Article contents
Structural characterisation of $(11{\bar 2}0)$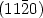 4H-SiC substrates bycathodoluminescence and X-ray topography
4H-SiC substrates bycathodoluminescence and X-ray topography
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 July 2004
Abstract
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is a wide band gap
semiconductor, having opto-electronic properties that are suitable for
many applications. Some structural defects due to crystal growth
and/or doping technologies are commonly present in the substrates
of SiC. The $(11\bar{2}0)$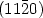 -oriented 4H-SiC bulk wafers are
particularly investigated, due to some advantages with respect to
the (0001)-Si face. One of these advantages is a better crystal
reordering during post-implantation annealing. In this paper
cathodoluminescence (CL) and X-Ray topography measurements have
been carried out in order to investigate the optical and
structural properties of commercial $(11\bar{2}0)$
-oriented 4H-SiC bulk wafers are
particularly investigated, due to some advantages with respect to
the (0001)-Si face. One of these advantages is a better crystal
reordering during post-implantation annealing. In this paper
cathodoluminescence (CL) and X-Ray topography measurements have
been carried out in order to investigate the optical and
structural properties of commercial $(11\bar{2}0)$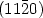 4H n+-type
substrates.
4H n+-type
substrates.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © EDP Sciences, 2004
References
- 2
- Cited by


