No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 December 2011
Open Answer Set Programming (OASP) is an undecidable framework for integrating ontologies and rules. Although several decidable fragments of OASP have been identified, few reasoning procedures exist. In this paper, we provide a sound, complete, and terminating algorithm for satisfiability checking w.r.t. Forest Logic Programs (FoLPs), a fragment of OASP where rules have a tree shape and allow for inequality atoms and constants. The algorithm establishes a decidability result for FoLPs. Although believed to be decidable, so far only the decidability for two small subsets of FoLPs, local FoLPs and acyclic FoLPs, has been shown. We further introduce f-hybrid knowledge bases, a hybrid framework where 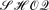 knowledge bases and FoLPs coexist, and we show that reasoning with such knowledge bases can be reduced to reasoning with FoLPs only. We note that f-hybrid knowledge bases do not require the usual (weakly) DL-safety of the rule component, thus providing a genuine alternative approach to current integration approaches of ontologies and rules.
knowledge bases and FoLPs coexist, and we show that reasoning with such knowledge bases can be reduced to reasoning with FoLPs only. We note that f-hybrid knowledge bases do not require the usual (weakly) DL-safety of the rule component, thus providing a genuine alternative approach to current integration approaches of ontologies and rules.
A preliminary version of this paper appeared in the Proceedings of the European Semantic Web Conference 20009 (ESWC2009). We extended that paper with detailed examples, a more detailed description of the algorithm and the fragment of f-hybrid knowledge bases, a detailed characterisation of simple FoLPs, as well as with proofs for all theorems (Feier and Heymans 2009).
This work is partially supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) under the projects P20305 and P20840, and by the European Commission under the project OntoRule (IST-2009-231875).