate. Three schools withdrew from the study after randomization and before the baseline measurement because they found the informed consent procedure too troublesome. Students (aged 12–13 years) received information and an informed consent form for themselves and their parents. Completed consent forms were returned by 883 students.
The intervention
The objective of the computer-tailored intervention was to contribute to the prevention of excessive weight gain among adolescents by improving dietary, physical activity and sedentary behaviours. Eight separate modules addressed the concept of weight management and energy balance-related behaviours. The feedback provided included several elements: behavioural feedback, comparing the student's behaviour with guidelines for that behaviour (normative feedback) and with the behaviour of peers (comparative feedback), decisional balance information to change attitudes, barrier identification and instructions on how to perform/change a behaviour to improve self-efficacy, suggestions on how to organize social support and prompts for intention formation. A multi-theoretical approach, including the Theory of Planned Behaviour( Reference Ajzen 18 ), the Precaution Adoption Process Model( Reference Weinstein, Rothman and Sutton 11 ) and implementation intentions( Reference Gollwitzer 19 ), was used to inform the intervention. By addressing several individual-level characteristics (e.g. gender, food preference, time of eating, foods consumed, way of transport generally used), we aimed that the intervention accounts for sociodemographic differences directly or indirectly. Some examples of direct tailoring on gender include implementing gender-specific naming, providing gender-specific comparative feedback and focusing on gender-specific motivators or barriers (e.g. perspiration due to sports). Furthermore, it was not always necessary to tailor on demographic characteristics explicitly, since the adolescents were provided with individual feedback about their personal behaviour, and when it came to strategies for change such as trying to taste new foods or mobilizing social support, adolescents were instructed to think of new (culturally appropriate) foods that they would like to taste or important people in their own social network whom they wanted to mobilize (indirect tailoring). In Dutch the name of the intervention is VETisnietVET, which has the connotation of ‘it is not cool to be overweight’ and we translated this as FATaintPHAT. The teachers were asked to allocate 15 min in eight lessons over 10 weeks for working with the programme according to a teacher manual.
Procedure
Data on the outcome measures were collected through electronic, self-report questionnaires that were completed by the adolescents during one school hour under the supervision of a research assistant. The same procedure was employed at baseline and 4-month follow-up assessments. Weight and height were measured by a trained research assistant at baseline. After the baseline assessment, the intervention was implemented by the teachers during a 10-week period. The control schools continued with the regular curriculum without extra activities.
Measurements
Self-reported behaviours
Dietary intake was assessed using a food questionnaire assessing the frequency and quantity of sugar-sweetened beverages consumed in the past week and a self-administered 24 h recall for snacks, fruits and vegetables. The questionnaires were based on validated FFQ for snack( Reference Van Assema, Brug and Ronda 20 ) and fruit and vegetable intakes( Reference Van Assema, Brug and Ronda 21 , Reference Bogers, Van Assema and Kester 22 ). All dietary data were expressed as intake per day.
A 24 h recall is found to be superior over a frequency questionnaire to get reliable estimates of group mean intake levels and to detect differences between groups( Reference Collins, Watson and Burrows 23 , Reference Haraldsdottir, Thorsdottir and de Almeida 24 ). Therefore, the 24 h recall data were used for the analyses. The variable for sugar-sweetened beverage consumption was not normally distributed and therefore a dichotomized variable was used in the analyses (≤400 ml/d v. >400 ml/d). Because a dichotomized 24 h recall does not produce a reliable assessment of usual individual intake levels, usual intake of sugar-sweetened beverages as assessed with the food frequency questions was used. The questionnaire items are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Questionnaire items and answer categories used to examine dietary behaviours

Moderating variables
Questions on sociodemographics included gender, age, educational level, country of birth and parents’ country of birth. Ethnicity was defined according to standard procedures of Statistics Netherlands as either Western (both parents born in Europe, North America, Oceania, Indonesia or Japan) or non-Western (at least one parent born elsewhere)( 25 ). Educational level was defined as vocational or academic preparatory (preparatory for bachelor education). A variable for awareness of risk behaviour was calculated based on perceived intake of the various food products and the measure of actual intake. Perceived intake was assessed as ‘Do you think you usually drink/eat small or large amounts of soda/snacks or candy/fruit/vegetables?’ (response categories from ‘very little’ (coded as −2) to ‘very much’ (coded as +2)) and dichotomized (−2, −1 and 0 v. 1 and 2). The intake measure was dichotomized to indicate compliance with the recommended intake level of each product according to cut-off levels as used in the intervention (sugar-sweetened beverages: ≤400 ml/d v. >400 ml/d; snacks: ≤3 pieces/d v. >3 pieces/d; fruit: <2 pieces/d v. ≥2 pieces/d; vegetables: <200 g/d v. ≥200 g/d). To create an indicator of awareness of risk behaviour, participants were then categorized as aware of their unhealthy behaviour v. all others (aware of healthy behaviour and unaware respondents). We chose this categorization because we hypothesized that students who were aware of their unhealthy behaviour were further in the process of behavioural change and therefore were the likely group to show behavioural change as a result of the intervention, whereas the other categories of participants were the ones who already behaved according to the guidelines (expecting no improvement because they did not receive an advice to change their behaviour) or were unaware of their unhealthy behaviour (expecting predominantly changes in awareness and motivation, but not necessarily in behaviour). Intention to change was assessed with one 5-point scale item for each behaviour: ‘Do you intend to drink/eat less soda/less candy or snacks/more fruit/more vegetables in the next year?’ (response categories from ‘certainly not’ (coded as −2) to ‘certainly yes’ (coded as +2)). This variable was then dichotomized into a negative/neutral intention (−2, −1 and 0) and a positive intention (1 and 2). Availability of food at home was assessed with one item per behaviour (e.g. ‘Are sugar-sweetened beverages available at home? Never, seldom, sometimes, almost always, always’). Because of few observations in the ‘never’ and ‘seldom’ answer categories of the availability variable, the categories ‘never’, ‘seldom’ and ‘sometimes’ were combined into one category (resulting in a variable with three answer categories) that was used for the stratified analyses.
Weight status
Height was measured twice without shoes using a Seca 225 mobile height rod with an accuracy of 0·1 cm and the average was calculated. A calibrated electronic digital floor scale (Seca 888 class III) was used to measure the body weight of the students who wore light clothes (shorts and T-shirt or underwear) with an accuracy of 0·2 kg. BMI was calculated as weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of height (in metres). Weight categories were defined according to the cut-off points defined by the International Obesity Taskforce( Reference Cole, Bellizzi and Flegal 26 ).
Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe the study population in each study arm. Differences between the groups at baseline were tested using multilevel multivariate logistic regression analyses with group as dependent variables and the demographics as independent variables. Analyses were performed in the statistical software package SPSS version 15·0. The significance level was set at 0·05 and tests were two-sided.
Moderation was tested by assessing the significance of the group × potential moderator interaction term in multilevel linear and logistic regression models( Reference Hayes and Matthes 27 ). We used random intercept models with school as level to account for clustering within schools. The regression of each outcome measure (dietary behaviour) was performed v. group (intervention/control), the baseline value of the outcome measure, gender (girls/boys), education (academic preparatory/vocational), ethnicity (non-Western/Western), the potential moderator and the group × potential moderator interaction terms in separate analyses. The interaction terms were intervention × gender, intervention × education, intervention × ethnicity, intervention × awareness, intervention × intention and intervention × home availability. Since interaction terms have less power, P values of interaction terms are recommended to be set at 0·10( Reference Twisk 28 ). When an interaction term was significant, this was an indication that stratified analyses would be warranted. The intervention effects were re-examined in subgroups stratified by the levels of the moderator variable( Reference Bauman, Sallis and Dzewaltowski 29 ) by performing linear (providing a B value) or logistic regression (providing an odds ratio) analyses. The multilevel regression analyses (with school as level) were performed with PROC MIXED and PROC GLIMMIX (method = gauss(qpoints = 10)) in the statistical software package SAS version 9·2.
Results
Student characteristics
As shown in Table 2, the intervention group consisted of more boys and of more vocational-level students compared with the control group.
Table 2 Characteristics at baseline according to study group: students (n 883) aged 12–13 years, FATaintPHAT intervention, the Netherlands, 2006–2007 school year

*P value from the test for a significant difference between the intervention and control groups by multilevel multivariate logistic regression analysis.
†Based on the cut-off points of the International Obesity Taskforce( Reference Cole, Bellizzi and Flegal 26 ).
Moderation by sociodemographic factors
Of the twelve potential sociodemographic moderation tests (three possible moderators × four behaviours), one was statistically significant. Education moderated the intervention effect on sugar-sweetened beverage consumption (group × education: P = 0·009; Table 3). Academic preparatory students in the intervention group were 0·32 times less likely to drink >400 ml sugar-sweetened beverages/d, while there was no significant effect among vocational students (Tables 4 and 5).
Table 3 P values of the interaction terms from the regression analyses to test the significance of potential moderators on dietary behaviours: students (n 883) aged 12–13 years, FATaintPHAT intervention, the Netherlands, 2006–2007 school year

*SSB (sugar-sweetened beverage) consumption, usual: % >400 ml/d (v. ≤400 ml/d).
†Snack consumption, pieces/d (24 h recall).
‡Fruit consumption, pieces/d (24 h recall).
§Vegetable consumption, g/d (24 h recall).
∥P value of group × moderator interaction.
Table 4 Descriptive statistics for dietary behaviours according to each level of the moderator: students (n 883) aged 12–13 years, FATaintPHAT intervention, the Netherlands, 2006–2007 school year

SSB, sugar-sweetened beverages; IG, intervention group; CG, control group.
Stratified descriptive statistics according to the different moderator levels are presented only for the statistically significant moderators.
Table 5 Regression outcomes from the stratified analyses for the various levels of the significant moderator variables: students (n 883) aged 12–13 years, FATaintPHAT intervention, the Netherlands, 2006–2007 school year

SSB, sugar-sweetened beverages.
Results of the stratified analyses for the intervention effect on the outcome behaviours according to the different moderator levels are presented only for the statistically significant moderators.
Moderation by cognitions
Of the eight potential cognitive variable moderation effects (two possible moderators × four behaviours), only one was statistically significant. Awareness moderated the intervention effect of fruit consumption (group × awareness: P < 0·001; Table 3). Adolescents in the intervention group who were aware of their low fruit intake at baseline increased their fruit consumption by 0·51 pieces/d compared with students in the control group, while there was no effect among students unaware of their low intake or students with baseline intake of ≥2 pieces/d (Tables 4 and 5).
Moderation by home availability
Of the four potential moderation tests by home availability (one possible moderator × four behaviours), one was statistically significant. Home availability moderated the intervention effect on vegetable consumption (group × availability: P = 0·007; Table 3). Adolescents in the intervention group who perceived that they had always vegetables at home increased their vegetable consumption by 33 g/d compared with the control group, while there was no significant intervention effect among students who perceived there were never, seldom, sometimes or almost always vegetables at home (Tables 4 and 5).
Discussion
Main findings
The exploration of potential moderation of intervention effects by sociodemographic, cognitive and environmental factors for four dietary behaviours (twenty-four interactions) resulted in three significant interaction effects. Thus, in general, the intervention was equally effective in modifying dietary behaviours, regardless of sociodemographic or cognitive differences. However, results showed that the effects of the intervention on intakes of sugar-sweetened beverages and fruit were significantly moderated by level of education and awareness of personal intake levels, respectively. The intervention significantly impacted sugar-sweetened beverage consumption among academic preparatory students only, while effects on fruit intake were observed only among students who were aware of their low fruit intake levels at baseline. Furthermore, the presented results provided some indication that the home environment can moderate the intervention effect on dietary behaviours. The results showed that the effect of the intervention on vegetable intake was significantly moderated by perceived home availability. The effect on vegetable consumption was found only among students who reported that vegetables were always available at their home.
Interpretation of the findings
Computer tailoring is a health education technique specifically suited to make use of individual differences in sociodemographic, social cognitive and environmental correlates of intake levels, to personalize and individualize feedback and advice. The present study therefore hypothesized that the intervention effect would not be moderated by sociodemographic factors. In line with this hypothesis the study found no differences in effects according to gender and ethnicity, or according to education for three of the four dietary behaviours studied. These findings are largely in line with studies among adults, where no differential effects were found for educational level on fat intake and physical activity( Reference Brug and van Assema 8 , Reference van Stralen, de Vries and Bolman 9 ). A study among lower-income adults in the USA, however, found that the computer-tailored intervention was more effective in improving fruit and vegetable intake among lower educated compared with higher educated participants( Reference Gans, Risica and Strolla 10 ). In contrast, the FATaintPHAT intervention was not effective in modifying sugar-sweetened beverage intake among lower educated students, while it did among the higher educated. Possible reasons for this may be that the information was appreciated or comprehended less by the lower educated students. In the process evaluation of FATaintPHAT, differences in appreciation and use of the intervention according to educational level were analysed. Results of the process evaluation of FATaintPHAT indeed showed that the information was better comprehended by the higher educated students as compared with the lower educated students, even though lower educated students appreciated the intervention better, read it more carefully and more often discussed it with their parents( Reference Ezendam, Brug and Oenema 6 ). To our knowledge, the present study is the first one to assess differential effects of computer-tailored information according to ethnicity and the fact that the results did not show differential effects is promising for the implementation of computer-tailored interventions in ethnically diverse populations.
The results of the present study show the anticipated moderation effect of awareness of low fruit intake. A possible explanation for why awareness moderated only fruit intake, but not the other behaviours, might be that the recommendation for fruit intake in the Netherlands is clear and this recommendation has been communicated intensively, making the aware students more responsive to take action. The suggestions for taking action and the action planning tool may also have helped these adolescents in actually improving their fruit intake. In contrast to what was hypothesized, students with a positive intention at the start of the study did not benefit more from the action planning part of the intervention compared with students with a neutral or negative intention to change behaviour. This suggests that the methods/strategy of the FATaintPHAT intervention to improve intentions might have been effective and both high and low intenders at baseline benefitted equally from the action planning part of the intervention. Contrary to our hypothesis and findings, a study among adults focusing on physical activity showed that highly motivated individuals were unresponsive to the tailored intervention( Reference van Stralen, de Vries and Bolman 9 ).
The hypothesis was that high availability of healthful and low availability of less healthful options would facilitate healthy behaviour change, since opportunity is an important determinant of dietary behavioural change( Reference Brug 30 ). Previous studies have shown that home availability of sugar-sweetened beverages is a predictor of sugar-sweetened beverage consumption( Reference Ezendam, Evans and Stigler 31 ), home availability of fruit and vegetables is correlated with fruit and vegetable consumption( Reference Kremers, van der Horst and Brug 14 , Reference Wind, te Velde and Brug 32 ), and home availability of unhealthy foods is a predictor of lower fruit and vegetable consumption( Reference Vereecken, Haerens and De Bourdeaudhuij 33 ). Thus, as the availability of foods at home is associated with intake levels, it is likely that intervention effects depend on home availability levels as well. Furthermore, it is expected that it is easier for adolescents to translate this intention into action when the environment is supportive as opposed to a situation where adolescents first have to overcome environmental barriers. The results showed that only for vegetable consumption did perceived home availability appear to be a prerequisite for an intervention effect. Vegetable intake in the Netherlands is very much dependent on family meals eaten at home. It is likely that for interventions to have an effect, home availability is of less importance for foods that are less family meal dependent and often eaten outside the home environment. Another explanation may be that adolescents learned sufficient skills using the intervention to deal with environmental barriers for the other behaviours. Adolescents were for instance encouraged to discuss with parents to buy specific fruits, low-energy snacks or sugar-free drinks that they liked.
Study strengths and limitations
The strength of the present study is that it is one of few to investigate moderation effects of computer-tailored interventions, adding to the understanding of the effectiveness of computer tailoring among specific subgroups. Moreover, as recommended, the present study investigated formal moderation effects by means of interaction analyses, as opposed to a priori stratified analyses which should be avoided( Reference Kremers, de Bruijn and Droomers 1 , Reference Kraemer, Wilson and Fairburn 2 ).
A limitation of the study is that it was not designed for, and thus was underpowered for, moderation and stratified analyses. Even though the study used the recommended significance level of P < 0·1 to test the significance of interaction terms, interaction effects could have remained undetected. On the other hand, the fact that the study tested for six moderators for four behaviours led to multiple testing, increasing the odds of finding statistically significant interactions that are in fact chance findings. The magnitude of the interaction effects is, however, quite large. So even if a stricter significance level (i.e. P < 0·01) had been used, the interaction effects would still be significant. The present study results need replication. Moreover, future intervention studies could try to affect the important moderator variables to examine if these variables can be changed and if these changes lead to better outcomes. Furthermore, like in most studies on dietary change, the dietary outcomes and the moderators were assessed with self-report measures which increase the likelihood of random measurement error. This might have weakened the effects found.
Conclusions
In general, the effects of the intervention did not differ according to sociodemographic factors, prior awareness or intention levels. Nevertheless, the differential effects of educational level on sugar-sweetened beverage intake and of awareness on fruit intake need to be further explored. The significant moderation by home availability illustrates that the environment can influence effects of educational interventions, and in future research this could be explored more often.
Acknowledgements
Source of funding: This work was supported by a grant from ZonMw, the Netherlands Organization for Health Care Research and Development (grant number 62200020). Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interests. Authors’ contributions: N.P.M.E., J.B., P.E. and A.O. contributed to the study question; N.P.M.E., G.B., P.E. and A.O. contributed to the analyses; all authors contributed to the drafting of the paper.








