Introduction
Kochia is an invasive annual forb native to Asia, introduced into the United States at the end of the 1800s as an ornamental from Europe (Friesen et al. Reference Friesen, Beckie, Warwick and Van Acker2009; Whitson et al. Reference Whitson, Burrill, Dewey, Cudney, Nelson, Lee and Parker2000). Kochia is widespread throughout the northwestern United States, where it is found growing in grasslands, pastures, prairies, roadsides, ditch banks, wastelands, floodplains, riparian habitats, and cultivated fields (Casey Reference Casey2009; Ou et al. Reference Ou, Thompson, Stahlman, Bloedow and Jugulam2018; Stubbendieck et al. Reference Stubbendieck, Coffin and Landholt2003). Kochia was ranked among the most serious weed species in the northwest United States due to its high rate of spread (Forcella Reference Forcella1985). Factors contributing to the distribution and troublesome nature of kochia include seed germination characteristics, high seed production, and an effective tumbleweed dispersal mechanism (Beckie et al. Reference Beckie, Blackshaw, Hall and Johnson2016; Dille et al. Reference Dille, Stahlman, Du, Geier, Riffel, Currie, Wilson, Sbatella, Westra, Kniss, Moechnig and Cole2017; Everitt et al. Reference Everitt, Alaniz and Lee1983).
Kochia is a major concern across the western United States, because it is competitive with many crop species. Features such as early-season emergence, rapid growth, and drought tolerance confer upon kochia a unique competitive ability in many western U.S. cropping systems (Friesen et al. Reference Friesen, Beckie, Warwick and Van Acker2009; Schwinghamer and Van Acker Reference Schwinghamer and Van Acker2008). In surveys by Weed Science Society of America members, kochia ranked as one of the top six most troublesome weeds of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), canola (Brassica napus L.), pulse crops, sugar beet, corn, and spring grains (Van Wychen Reference Van Wychen2016, Reference Van Wychen2017). Yield loss from kochia competition has been documented in many crops, including oats (Avena sativa L.), wheat, sugar beet, sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.), and alfalfa (Calpouzos et al. Reference Calpouzos, Lee and McNeal1980; Friesen et al. Reference Friesen, Morrison, Rashid and Devine1993; Lewis and Gulden Reference Lewis and Gulden2014; Manthey et al. Reference Manthey, Hareland, Zollinger and Huseby1996; Mesbah et al. Reference Mesbah, Miller, Fornstrom and Legg1994). In addition to these competitive traits, kochia is adapted to a variety of common agricultural practices. For example, kochia is very responsive to nitrogen and thrives under different tillage practices and crop rotations (Anderson et al. Reference Anderson, Stymiest, Swan and Rickertsen2007; Friesen et al. Reference Friesen, Beckie, Warwick and Van Acker2009; Lugg et al. Reference Lugg, Cuesta and Norcross1983; Miller Reference Miller1986; Watson et al. Reference Watson, Derksen, Thomas, Turnbull, Blackshaw, Leeson, Legere, Van Acker, Brandt, Johnston, Lafond and McConkey2001). Therefore, effective kochia management is a priority in most crop production systems.
Herbicides are a major component of kochia control programs, particularly in commercial crop production system. The outcome of relying on herbicides, combined with kochia characteristics such as high genetic diversity among and within populations, has led to weed population shifts and to the evolution of herbicide-resistant populations (Friesen et al. Reference Friesen, Beckie, Warwick and Van Acker2009; Godar et al. Reference Godar, Stahlman, Jugulam and Dille2015; Mengistu and Messersmith Reference Mengistu and Messersmith2002; Sbatella and Wilson Reference Sbatella and Wilson2010; Wilson et al. Reference Wilson, Miller, Westra, Kniss, Stahlman, Wicks and Kachman2007). Kochia has evolved resistance to at least four herbicide sites of action, including acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitors, synthetic auxins, photosystem II (PSII) inhibitors, and 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) inhibitors (Bell et al. Reference Bell, Nalewaja and Schooler1972; Foes et al. Reference Foes, Liu, Vigue, Stoller, Wax and Tranel1999; Heap Reference Heap2019; Saari et al. Reference Saari, Cotterman and Primiani1990). Kochia populations resistant to PSII herbicides have been reported in Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, and Wyoming (Heap Reference Heap2019). EPSPS-inhibitor-resistant populations were also found in Colorado, Idaho, Kansas, Montana, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Oregon, and Wyoming. In addition, populations resistant to synthetic auxins have been reported in Colorado, Idaho, Kansas, Montana, Nebraska, and North Dakota (Heap Reference Heap2019). ALS-inhibitor-resistant kochia populations have been reported in all the states listed above and in Michigan, New Mexico, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Wisconsin, and Washington. In addition to this widespread resistance, resistance to herbicides with multiple sites of action has been reported for kochia populations in several states (Heap Reference Heap2019; Kumar et al. Reference Kumar, Jha, Jugulam, Yadav and Stahlman2019). At least one population in Kansas has been shown to be resistant to all four of these herbicide sites of action (Varanasi et al. Reference Varanasi, Godar, Currie, Dille, Thompson, Stahlman and Jugulam2015).
Glyphosate-resistant (GR; EPSP synthase inhibitor) kochia is widespread in the Great Plains (Kumar et al. Reference Kumar, Jha, Jugulam, Yadav and Stahlman2019). Surveys conducted from 2011 to 2014 showed that 39% to 60% of kochia populations in eastern Colorado were resistant to glyphosate (Westra Reference Westra2016). Although it is unclear what proportion of crop fields in each state have confirmed cases of GR kochia, there have been 13 cases of GR kochia in cereals, including corn, wheat, and sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] in 12 states, 4 cases in soybean in 4 states, and 3 cases in sugar beet in 3 states (Heap Reference Heap2019). GR kochia is especially concerning to farmers in the Central and Northern Great Plains region, because glyphosate is relied upon heavily in many cropping systems. GR corn and soybean are common rotational crops in the eastern and southern part of the region (Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota) for both irrigated and rainfed conditions. Glyphosate-resistant sugar beet is grown under irrigation in several states in the United States, including Wyoming, Colorado, and Nebraska, and kochia is among the most troublesome and difficult to control weeds in sugar beet. Winter wheat–fallow is a common rotation in nonirrigated portions of this region. Glyphosate remains the primary weed control tool in GR crops (Kniss Reference Kniss2018) and in the fallow and postharvest phase of the wheat–fallow rotation; therefore, alternatives to glyphosate are needed to manage GR kochia populations in all of these cropping systems. The objective of this study was to evaluate non-glyphosate herbicide options for kochia control that are available in commonly grown crops and fallow fields in the Central and Northern Great Plains.
Materials and Methods
Field studies (a total of 10 sites) were conducted across five states (Lingle, WY; Fort Collins, CO; Hays, KS; Scottsbluff, NE; and Brookings, SD) over 2 yr (2010 and 2011). Soils of the experimental sites were loam in Brookings and Fort Collins, silty clay loam in Hays, silt loam in Lingle, and sandy loam in Scottsbluff. The pH of the soils ranged from 6.8 to 8.2. Kochia populations at all study sites were glyphosate susceptible. Herbicide treatments were applied to a fallow site with no crop established to evaluate herbicide efficacy while avoiding the confounding factor of differences in crop competition; kochia control was a function of herbicide treatments only. Three non-glyphosate herbicide treatments were chosen for each of five common cropping scenarios in the region: winter wheat, fallow, corn, soybean, and sugar beet. Herbicide treatments were chosen based on predicted efficacy on GR kochia, cost, and crop-rotation concerns. Although not exhaustive, the chosen herbicide programs were a representative sample of possible herbicide combinations that would provide the best kochia control within each crop of interest (Table 1). A glyphosate treatment and a nontreated control were also included at each experimental site for a total of 17 treatments per site.
Table 1. Herbicide treatments used in this study.

a Monsanto Company, St Louis, MO.
b Bayer CropScience, Research Triangle Park, NC.
c DuPont, Wilmington, DE.
d BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC.
e FMC, Philadelphia, PA.
f Syngenta, Greensboro, NC.
g AMVAC Chemical Corporation, Los Angeles, CA.
h Valent, Walnut Creek, CA.
i Dow AgroSciences, Indianapolis, IN.
Visual estimates of kochia control were made approximately 30 d after the final POST herbicide was applied using a scale of 0 (no visible kochia injury or apparent density reduction) to 100 (complete death or absence of kochia in the plot). Aboveground kochia biomass production was measured by cutting all kochia at the soil surface in a 1- to 3-m2 area per plot (depending on location) approximately 60 d after the final POST herbicide was applied at all sites, except Kansas in 2011 or South Dakota in both years (biomass was not collected at those three sites).
Data analyses were performed in R statistical software v. 3.4.4 (R Core Team 2018) using the lmer and glmer functions in the lme4 package (Bates et al. Reference Bates, Mächler, Bolker and Walker2015). Visual estimates and biomass production were analyzed using a mixed-effects model, in which crop scenario was considered a fixed effect, and experimental site (combination of state and year) and herbicide treatment within a crop scenario were considered random effects. This approach was used because the herbicide treatments (Table 1) were considered a representative sample of kochia control that could be possible within each crop scenario of interest, and the main interest was whether GR kochia could be controlled adequately with herbicides within each crop scenario. Herbicide treatments within each crop scenario were then compared to determine whether there were differences between herbicide programs within a crop scenario. For this comparison, a similar mixed-effects model was used, but herbicide treatment was considered a fixed effect. Post hoc Tukey-adjusted pairwise treatment comparisons were performed at an alpha of 0.05 using the emmeans package (Lenth Reference Lenth2018).
Results and Discussion
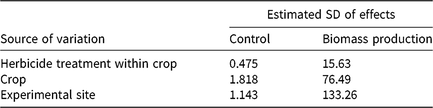
Experimental site explained more variation in control estimates compared with herbicide treatment within the crop scenario; the crop scenario for which herbicide treatments were registered explained the greatest amount of kochia control variance (Table 2). This suggests that the environment (and possibly kochia biotype) could have a great influence over kochia control. Experimental site explained more of the variance in kochia biomass production than either crop or herbicide within a crop (Table 2). Kochia biomass production is limited in nonirrigated fallow systems by soil water availability, which was expected to differ between sites.
Table 2. Variance components for crop, herbicide within crop, and experimental site for kochia control and kochia biomass production.
The five states (Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota) where the studies were conducted were expected to have substantially different environmental conditions, especially temperature and humidity, which are known to affect weed control with herbicides. For example, warmer temperatures can improve herbicide absorption and efficacy (Ganie et al. Reference Ganie, Jugulam and Jhala2017; Schultz and Burnside Reference Schultz and Burnside1980). However, kochia control with glyphosate and dicamba can be reduced at elevated (32.5/22.5 C day/night) temperatures (Ou et al. Reference Ou, Thompson, Stahlman, Bloedow and Jugulam2018). Ou et al. (Reference Ou, Thompson, Stahlman, Bloedow and Jugulam2018) recommended that for best control, glyphosate and dicamba must be applied at day/night temperatures around 25/15 C. Herbicide tolerance can also differ among susceptible weed populations. For example, a 2.8- to 4.2-fold difference in glyphosate susceptibility has been demonstrated among non-resistant common lambsquarters (Chenopodium album L.) accessions (Coburn Reference Coburn2017).
One of the challenges in weed management is dealing with the often-unpredictable variability caused by environmental or biological differences between sites. With the herbicide programs selected, those registered for corn and soybean demonstrated less variability in kochia control compared with fallow, wheat, and sugar beet (Figure 1). This suggests that crop choice is at least as important as herbicide choice within a crop when developing recommendations for GR kochia control; and in fact, crop explained more variance in kochia control compared with either experimental site or herbicide within a crop (Table 2). The potential for kochia control failure was relatively low for corn, regardless of herbicide program (median kochia control = 98%), whereas there was no herbicide program evaluated in sugar beet that provided greater than 86% control at any site, with a median kochia control of 39% across all sites (Figure 1). Thus, effective long-term GR kochia management in sugar beet will likely depend on rotating with crops such as corn and soybean, for which effective herbicides are available. Long crop-rotation restrictions will prove challenging, as only one corn herbicide program and one soybean herbicide program evaluated in this study would allow planting of sugar beet the following year.
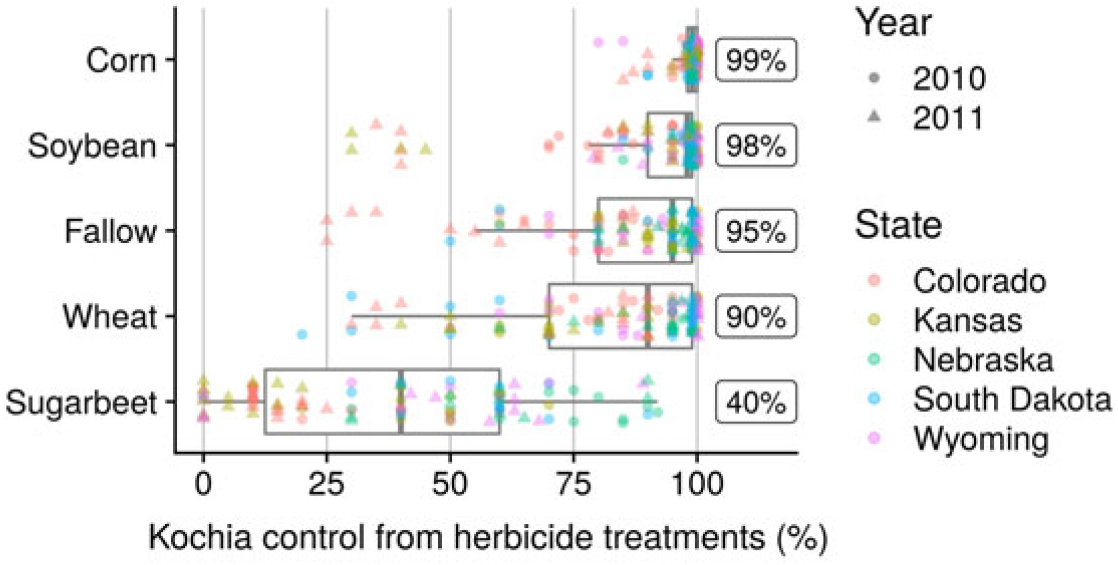
Figure 1. Kochia control ratings 30 d after final application of herbicide treatments labeled for corn, soybean, fallow, wheat, and sugar beet. Each point represents one plot at one site in one year. Numbers next to box plots are the median kochia control from herbicide treatments registered for each crop. Individual herbicide treatments are described in Table 1.
Herbicide choice within a crop influenced visually assessed kochia control in soybean, wheat, and fallow, but not in corn or sugar beet (Supplementary Table 1; Figure 2). Kochia control with herbicides currently labeled for use in sugar beet averaged 32% across locations (Table 3), and the biomass produced was 2- to 8-fold greater following sugar beet herbicides than the biomass measured in other crop herbicide treatments (Table 3). This was expected, because sugar beet is one of the crops with the fewest herbicides available, and poor kochia control in conventional sugar beet was a primary factor in the rapid and widespread adoption of GR sugar beet (Fernandez-Cornejo et al. Reference Fernandez-Cornejo, Wechsler and Milkove2016; Kniss Reference Kniss2010). Thus, the evolution of GR kochia populations is likely to have the greatest impact on sugar beet production among the cropping systems considered in this research.
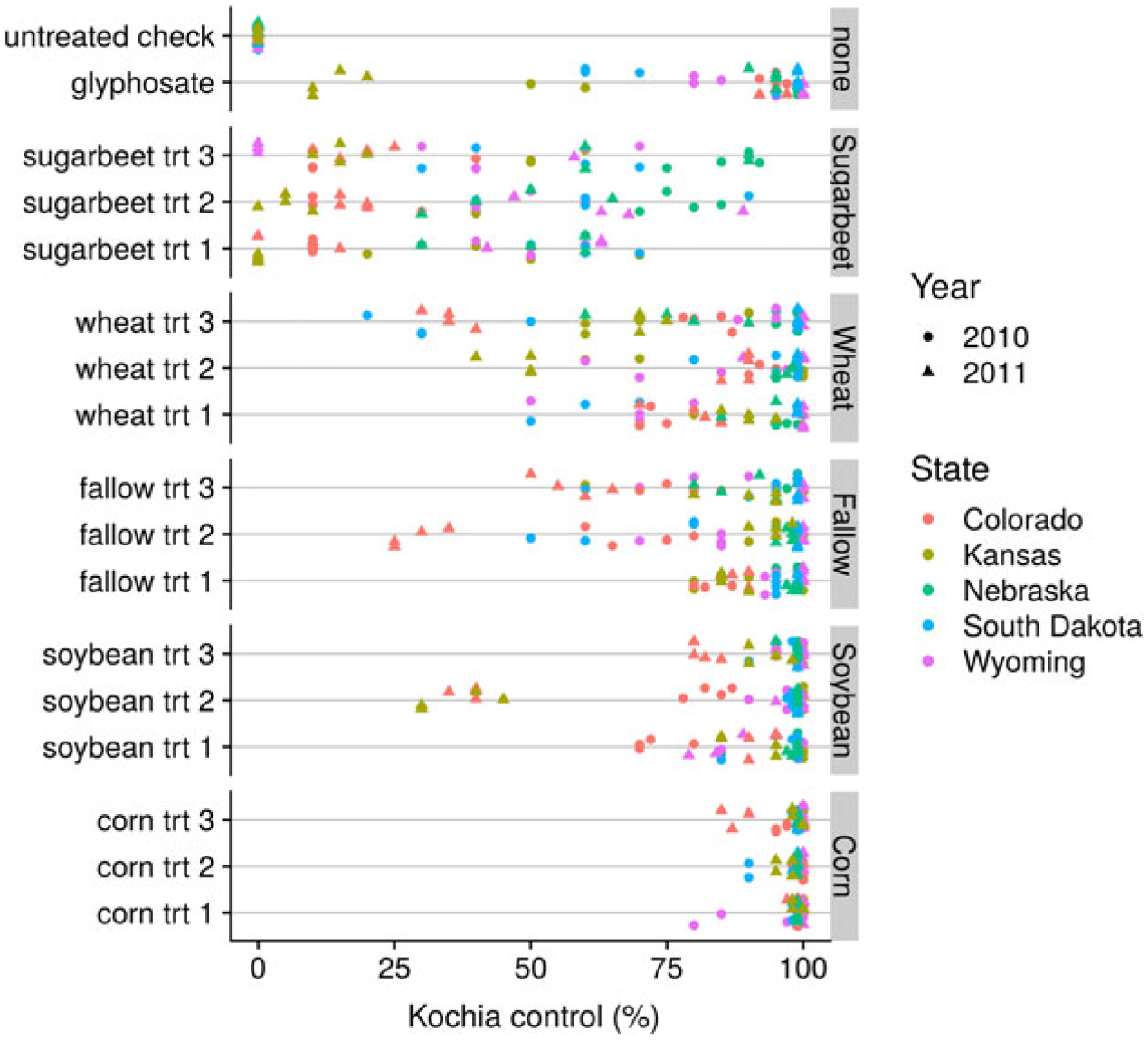
Figure 2. Kochia control provided by each herbicide treatment registered for use in five different crop scenarios (corn, soybean, fallow, wheat, sugar beet) across five states and 2 yr. Each point represents the visible kochia control estimate 30 d after final herbicide application in one plot. Individual herbicide treatments are described in Table 1.
Table 3. Kochia control and biomass production estimated marginal means as affected by herbicide treatments registered for use in five different crop scenarios.a
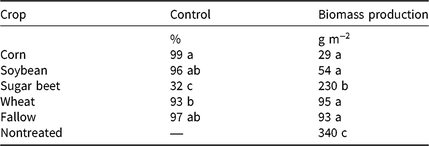
a Estimated marginal means within a column followed by the same letter are not significantly different according to Tukey-adjusted pairwise comparisons (alpha = 0.05).
Conversely, there are diverse groups of herbicides registered for use in the other crop scenarios in this analysis, making it possible to select herbicides with better kochia control efficacy. This was especially true for corn and soybean herbicide treatments, for which median kochia control across experimental sites was greater than 90% (Figure 1), and kochia biomass was reduced by more than 84% (Table 3) compared with the nontreated. The corn and soybean herbicide treatments included combinations of PRE plus POST herbicide applications. The PRE herbicides used in corn and soybean have been shown to provide good kochia control. For example, acetochlor + atrazine provided 100% kochia control for up to 8 wk after treatment (Kumar and Jha Reference Kumar and Jha2015), and PRE application of sulfentrazone and flumioxazin in GR soybean provided 81% to 92% and 88% to 98% kochia control, respectively, within 10 wk after treatment (Hulse Reference Hulse2012).
This work has shown that the selected herbicides for the corn scenario provided the most efficacious and consistent control of kochia. But it is important to note the presence of crops would have further reduced kochia density and biomass production in most of the crop scenarios we evaluated, especially corn, soybean, and wheat. Kochia is an early-emerging annual weed, so crop planting date influences kochia population and density. A crop such as winter wheat that is established before kochia emerges will have a competitive advantage, and kochia would likely have been reduced further by wheat herbicides if a wheat crop were present. Previous research in Montana, Wyoming, and Nebraska has shown crop rotations with wheat can significantly reduce kochia density and seed production (EM Mosqueda et al., unpublished data). Likewise, in corn and soybean, at least some of the kochia would be controlled during field preparation (preplant burndown herbicides or tillage), and this could further reduce kochia density to be controlled with PRE and POST herbicides.
In contrast, a majority of kochia seeds emerge after sugar beet is planted, and sugar beet is a poor competitor with kochia, because it is a low-stature rosette-forming crop, exacerbating poor kochia control provided by available herbicides. Corn, soybean, and wheat have much denser canopies forming early in the growing season, making them good competitors with kochia. In a previous study, inclusion of competitive crops (corn or barley [Hordeum vulgare L.]) and a late-planted crop (dry bean [Phaseolus vulgaris L.]) reduced kochia density by 98% (Lim et al. Reference Lim, Mosqueda, Jha, Kniss, Sbatella and Lawrence2018). Thus, in managing GR kochia, the choice of crop is very important. This explains why diverse crop rotations and effective herbicide mixtures are a good strategy for kochia control.
Supplementary material
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/wet.2019.48
Acknowledgments
Partial funding for this research was provided by Monsanto Company, and Monsanto employees were involved in the design of this research. In addition, funding has been previously provided to the University of Wyoming, Colorado State University, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, South Dakota State University, and Kansas State University in support of the authors’ research programs by one or more of the following companies that produce and have financial interests in the herbicides used in this research: Bayer CropScience, DuPont, BASF, FMC, Syngenta, AMVAC Chemical Corporation, Valent, and Dow AgroSciences; these companies were not involved in this research.







