The South Korean Twin Registry (SKTR) is an ongoing nationwide volunteer registry of South Korean twins and their families. The general goal of the SKTR is to understand the interplay of genetic and environmental influences on psychological and mental health traits in South Koreans. Since its inception, multiple cross-sectional twin studies that span preschool age to early adulthood have been conducted (Hur, Reference Hur2002; Hur et al., Reference Hur, Shin, Jeong and Han2006, Reference Hur, Jeong, Chung, Shin and Song2013). Relative influences of genetic and shared environmental factors in many psychological, mental health and physical traits found in these studies were similar to those reported in Western twin samples, although absolute phenotypic, genetic and environmental variances were found to be different to those discovered in Western samples (Hur et al., Reference Hur, Kaprio, Iacono, Boomsma, McGue, Silventoinen and Mitchell2008), suggesting that further analyses are necessary to determine genetic and environmental etiologies of variations across human populations. Current major research issues of the SKTR include detection of environmental variables that interact with genetic factors as well as identification of the process of gene-by-environment interaction in psychological and mental health in children and adolescents. Recently, we have also begun exploring genetic influences on mental health unique to South Koreans, such as hwabyung (anger syndrome), which most Korean mental health professionals and the layperson have assumed to be environmental in origin (Hur, Choi et al., Reference Hur, Choi, Kim, Jin and Lee2018; Hur, Jin, Lee, et al., Reference Hur, Jin, Lee and Kim2019. The SKTR has been a partner contributing to the international consortiums such as the Cohort Description of Collaborative Project of Development of Anthropometrical Measures in Twins (CODATwins; Silventoinen et al., Reference Silventoinen, Jelenkovic, Yokoyama, Sund, Sugawara, Tanaka and Kaprio2019) and is ready to serve as other international collaborations to identify genetic and environmental origins of human psychological and health traits.
Recruitment Strategies
We identify twins mainly from schools, large maternity hospitals and the websites of the twins’ mothers’ clubs throughout South Korea. We ask city and provincial education offices to send our invitation letters to each school to obtain contact information (typically, telephone number) of twins interested in participation in our research. In addition, we obtain contact information about mothers of twins from large maternity hospitals. Once we receive contact information, our trained research staff telephone twins or mothers of twins, explain our research in detail and then give telephone interviews. We also advertise our research on the websites of twins’ mothers’ clubs. Typically, we attach online questionnaires to the websites and ask mothers of twins to complete the questionnaire online.
Sample and Zygosity Assessment
Table 1 presents the number of individual twins who have been participated in studies of the SKTR by age group and zygosity. Because residents in large cities in South Korea move around quite often, we have lost the contact information of twins during the past years. To supplement the registry membership, however, we have recruited new volunteer twins whenever fund is available.
Table 1. Number a of twins participated in studies of the South Korean Twin Registry by age group and zygosity
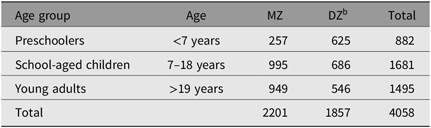
Note: MZ = monozygotic twins; DZ = dizygotic twins.
a Number of twin individuals.
b Opposite-sex DZ are included.
While opposite-sex twins in the SKTR are automatically assigned to dizygotic (DZ) twins, same-sex twins complete a three-item zygosity questionnaire to determine their zygosity. For twins under age 13, we ask mothers of twins to complete the zygosity questionnaire, whereas for twins aged 13 years or older, we ask twins to complete the zygosity questionnaire. For preschool-aged twins ascertained from maternity hospitals, information on chorionicity of twins is additionally used to determine zygosity. As indicated in Table 1, while monozygotic (MZ) twins outnumbered DZ twins in both the school-aged and young adult groups, the number of DZ twins is much greater than MZ twins in the preschooler group, which reflects recent changes of DZ twin birth rates in South Korea (Hur & Kwon, Reference Hur and Kwon2005; Hur & Song, Reference Hur and Song2009).
Measures
The instruments used for studies of the SKTR have been selected for their high psychometric properties and compatibilities with other twin studies in the world. Assessment categories of the SKTR include childhood temperament, personality, cognitive abilities, problem behaviors and mental health, family physical and psychological environment, and physical traits. To measure childhood temperament, the Emotionality, Activity, and Sociability scale (Buss & Plomin, Reference Buss and Plomin1984) has been used for mothers of preschooler twins (Hur, Reference Hur2009a; Veselka et al., Reference Veselka, Schermer, Just, Hur, Rushton, Jeong and Vernon2012). The Eysenck Personality Scale (Eysenck & Eysenck, Reference Eysenck and Eysenck1991), grit (Duckworth & Quinn, Reference Duckworth and Quinn2009) and economic behavior have been used with adolescent and young adult twins for personality assessment (Hur, Reference Hur2007a; Hur et al., Reference Hur, Jeong, Schermer and Rushton2011; Rushton et al., Reference Rushton, Ann Bons and Hur2008, Reference Rushton, Ann Bons, Ando, Hur, Irwing, Vernon and Barbaranelli2009). The Standard Progressive Matrices-Plus version (Raven, Reference Raven2008) has been used for assessment of cognitive abilities for school-aged twins. To measure problem behaviors and mental health traits, the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (Goodman, Reference Goodman1997), hostility (Koskenvuo et al., Reference Koskenvuo, Kaprio, Rose, Kesaniemi, Sara and Heikkila1988), Launey–Slade Hallucination Scale – Revised (Launay & Slade,Reference Launay and Slade1981), clinical symptoms of Personality Assessment Inventory (Morey, Reference Morey1991), Center for Epidemiological Studies-Depression scale (Radloff, Reference Radloff1977), and Maudsley Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory (Hodgson & Rachman, Reference Hodgson and Rachman1977), and hwabyung (anger syndrome), have been administered to adolescent and young adult twins (Hur, Reference Hur2006, Reference Hur2007b, Reference Hur2008, Reference Hur2009b, Reference Hur2014, Reference Hur2015; Hur et al., Reference Hur, Hwang and Chung2015; Hur, Cherny et al., Reference Hur, Cherny and Sham2012; Hur, Choi et al., Reference Hur, Choi, Kim, Jin and Lee2018; Hur & Jeong, Reference Hur and Jeong2008; Hur, Jin, Lee et al., Reference Hur, Jin, Lee and Kim2019; Hur & Rushton, Reference Hur and Rushton2007). To assess physical and psychological family environment, the Family Asset Questionnaire and the Family Adaptability and Cohesion Scale (Olson et al., Reference Olson, Portner and Lavee1985) have been administered to twins or parents of twins. For physical traits, height, weight, birth weight and Sasang constitution types have been obtained either through parental report or self-report for most twins. In addition, pubertal timing (Hur, Reference Hur2007c; Hur, Jin, & Lee, Reference Hur, Jin and Lee2019; Hur, Lee, & Jin, Reference Hur, Lee and Jin2018; Hur & Shin, Reference Hur and Shin2008; Hur et al., Reference Hur, Luciano, Martin, Boomsma, Iacono, McGue and Han2005, Reference Hur, Kaprio, Iacono, Boomsma, McGue, Silventoinen and Mitchell2008) and cold hands symptoms (Hur, Chae et al., Reference Hur, Chae, Kim, Jeong, Kim, Seo and Kim2012; Hur, Jin et al., Reference Hur, Jin and Lee2018; Hur, Yu et al., Reference Hur, Yu, Jin and Lee2018) have been collected from adolescent and young adult twins.
Future Directions
To date, the vast majority of twin studies have been conducted in Australia, Europe and the USA, although more recently, they have been extended to non-Western countries. As one of only several twin registries in Asia, the SKTR has published over 50 research papers in international scientific journals, enhancing our understanding of human population differences and similarities in genetic architectures of complex traits.
Traditionally, twins were uncommon in South Korea (Hur & Kwon, Reference Hur and Kwon2005). However, recently, the DZ twin birth rates have increased very sharply in South Korea due to the widespread use of artificial reproductive technology (Hur & Song, Reference Hur and Song2009). We thus have the potential to add a substantial number of new twins each year to the registry. In the future, we plan to investigate how genetics exert their influences on treatment outcomes and effects of intervention in problem behaviors and mental health traits in South Koreans. Additionally, efforts will be made to identify polymorphisms associated with the psychological and mental health traits in South Koreans.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank twins and their families and many research assistants who participated in the SKTR. The SKTR has been supported by National Research Foundation grants in Korea (NRF-2001-041-C00548, NRF-2008-327-B00003, NRF-2011-371-B00047), Pioneer Fund (USA) and Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine (K18092; K18095).



