In the World Alzheimer’s Report 2016: Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia, Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI) highlighted the role of primary care in dementia (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1). With overly specialised healthcare systems and stretched specialist workforce, dementia is currently under-diagnosed and under-managed. There are 55 million people living with dementia globally, with an increase of nearly 10 million people each year (2). As a public health priority (3), dementia diagnosis and management need primary care involvement.
The idea of involving primary care in dementia is not something new or unconventional – similar developments have been witnessed in other chronic diseases such as diabetes. While various service models have been trialled in different parts of the world, several barriers remain; among them are (when it comes to dementia) a lack of a gatekeeping role for primary care in highly stretched healthcare systems and a perception that primary care is of a lower service quality (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1). The two barriers can be interrelated: high-quality care (and the development of reputation and trust) requires sufficient clinical exposure supported with the right amount of training, while a reputation of high-quality care is needed for primary care to be entrusted with the gatekeeping role.
In the next two chapters, where readers will learn from 99 real cases of people with suspected dementia seeking help from a dementia early intervention service operated by a primary care team, the purpose is to share our experience and lessons learned from these clinical exposures – which can be used as part of a training programme to ensure high-quality dementia care in primary care. Before we move on to these cases, in this chapter we wish to briefly review and outline the possible roles of primary care, including gatekeepers, based on the concepts and practices of task-shifting or task-sharing in dementia care.
1.1 Concepts and Practices of Task-Shifting or Task-Sharing in Dementia Care
What Is Task-Shifting or Task-Sharing?
Task-shifting or task-sharing refers to the ‘rational redistribution of tasks among the health workforce – specific tasks are moved, where appropriate, from highly qualified health workers to health workers with shorter training and fewer qualifications’ (4). This redistribution of tasks can be to an existing group of healthcare professionals, with tailored training that is more narrowly focused (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1, Reference Kakuma, Minas, van Ginneken, Dal Poz, Desiraju and Morris5).
Task-shifting or -sharing in dementia care may involve reallocating tasks from specialists, who are more broadly trained in their respective specialities (e.g., geriatric medicine, psychiatry, and neurology), to primary care. As can be seen from the definition, the focus is one that concerns the allocation of human resources in healthcare, although there are other rationales for involving primary care in dementia care.
Why Shift/Share Tasks in Dementia?
In the Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia 2017–2025 (6), a (justly) ambitious goal was set out to ensure people with dementia and their carers ‘live well and receive the care and support they need to fulfil their potential with dignity, respect, autonomy, and equality’.
This goal is ambitious for at least two reasons. First, the current workforce is already struggling to meet the current needs for diagnosis and continuing care (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1). Difficult-to-access services and long waiting times are common problems in dementia (Reference Lee, Hillier, Heckman, Gagnon, Borrie and Stolee7). With the projected increase in dementia prevalence, it is unrealistic to wish that the world will be able to meet the demand by continuing with the current way dementia care tasks are allocated (e.g., by training dementia care specialists only). Second, the societal impacts of dementia care are wide within and outside the healthcare system, and include carer support and labour force participation, housing and environmental design, and legal and financial planning, to name a few. The complexity of care needs in dementia means that without proper coordination, the care and service systems will be fragmented, if not impossible to navigate. Governments across the world are working to develop national dementia strategies (8).
Particularly for the second reason, primary care is in a good position to help – by minimising service fragmentation or transition and taking care of the person’s other health and social care or support needs, with a person-centred approach and collaborative interdisciplinary care. In countries or areas where family physicians or primary care physicians have an existing rapport with the family, their involvement in dementia care may also reduce the barriers of fear and stigma surrounding the dementia diagnosis (see Section 5.3) to encourage timely help-seeking, as well as decrease the possibilities of the person dropping out from service (Reference Dodd, Cheston and Ivanecka9–Reference Hawkins12).
Alongside these obvious reasons to promote primary care involvement in dementia care, some worries remain: is it feasible to shift/share the task with primary care? What tasks can be shifted/shared? Is such a model as effective and safe as services provided by specialists – a question about service quality (and equity, if both primary care and specialist care are available) – and in what ways?
Task-Shifting/-Sharing in Dementia Care: Real-World Implementation
The above are questions that many practitioners and researchers around the world have been trying to answer. Since the publication of the World Alzheimer’s Report 2016 (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1), experience is quickly accumulating in involving primary care in dementia care. As task-shifting/-sharing is essentially a complex intervention, its development and evaluation are still evolving with new methodological and theoretical approaches (Reference Skivington, Matthews, Craig, Simpson and Moore13); nevertheless, some models have been implemented and evaluated, with evidence of improved service supply and maintained service quality in diagnosis and continuing care (Reference Lee, Hillier, Heckman, Gagnon, Borrie and Stolee7, Reference Greaves, Greaves, Walker, Greening, Benbow and Jolley10, Reference Banerjee, Willis, Matthews, Contell, Chan and Murray11, Reference Jolley, Greaves and Clark14–Reference Buttorff, Hock, Weiss, Naik, Araya and Kirkwood20).
In some countries such as New Zealand, a shift of the diagnosis and management of uncomplicated dementia cases to primary care has been recommended in their national framework, freeing up specialists who can then provide episodic support/advice to primary care (21). Elsewhere in other high-income countries such as the UK and Sweden, various services have been piloted and developed. Here is a snapshot:
In the UK, the impacts of the National Dementia Strategy with a focus on increasing the dementia diagnostic rate with financial incentive schemes for primary care have been evaluated. The policy was introduced in 2009, and incentive schemes were introduced between 2013 and 2015 to increase the diagnosis of dementia by encouraging general practitioners to proactively identify undiagnosed cases and develop collaborative care packages. The incentives seem to have effectively boosted diagnostic rates (Reference Mason, Liu, Kasteridis, Goddard, Jacobs and Wittenberg22) and the quality of drug treatment (Reference Donegan, Fox, Black, Livingston, Banerjee and Burns23). More recently, applying the Quality and Outcomes Framework and patient experience measurements, the schemes have been shown to have a positive impact on quality outcomes, including spillover effects in other clinical areas, although there were also some unintended negative impacts on patient experience, such as continuity of care (possibly due to efforts being diverted away from other patients) (Reference Liu, Green, Kasteridis, Goddard, Jacobs and Wittenberg24).
In Sweden, primary care was compared with specialist care for the diagnostic process and management of Alzheimer’s disease, using data from the Swedish Dementia Registry (Reference Garcia-Ptacek, Modeer, Kareholt, Fereshtehnejad, Farahmand and Religa25). There were no differences in the use of cholinesterase inhibitors between the services, with primary care associated with a higher likelihood of home care or day care use. Primary care physicians were, however, less likely to have ordered neuroimaging or completed a Clock Drawing Test (see Section 1.3). Although these observations do not imply differences in service quality (as there were differences in patient characteristics between services), they provided some ideas about the existence of any important differences in practice.
With these accumulating experiences, we are witnessing burgeoning developments of primary care models in dementia. From a more forward-looking perspective, future generations of primary care physicians also appeared positive about having a role in early intervention for dementia with community-based care and post-diagnostic support services established (Reference Tang, Birdi and Robinson26).
In Section 1.2, we outline a few selected primary care models for reference. While it is not the goal of this book to provide a comprehensive review of these rapidly evolving service models and developing evidence, examples are included here to put the cases presented in this book in context for potential application in our readers’ local setting. The cases involved participants from a primary care model with developing integrated health and social care in Hong Kong, which we will describe in Section 1.5.
1.2 Primary Care Models in Dementia: Some Examples
The below examples were selected to illustrate the diversity of possible models and where more detailed information can be found on their operations and outcomes. The examples are organised around the following models: (a) a primary care service with specialist outreach; (b) a specialist service with primary care support; and (c) an integrated multidisciplinary team. Readers who are interested in finding out more about these services are encouraged to visit the online resources provided.
Primary Care Service with Specialist Outreach: An Example
Gnosall Primary Care Memory Clinic in the UK (Reference Greaves, Greaves, Walker, Greening, Benbow and Jolley10, Reference Hawkins12) (see www.england.nhs.uk/2015/09/leading-models-dementia/ for details in an NHS England report) is a primary care-based service, with specialist input to support the diagnosis, initial treatment, and ongoing patient review and to provide supervision. The service’s ethos is to ‘bring the best of secondary care into the primary care service’. A general practitioner would identify people with suspected dementia, who would then be referred to an eldercare facilitator for further assessments – including a Clock Drawing Test and the General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition (GPCOG; see Chapter 4) – and service coordination. When needed, a specialist (a consultant psychiatrist) who spends 3.5 hours per month on site would meet with the person with dementia, the carer, and the facilitator in a monthly memory clinic session to discuss the diagnosis and care. He/she would also provide support to the primary care through phone calls in between the monthly sessions. For the family of the person with dementia, the facilitator is their single point of contact, who works closely with the general practitioner and the specialist.
Benefits noted of the model include minimised delays in access to the service, a nearly 100 per cent attendance rate, identification and treatment of comorbidities, reduced secondary healthcare costs (mainly from reduced acute hospital service use), high levels of user satisfaction, and reduced stigma about seeing a psychiatrist. A key message for effective service is close collaboration with the local mental health partnership service.
Specialist Service with Primary Care Support: An Example
The Dementia Community Support Scheme in Hong Kong (Reference Wong, Lum, Tang, Kwan, Chan and Cheung27) (see www.communitycarefund.hk/download/Evaluation_Report_Dementia_eng.pdf for details in an evaluation report of the pilot service) is a medical–social collaboration model to provide community care services for people with mild or moderate dementia and their carers. People living with dementia receive diagnostic and follow-up consultation services from a specialist outpatient clinic (psychiatry or geriatric medicine) in a public hospital, and are referred to a nearby District Elderly Community Centre, where he/she and the carers would receive a care planning service and corresponding activity support to enhance cognition, daily activity, physical and social functioning; to improve home safety; alleviate carer burden; and to maintain the quality of life of both the person with dementia and their carers. The service is provided by a multidisciplinary allied healthcare and social care team (mostly comprised of a nurse, a social worker, and an occupational therapist/physiotherapist) in the community centre, who work with the hospital specialist team through case conferences and other means of communication (e.g., phone calls). People with suspected dementia identified by the multidisciplinary team may also receive diagnostic consultation and follow-up by a trained primary care physician in private practice and be provided with the same community support.
Benefits of the model identified in the pilot phase include reduced carer burden, particularly among those experiencing a greater burden before reaching the service; a high level of user satisfaction; enhanced collaboration between specialist outpatient clinics and community centres; and maintained quality of life despite deterioration in functioning and symptom severity. Lessons learned from this model include the need for equal-status partnership, joint decision-making, and an information-sharing system when the service crosses the two sectors/settings (medical and social/hospital and community).
Integrated Multidisciplinary Team: An Example
Multispecialty Interprofessional Team (MINT) memory clinics (previously referred to as Primary Care Collaborative Clinics) in Canada (Reference Lee, Hillier, Heckman, Gagnon, Borrie and Stolee7, Reference Lee, Hillier, Stolee, Heckman, Gagnon and McAiney17, Reference Lee, Weston and Hillier28–Reference Lee, Kasperski and Weston30) (see https://mintmemory.ca/ for details) are an integrated model with a team comprising the person’s family doctor, nurses, social workers, pharmacists, and other related professionals (e.g., occupational therapists) who work with other specialists and representatives from local community groups such as the Alzheimer’s Society. Upon referral to the memory clinics, the person’s assessment results are reviewed by the team for an initial diagnosis and management plan, which are shared with the specialist, and complex cases are referred to the appropriate service. Professional team members have to go through standardised accredited training (Reference Lee, Weston and Hillier28).
Benefits observed with this model include reduced costs in the healthcare system (including a reduction in inpatient and emergency department visit costs) and reduced waiting times of nearly 50 per cent. This model highlighted the need to equip the team with training and on-the-job education, to ensure care quality when the complex task of dementia care is shifted/shared with primary care; it also reflects the importance of service integration with a primary care and care management partnership, which was noted in a systematic review of the effectiveness of various post-diagnostic dementia care models delivered by primary care (Reference Frost, Walters, Aw, Brunskill, Wilcock and Robinson31).
Learning Points from the Three Examples
The above examples illustrate the potential roles of primary care in dementia work-up, diagnosis, and management within various primary care models; family physicians, as part of a primary care team, should arguably be involved in all key aspects of dementia care (Reference Moore, Frank and Chambers32), including prevention, providing a timely diagnosis, dementia staging, determining dementia subtypes, differentiating other conditions with similar presentations to dementia, communicating the diagnosis while protecting the person’s dignity and balancing the family’s needs, and providing person-centred, post-diagnosis management support.
1.3 Overview on Dementia: Work-up, Diagnosis, and Management
With the above-mentioned extensive role of primary care in dementia services, an in-depth review of each of the key aspects would be beyond the scope of this casebook (for more detailed reviews and clinical guides, see Reference Livingston, Huntley, Sommerlad, Ames, Ballard and Banerjee33–Reference Barrett and Burns36). As our purpose here is to share knowledge that would enable the primary care team to function as gatekeepers in the health and social care system to avoid secondary and tertiary care becoming overwhelmed, we will focus on work related to simple, uncomplicated Alzheimer’s disease, while also touching on issues surrounding recognising complex cases when referral or collaboration beyond primary care is warranted.
Common Dementia Subtypes
There are various subtypes of dementia, reflecting different symptomatology and pathology. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common subtype of dementia, accounting for 60 per cent to 80 per cent of cases (37). The condition is characterised by an insidious, slow onset and gradual progression over many years. The most common clinical presentation is episodic memory impairment, in which individuals have difficulty learning and recalling recently learned information. Cognitive dysfunction may also present in language ability, such as deficits in word finding, and executive dysfunction, including impaired reasoning, judgement, and problem-solving. Individuals may also present with visuospatial problems, such as object agnosia, impaired face recognition, simultanagnosia, and alexia (Reference McKhann, Drachman, Folstein, Katzman, Price and Stadlan38, Reference McKhann, Knopman, Chertkow, Hyman, Jack and Kawas39). The neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease is marked by the accumulation of plaques, which are extracellular deposits of β-amyloid peptides, and neurofibrillary tangles (Reference Montine, Phelps, Beach, Bigio, Cairns and Dickson40). The underlying cause of Alzheimer’s disease is still unknown, but several possible pathological pathways have been suggested. According to the widely accepted ‘amyloid cascade hypothesis’ (Reference Hardy and Higgins41), the condition is initiated by the progressive accumulation and disposition of β-amyloid, leading to the formation of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles and ultimately neuronal death and dementia.
Vascular dementia is the most common comorbid condition with Alzheimer’s disease (Reference Kapasi, DeCarli and Schneider42, Reference Brenowitz, Hubbard, Keene, Hawes, Longstreth and Woltjer43). The brain infarcts or white matter lesions associated with the condition can develop from cerebrovascular incidents, such as a stroke. The condition is diagnosed when there is a relationship between dementia and cerebrovascular disease, where the onset of dementia is within three months following a recognised stroke, an abrupt deterioration in cognitive functions, or a fluctuating, stepwise progression of cognitive deficits (Reference Roman, Tatemichi, Erkinjuntti, Cummings, Masdeu and Garcia44). Individuals with the condition show gait disturbances in the early stages, such as small-step gait or parkinsonian gait, a history of unsteadiness, and frequent, unprovoked falls. They may also experience early urinary frequency, urgency, and other urinary symptoms that are not explained by urologic disease. Other clinical features include pseudobulbar palsy, personality and mood changes, abulia, depression, emotional incontinence, and other subcortical deficits, including psychomotor retardation and abnormal executive function. Memory, language ability, motor skills, and insight are relatively intact in the early stages of the condition.
Other major subtypes of dementia include dementia with Lewy body (DLB) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). The former has a slow onset and progresses gradually over months and years (Reference McKeith, Boeve, Dickson, Halliday, Taylor and Weintraub45). Memory impairment may not necessarily occur in the early stages, but it usually increases as the disease progresses. Deficits in attention, executive function, and visuospatial ability may be especially prominent. The core features of DLB include fluctuating levels of attention and alertness, well-formed and detailed recurrent visual hallucinations, which are generally present in the early course of the disease, and spontaneous features of parkinsonism, such as bradykinesia and rigidity (Reference McKeith, Boeve, Dickson, Halliday, Taylor and Weintraub45, Reference Postuma, Berg, Stern, Poewe, Olanow and Oertel46). Individuals with DLB are likely to present with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behaviour disorder, severe neuroleptic sensitivity, and low dopamine transporter uptake in the basal ganglia as demonstrated by SPECT or PET imaging. Other common features include repeated falls and syncope; transient, unexplained loss of consciousness; severe autonomic dysfunction (such as orthostatic hypotension and urinary incontinence); hallucinations in other modalities; systematised delusions; and depression. The pathology of the condition is marked by the presence of Lewy bodies and neurites, with the anatomical distribution of Lewy bodies rather than the severity of Lewy pathology more likely to determine the clinical presentation of the condition (Reference Kon, Tomiyama and Wakabayashi47).
Frontotemporal dementia has an insidious onset and slow progression (48). Individuals with the condition exhibit early loss of personal awareness, such as neglect of personal hygiene and grooming; social awareness, including lack of social tact and misdemeanours such as shoplifting; and signs of disinhibition, which include unrestrained sexuality, violent behaviour, inappropriate jocularity, and restless pacing. They may have utilisation behaviour, exploring objects in the environment unrestrainedly. Affected individuals may also show mental rigidity and inflexibility. Hyperorality, such as dietary changes, excessive smoking, and alcohol consumption, is common with the condition. Individuals may also demonstrate stereotyped and preservative behaviours, including wandering and mannerisms, such as clapping, singing, and dancing, and ritualistic preoccupations, such as hoarding, toileting, and dressing. They may be easily distracted, impulsive, and impersistent and lack insight into the altered condition due to a pathological change in their own mental state. Individuals with FTD may also have speech disorders. Examples might be progressive reduction of speech, including aspontaneity and economy of utterance; stereotypy of speech, such as repetition of a limited repertoire of words, phrases, or themes; echolalia and perseveration; and late mutism. The pathologic feature of the condition is focal brain atrophy in the frontal and/or anterior temporal lobes, while the other areas are relatively spared. The condition shows a slow onset and gradual progression over months or years (Reference Arvanitakis, Shah and Bennett49).
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
A number of established criteria are available to guide dementia diagnosis and subtyping (35), which are listed in Box 1.1 for readers who wish to read further. For the diagnosis of dementia, a few key points (Reference Arvanitakis, Shah and Bennett49) are highlighted here:
the diagnosis of dementia requires a history of
cognitive decline and
impairment in daily activities; and
it necessitates
corroboration from a knowledgeable informant and
a cognitive examination.
Box 1.1 Criteria for Diagnosing and Subtyping Dementia: Further Reading
General Diagnostic Criteria
Mild Cognitive Impairment
‘The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging – Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease’ (Reference Albert, DeKosky, Dickson, Dubois, Feldman and Fox55)
Alzheimer’s Disease
NINCDS-ADRDA criteria: The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging – Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease (Reference McKhann, Knopman, Chertkow, Hyman, Jack and Kawas56)
Vascular Dementia
Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and Association Internationale pour la Recherche et l’Enseignement en Neurosciences (NINDS‐AIREN) International Workshop (Reference Roman, Tatemichi, Erkinjuntti, Cummings, Masdeu and Garcia57)
Frontotemporal Dementia
Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants (Reference Gorno-Tempini, Hillis, Weintraub, Kertesz, Mendez and Cappa58).
Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia (Reference Rascovsky, Hodges, Knopman, Mendez, Kramer and Neuhaus59)
Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium (Reference McKeith, Boeve, Dickson, Halliday, Taylor and Weintraub45)
Cognitive decline refers to a decline from the person’s own previous level of function, which is why corroboration is needed. With many of the cognitive screening tests, if done only cross-sectionally (i.e., once), the scoring against locally validated cut-off scores essentially provides only a statistical reference for how likely or unlikely a person’s performance is ‘normal’ compared with his/her peers, without giving information on the decline. It should also be noted that decline can be present in cognitive domains other than memory and learning, including executive function, attention, language, perceptual-motor, and social cognition.
The criteria for dementia differ from those for mild cognitive impairment: for mild cognitive impairment, the cognitive decline has yet to significantly impair the person’s independence in daily living. For people with self-experienced cognitive decline with normal performance on standardised cognitive tests, the category ‘subjective cognitive impairment’ (Reference Jessen, Amariglio, Buckley, van der Flier, Han and Molinuevo50) can be considered. While there are debates over their clinical significance, subjective complaints in primary care settings may predict future dementia and should be taken seriously (Reference Numbers, Crawford, Kochan, Draper, Sachdev and Brodaty51).
Work-up and further history are needed to determine the possible aetiology of dementia (Reference Arvanitakis, Shah and Bennett49); some may be potentially treatable or reversible (such as depression, which has been referred to as ‘pseudodementia’; see (Reference Brodaty and Connors52) for a review of the concept). These work-ups (see Chapter 4) include the following:
neurological, general medical, and family history;
physical examination of neurological signs and pertinent systemic signs;
neuropsychological testing;
laboratory testing, including thyroid function and vitamin B12;
brain imaging if needed (e.g., to exclude other abnormalities such as a brain tumour).
Staging
The manifestation of Alzheimer’s disease varies depending on the disease stage. Several clinical criteria have been developed to assess dementia severity, and some of the more widely used criteria are the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) (60), the Global Deterioration Scale (GDS) (61), and the Functional Assessment Staging (FAST) in Alzheimer’s Disease (Reference Reisberg62, Reference Sclan and Reisberg63). In the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, individuals may present with memory impairments that interfere with daily activities, especially decreased knowledge of current and recent events. Orientation to time and place, as well as recognition of familiar people and faces, would be relatively intact; they may be able to travel to familiar places, but may have difficulty with time relationship. People with early Alzheimer’s disease may have difficulty solving problems and engaging in abstract thinking about similarities and differences between things, although they are often intact in social judgements. In terms of community affairs, they may need some assistance in activities such as work, shopping, volunteering, or engaging in social groups. Even though impairments at this stage often remain mild, there can be obvious dysfunction at home, and the person may have given up more difficult or complicated chores, hobbies, and interests. They are, however, often still capable of personal care, although prompting may be needed.
In the moderate stage, individuals may show obvious memory impairments, with newly learned materials rapidly lost and only highly learned information retained. For example, people with moderate Alzheimer’s disease may not recall an address or telephone number they have been using for many years, forgetting the names of their grandchildren or the high school they graduated from. Disorientation to date, time, and place is common at this stage, and people tend to have severe difficulty with time relationship. The ability to solve problems and judge similarities and differences between things, as well as social judgement, can be severely impaired. Although engaging in community affairs independently is unlikely at this stage, people with moderate Alzheimer’s disease can be well enough to attend functions and events outside the home. At home, they may only be able to do simple chores and have very restricted interests. Regarding personal care, many require no assistance with toileting and eating, but may exhibit difficulty choosing proper clothing to wear.
In the severe stage, individuals would have severe memory impairment, with only fragments of memory remaining. They may be unaware of their surroundings and are oriented towards people only. While they may be able to distinguish familiar people from unfamiliar ones, they may occasionally forget the names of close family members such as their spouse. People at this stage are often unable to make a sound or safe judgement, solve problems, or engage in community affairs. They may also be too ill to be taken to events outside the home. People at this stage of Alzheimer’s disease would be unable to function at home and require much assistance with personal care, including toileting and feeding. All verbal abilities are lost at this advanced stage, with only unintelligible utterances and rarely some pieces of words and phrases produced.
Communicating Diagnosis
It is not an uncommon practice to avoid direct and clear communication of the diagnosis, perhaps out of concerns for preserving hope; however, it would also compromise understanding and future planning (Reference Dooley, Bass and McCabe64), affecting the person’s opportunities to getting proper support, such as early interventions that can maintain cognitive function and prolong community living (65).
Communication of the diagnosis should be handled with sensitivity, considering individual needs. An important point to note in the process is to explain in easy-to-understand language the symptoms, what to expect, and what can be done. It is good practice to allow time for processing the information and give written information with contact details of the service for reference.
Post-diagnostic Management
There is currently no cure or widely available disease-modifying treatment to slow or stop the progression of dementia; however, treatments that may change the experience of dementia by temporarily improving the symptoms are available (Reference Livingston, Sommerlad, Orgeta, Costafreda, Huntley and Ames34). Drug treatments for cognitive symptoms of dementia have been approved for Alzheimer’s disease, DLB, and Parkinson’s disease dementia. They target biochemical abnormalities due to neuronal loss but do not alter the underlying neuropathology or its progression. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs: donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine) have proven yet modest effects in maintaining or delaying cognitive decline (Reference Birks66–Reference Prince, Bryce and Ferri68). Donepezil and rivastigmine also have a positive effect on hallucinations in DLB. Memantine has a smaller effect in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease (Reference Livingston, Sommerlad, Orgeta, Costafreda, Huntley and Ames34). For people with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, the intervention goals include delaying cognitive decline, optimising functioning, and minimising secondary morbidity. It should be noted that depending on local regulations, primary care physicians may or may not be allowed to prescribe dementia drugs, which can have an effect on their engagement level in dementia work-up (Reference Yaman69).
The effects of psychosocial interventions on improving cognitive symptoms of dementia have been reviewed (70). These include cognitive stimulation, cognitive training, cognitive rehabilitation, reality orientation, combined cognitive and exercise programmes, and computer-based cognitive interventions. Cognitive interventions can be categorised as follows (71):
Cognitive stimulation is the engagement in activities and discussions with the aim of enhancing general cognitive and social functioning;
Cognitive training is guided practice on a set of standard tasks designed to improve specific cognitive function, such as working memory;
Cognitive rehabilitation is an individualised approach where personal goals are identified and the therapist works with the person and his or her family to create strategies to address the goals.
In people with mild to moderate dementia, more consistent evidence is available for cognitive stimulation, with group-based cognitive stimulation therapy (CST) (Reference Woods, Aguirre, Spector and Orrell72) and a range of activities tailored to the person’s preferences being recommended in clinical guidelines (35). Other strategies such as reminiscence therapy, cognitive rehabilitation, or occupational therapy are also recommended for consideration (35). Music for agitation (Reference Pedersen, Andersen, Lugo, Andreassen and Sutterlin73), physical exercise for fitness (Reference Lamb, Sheehan, Atherton, Nichols, Collins and Mistry74), social interaction, a healthy diet, adequate sleep, safety, advance directives, and advance care planning (Reference Arvanitakis, Shah and Bennett49) are potential strategies. As for carers, multicomponent carer support programmes such as Resources for Enhancing Alzheimer’s Carer Health (REACH) (Reference Gitlin, Belle, Burgio, Czaja, Mahoney and Gallagher-Thompson75) and STrAtegies for RelaTives (START) (Reference Livingston, Barber, Rapaport, Knapp, Griffin and King76) are evidence-based, time-limited interventions that can improve carer outcomes such as burden and quality of life, as well as the distressed behaviours and neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia.
The multitude of post-diagnostic interventions and care available and diverse individual situations require individual care plans and care coordination. The actual practice of care planning varies (see Section 1.5 for an example of a ‘Certified Dementia Care Planner’ in Hong Kong, with training content developed with support from Alzheimer’s Disease International); in general, a named professional would be responsible for assessing the person’s needs, strengths, and preferences; providing information about services; and developing (in collaboration with the family where appropriate), reviewing, and evaluating the individual care plan (35). As with a comprehensive geriatric assessment (77), in dementia an individual care plan is a tool used as a form of integrated care, where the care plan is formulated to address the issues of concern to the person and his/her family members and carers, based on assessments that may cover physical/functional, psychosocial/behavioural, carer support needs, and environmental factors. The coordinated services may include the above pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, as well as legal and financial advice, education, and carer support groups.
1.4 Integrated Health and Social Care: Rationales and Evidence
Models of Dementia
In the primary care models and dementia management approaches described above, both biological and psychosocial aspects are emphasised. This reflects a shift over the past decades in the conceptualisation of dementia: from a focus on a medical perspective, moving to a dialectical view, and more recently to an integrated biopsychosocial model of dementia.
From a medical perspective, dementia is a condition caused by neurological problems, and management should therefore focus on biological factors (Reference Lyman78). In the 1990s, Tom Kitwood introduced the concept that dementia is a manifestation of an interaction between neuropathology and psychological factors (including personality, biography, and social psychology), putting an emphasis on ‘personhood’ and person-centred care (the ‘dialectic model’) (Reference Kitwood79). This view has revolutionised the way people living with dementia are being cared for. Building on this theoretical foundation, the biopsychosocial model expanded the factors to include mental stimulation, sensory stimulation, environment, life events, and mood in the manifestation of dementia (80).
A range of interventions targeting each of the tractable factors can be effective dementia management strategies, based on the biopsychosocial model, to reduce excess disability and promote independence. Table 1.1 lists some suggested factors and interventions (modified from (80)). An integrated health and social care service allows for more efficient delivery of these psychosocial and biological interventions.
Service Integration: The Role of Primary Care
In countries where health and social care services are delivered by different organisations and monitored by different governmental departments/bureaus, provision and coordination of these psychosocial and biological interventions for people living with dementia can be challenging. Service fragmentation and overlap can result in gaps and inefficient resource use. Integrated care has been proposed in these situations for delivering services and implementing complex interventions (81), to enhance system efficiency while benefiting the person requiring care (82).
The integration of healthcare and social care can occur at various levels and care settings. In the healthcare system, it could range from general practice to a specialist clinic in the community, from subacute care to acute care; within social care, it could include community aged care services (e.g., social centres), home care, day care centres, and long-term care facilities. In people with mild dementia, community-based integrated health and social care may slow deterioration, maintain quality of life, and delay institutionalisation (Reference Maki and Yamaguchi83, Reference Michalowsky, Xie, Eichler, Hertel, Kaczynski and Kilimann84). While existing models of integration vary in the involvement of primary and specialist care, an emphasis on early detection and integration into general health and social care has been recommended (Reference Draper, Low and Brodaty85).
Depending on the dementia stage, integration of health and social care at the primary care level can represent an ideal option. Figure 1.1 illustrates a possible arrangement of services by dementia stage.
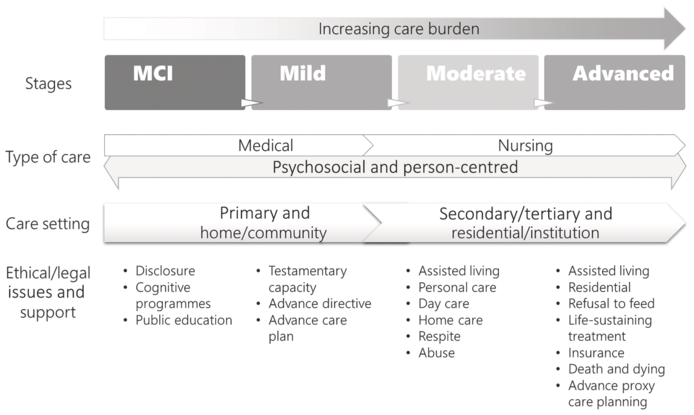
Figure 1.1 Possible service arrangements by dementia stage: An illustration
In this illustration, throughout the dementia trajectory, primary care (including primary health and social care) can serve as a base to provide early intervention services in the earlier stages of the illness, and signposting and transitioning to secondary and tertiary care as needs arise. Especially in simple, uncomplicated early Alzheimer’s disease, with a relatively predictable disease trajectory, primary care could be the starting point for outreach detection, delivery of pharmacological and non-pharmacological intervention, and advance care planning to ensure a continuum of care. Here, the disease journey begins with early diagnosis and psychosocial support that is culturally appropriate. Families are supported by a care planner who can advise on the different needs of the person with dementia and the carer. At different dementia stages, the family is advised in advance on the next stage of management: as Alzheimer’s disease has a predictable trajectory, according to the FAST staging, in the moderate stage the person would, for example, present with dressing apraxia and need more assistive care for getting dressed, proceeding to needing assistance in bathing and then in toileting. As s/he enters the advanced stage, more attention is needed for mobility and swallowing problems. Home care and the prospect of institutionalisation should therefore be discussed.
With an integrated care service, ethical and legal considerations are also taken care of. During the early stages, the will, powers of attorney, and advance directives are discussed, and consensus from the person and the family is gained. At the other extreme, end-of-life care and the related ethical issues need to be considered and discussed. Advance care planning is needed, considering the typical trajectory of Alzheimer’s disease and the multidimensional needs at different stages. As regular interactions among the person living with dementia, the family, and the care provider are needed, a care planner in an integrated health and social care service can act as a moderator to coordinate all care issues. This arrangement has the potential to improve quality of life, while saving scarce secondary and tertiary care resources. An example of an integrated primary health and social care service is given in Section 1.5.
1.5 Lessons Learned from 15 Years of Early Intervention Service
Service Context and Design
In Hong Kong, an early detection scheme (EDS) was developed in 2005 by the Hong Kong Alzheimer’s Disease Association as a community-based, territory-wide programme to provide early intervention for people with suspected dementia (Reference Tang, Wong, Ng, Kwok, Lee and Dai86). The service was originally developed out of a need for earlier dementia diagnosis, especially Alzheimer’s disease, to cut down the waiting time for establishing a diagnosis and to provide timely health and social care services.
As with many Asian areas, Hong Kong is one of the most rapidly ageing societies in the world. With a population of approximately 7 million, over 100,000 people were living with dementia in 2009, a number that is projected to reach over 330,000 by 2039 (Reference Yu, Chau, McGhee, Cheung, Chan and Cheung87). The diagnostic rate in Hong Kong has been low, at 11 per cent, based on an earlier study (88). While the low diagnostic rate could be related to low awareness among people needing help, provider factors such as service accessibility (e.g., long waiting times for the first diagnostic consultation with a public memory clinic) are also barriers to help-seeking (Reference Ng, Leung, Cai and Wong89).
The EDS is accessible by open referral. People with suspected dementia and/or their carers can self-refer to arrange an assessment by trained social care professionals, such as occupational therapists and social workers, who would gather necessary information (such as history and complaints) and conduct a series of locally validated assessments that include clinical, neuropsychological, functioning, and mood measures (see Chapter 4 for details). The tools were selected balancing psychometric properties and appropriateness for use in service, including applicability in older people with no or very limited formal education (common in Hong Kong). By facilitating early help-seeking, which is linked with milder symptoms (Reference Tang, Wong, Ng, Kwok, Lee and Dai86), the EDS serves as a useful component of a dementia triage system (Reference Tang, Wong, Ng, Kwok, Lee and Dai86, 90) to promote early intervention.
Before 2015, people initially identified through EDS as probably having dementia would be referred to specialists for diagnosis. The barrier of long waiting times for diagnostic consultation remained: this contradicts the recommendation in the World Alzheimer’s Report (Reference Prince, Comas-Herrera, Knapp, Guerchet and Karagiannidou1) that the majority of cases of early Alzheimer’s disease can be diagnosed with treatment initiated by primary care, with only a small proportion requiring referral for secondary care. An enhanced, shared-care model was piloted (‘Project Sunrise’), with the following additional features:
training and support for primary care physicians in dementia diagnosis and management by an experienced specialist (geriatrician) (see Box 1.2 for the training curriculum);
care planning, coordination, and family carer support by a certified dementia care planner (see Box 1.3 for training curriculum);
information-sharing between EDS and the trained primary care physicians to facilitate diagnosis and management;
rapid referral of atypical cases to other potentially appropriate services; and
provision of post-diagnostic support with day centre services and primary care physicians.
Box 1.2 Training curriculum for primary care physicians in dementia care: An example in Hong Kong
Eighteen hours of in-depth training with lectures, case demonstrations, and case sharing:
Early clinical diagnosis of dementia – core clinical features and diagnostic criteria.
In-depth understanding of Alzheimer’s dementia
Strategic pharmacological intervention for dementia
Neuropsychological assessments and multidisciplinary collaboration to facilitate the diagnostic process.
Neuropsychiatric behaviours and psychological symptoms of dementia.
Mental capacity assessments, financial planning, and legal and ethical issues.
Skills in disclosure of diagnostic results and care planning advice.
With post-training support provided by a specialist, including advice on imaging/examination ordering and feedback on diagnosis.
Box 1.3 Training curriculum for a certified dementia care planner: An example in Hong Kong
Four modules (80 hours) of training co-developed by Alzheimer’s Disease International and the Hong Kong Alzheimer’s Disease Association with support from The University of Hong Kong to equip healthcare and social service professionals with competence in assessment, care planning, management, family-caregiver support, and coordination of community resources:
This community-integrated health and social care model for dementia was designed with the aim of promoting task-shifting or task-sharing. By shifting some of the diagnosis workload to trained primary care physicians, with support from EDS, the waiting time for receiving a diagnosis among help-seekers could be cut down, with a smaller proportion of people requiring referral for secondary care. In this model, collaboration between primary and secondary care is also advocated, so that specialists provide mentorship and support for primary care physicians for complicated cases and if there is a change in the condition of the person requiring secondary care, while the primary care physician would also collaborate with the specialist for referral of appropriate cases, eventually achieving task-sharing across disciplines and between primary and secondary care.
Lessons Learned among Primary Care Physicians
Using action research, several key lessons learned were identified from this model of community-integrated health and social care involving task-shifting/-sharing with primary care, including the following:
1. Primary care physicians considered the support from social care essential: collaboration was needed for engaging the person with dementia in general practice. This seems to be true, particularly among families of lower socioeconomic status, some of whom would have otherwise opted out of receiving a diagnosis and intervention. Informational support (e.g., assessment reports) from social care has also allowed more focused consultation sessions, shortening the time requirement in a busy clinic.
2. There is a need to prepare society for the role of primary care in dementia care: a challenge noted is to engage potential patients or carers in general practice, as the public is generally unaware of/sceptical about the role of primary care physicians in dementia diagnosis and treatment.
3. Good-quality non-pharmacological interventions provided by social care (e.g., person-centred care and effective cognitive interventions) are an important consideration among primary care physicians for collaborative care. A regular feedback system with brief reports on service status (e.g., when a home visit was arranged) is desired.
4. With training and support from EDS, primary care physicians reported that diagnosing typical cases of Alzheimer’s disease is straightforward in most cases. In cases with atypical presentations, where the diagnosis is less clear or when complications arise (e.g., mood symptoms) and an expert review would be needed, primary care physicians regarded themselves as having a clear understanding of when to refer. They also expressed confidence in providing medication treatment for early dementia, considering the stable and chronic nature of Alzheimer’s disease, although a mechanism of transition to specialist care would be needed when the disease progresses or when there are complications requiring stabilisation. Comparing the expert review with the initial diagnosis made by the primary care physicians, agreement in diagnosis was observed in the majority (>80 per cent) of cases.
5. There is a need for practicum, pedagogy, and clinical guidelines for primary care physicians to help them make decisions (e.g., when an MRI is indicated) in their daily practice. Regular case conferences were considered crucial. Attachment to a few consultation sessions by specialists and continuous post-training specialist support at a low level, such as by monthly phone consultation, were considered useful in the training.
In summary, with appropriate training and an integrated health and social care service, task-shifting/-sharing of dementia care with primary care can be feasible; the key is to focus on ‘simple, uncomplicated early Alzheimer’s disease’ in such a service model. In the next two chapters, we will review cases that fall into this category, and atypical cases in comparison, to facilitate an understanding of the target population of a primary care dementia service.



