Research Article
Broad but restricted detection of malacosporeans in a Neotropical cradle of diversification
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 511-518
-
- Article
- Export citation
Host-induced phenotypic plasticity in Saccocoelioides lamothei Aguirre-Macedo and Violante-González, 2008 (Digenea: Haploporidae) a parasite of freshwater, brackish and marine fishes from Middle America
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 519-531
-
- Article
- Export citation
Environmental factors drive the release of Perkinsus marinus from infected oysters
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2020, pp. 532-538
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distinct hepatic myeloid and lymphoid cell repertoires are associated with susceptibility and resistance to Ascaris infection
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2021, pp. 539-549
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Detection of enteric parasites and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis and Blastocystis sp. in patients admitted to hospital in Ankara, Turkey
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, pp. 550-561
-
- Article
- Export citation
Extra-hepatopulmonary cystic echinococcosis in Bulgaria: frequency, management and outcome of the disease
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2020, pp. 562-565
-
- Article
- Export citation
In vitro studies and preclinical evaluation of benznidazole microparticles in the acute Trypanosoma cruzi murine model
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 December 2020, pp. 566-575
-
- Article
- Export citation
Eurytrema coelomaticum natural infection in small ruminants: a neglected condition
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 December 2020, pp. 576-583
-
- Article
- Export citation
Taxonomic resolution affects host−parasite association model performance
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 December 2020, pp. 584-590
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epidemiological and pathological characteristics of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis from Baluchistan Province of Pakistan
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 December 2020, pp. 591-597
-
- Article
- Export citation
Setaria cervi (Filarioidea, Onchocercidae) undressing in ungulates: altered morphology of developmental stages, their molecular detection and complete sequence cox1 gene
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 January 2021, pp. 598-611
-
- Article
- Export citation
The impact of Anguillicoloides crassus (Nematoda) on European eel swimbladder: histopathology and relationship between neuroendocrine and immune cells
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2021, pp. 612-622
-
- Article
- Export citation
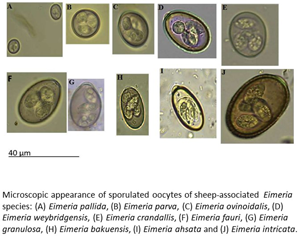
Determinants of Eimeria and Campylobacter infection dynamics in UK domestic sheep: the role of co-infection
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2021, pp. 623-629
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Therapeutic efficacy of mebendazole and artemisinin in different phases of trichinellosis: a comparative experimental study
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2021, pp. 630-635
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corrigendum
High-resolution analysis of baculovirus-induced host manipulation in the domestic silkworm, Bombyx mori – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2021, p. 636
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Diversity, distribution and changes in communities of fleas on small mammals along the elevational gradient from the Pannonian Plain to the Carpathian Mountains – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 February 2021, p. 637
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Front Cover (OFC, IFC) and matter
PAR volume 148 issue 5 Cover and Front matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2021, pp. f1-f2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Back Cover (IBC, OBC) and matter
PAR volume 148 issue 5 Cover and Back matter
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2021, pp. b1-b2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation