Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 November 2021
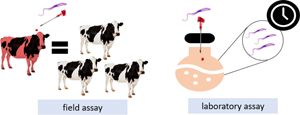
It was investigated how many cattle become infected with Trypanosoma vivax by subcutaneous (SC), intramuscular (IM) and intravenous (IV) routes, using the same syringe and needle from an animal with acute T. vivax infection. Besides, the T. vivax viability in 109 injectable veterinary drugs (antibiotics, antiparasitics, reproductive hormones, vitamin complex and derivatives, vaccines, anaesthetics, anti-inflammatory/antipyretics, antitoxics). In the field assay, four groups were performed: T01, T02 and T03 animals that received saline solution with the same syringe and needle contaminated with T. vivax via SC, IM and IV routes, respectively, and T04 control animals that received only saline solution with the same syringe and needle IV. In the laboratory, drugs had their pH measured and T. vivax viability verified. The number of cattle infected with T. vivax via SC (3/20) was lower (P ≤ 0.05) compared to via IM (9/20), which was lower (P ≤ 0.05) compared to IV (15/20). The solution pH did not influence T. vivax viability. In 44% (48/109) of the products, T. vivax remained viable regardless of time, stooding out that in 100% of oxytocins the protozoan was verified, at some evaluation times. The mean of T. vivax quantified in foot-and-mouth and brucellosis vaccines and in doramectin-based products were higher (P ≤ 0.05) than found in blood + saline solution.
Please note a has been issued for this article.