Sexual abuse and, to a lesser extent, physical abuse in childhood have both been associated with suicidality. Reference Santa Mina and Gallop1 These associations involve multiple mediating and moderating influences, Reference Kaslow, Thompson, Meadows, Jacobs, Chance, Gibb, Bornstein, Hollins, Rashid and Phillips2 and confounding by other types of early adversity. Consequently, identifying factors that differentiate between those who become suicidal and those who do not among people abused as children is a major research and clinical challenge. To address this challenge, we first examined rates of non-fatal suicidal behaviours in adults reporting negative and positive histories of contact sexual abuse, physical abuse or both types of abuse. We then qualified contributions of early and proximal correlates of suicide attempts, examining psychiatric, socio-demographic, personality and experiential domains. Reference Beautrais3,Reference Brezo, Paris and Turecki4 A novel contribution of this study is the examination of gender and abuse characteristics – sexual abuse severity and frequency, and abuser identity – as moderators modifying the likelihood of individuals acting on their suicidal thoughts.
Method
Study participants
In 1986–1988, families of children attending nursery school in public francophone schools in Quebec, Canada, were recruited using a multistage sampling procedure. From 4488 participating children, two subsamples were selected for follow-up. The first was a randomly selected group of 1001 boys and 999 girls: the representative subsample (R). The second was an additional group of 593 boys and 424 girls, oversampled for children exhibiting disruptive behaviours: the disruptive subsample (D). To reduce cultural heterogeneity, only children whose parents were born in Canada and whose mother tongue was French were included; 88% were of non-Hispanic White ethnicity.
The assessment schedule had three stages:
-
(a) wave 1 (childhood), yearly assessments age 6–12 years; representative sample n=2000, disruptive sample n=1017;
-
(b) wave 2 (mid-adolescence), average age 15.7 years (range 15–18); representative sample n=1233, disruptive sample n=482;
-
(c) wave 3 (adulthood), average age 21.4 years (range 19–24); representative sample n=1144, disruptive sample n=540.
Participants who had died, refused participation or could not be contacted accounted for an overall attrition rate of 44% (R 43%, D 47%). To adjust for this, we conducted multivariate analyses with and without weights, representing individual probabilities of remaining in the study conditional on variables related to attrition: mean early socio-economic adversity, which was higher in non-responders (R 0.32 v. 0.25, t (1,1893.5)=–7.410, P=0.0005; D 0.39 v. 0.32, t (1,1893.5)=–2.161, P=0.031), and male gender, as males were overrepresented among non-responders (R 50% v. 35%, χ2 1=46.05, P<0.05; D 55% v. 36%, χ2 1=36.30, P<0.05). The study was approved by the research ethics boards of the University of Montreal and McGill University. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Measures
Wave 1
Family Socio-economic Adversity Index. The Family Socio-economic Adversity Index (developed for this study) reflects the quality of the family environment. It is scored using a continuous scale based on the following measures: parental age at first child's birth, education, socio-economic status and living arrangements. Families at or below the 30th percentile in one of these areas (or non-intact families) were coded as having one adversity point. The total score is directly proportional to the level of early family adversity.
Social Behavior Questionnaire. The Social Behavior Questionnaire has 38 items measuring childhood behaviours and traits. Reference Masse and Tremblay5 We used teacher-assessed anxiousness (6 items) and aggression (13 items) at ages 6 years and 12 years.
Wave 2
Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children. Interviewers (psychology students) attended 1–1.5 days of training and a practice session in the use of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children (DISC–2), Reference Breton, Bergeron, Valla, Berthiaume and St-Georges6 using DSM–III–R criteria. Reference Robins, Cottler, Bucholtz and Compton7 Given the number of diagnoses and our interest in their collective impact, we considered disruptive disorders (attention-deficit hyperactivity, oppositional-defiant and conduct disorders), anxiety disorders (simple/social phobias, separation anxiety, panic, avoidant, overanxious and generalised anxiety disorders) and mood disorders (major depression and dysthymia) collectively.
Ideation. Pre-adolescent and adolescent suicidal ideation was assessed with one question: ‘Have you already seriously thought about suicide?’
Suicide attempts. The presence and frequency of early-onset suicide attempts over lifetime and in the past 6 months were assessed using parental/adolescent responses to a DISC–2 question from the major depression module: ‘Have you already attempted suicide?’ Either parental or self-report was sufficient for a person to be classified as an attempter.
Wave 3
Income. Adult income in the previous year was recorded.
Diagnostic Interview Schedule for adults. Interviewers (psychology students) had 1–1.5 days training and a practice session in the use of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule (DIS) for adults, based on DSM–III–R criteria. Reference Robins, Cottler, Bucholtz and Compton7 To reduce the number of statistical tests and evaluate their group impact, mood disorders (major depressive episode, mania and dysthymia) and anxiety disorders (generalised anxiety, panic and phobias) were considered collectively. Given the evidence of their independent contributions to suicidality, misuse and/or dependence on drugs, alcohol and nicotine were considered individually.
Scale for Suicide Ideation. The Scale for Suicide Ideation Reference Beck, Kovacs and Weissman8 is a 19-item scale measuring current attitudes towards living/dying, characteristics of suicidal ideation, and actualisation of contemplated attempt. Cronbach's α was 0.63.
Suicidal Intent Scale. The Suicidal Intent Scale is a 20-question instrument designed for administration to people who have attempted suicide. Reference Beck, Morris and Beck9 It assesses the ‘intensity’ of the wish to die at the most recent attempt (α=0.64).
Suicide attempts. Suicide attempt history in adults was assessed with Suicidal Intent Scale questions (‘Have you already attempted suicide?’ ‘How many attempts have you made prior to the one in question?’). Late-onset suicide attempts were those made after the age of 18 years. Repeated attempts occurred more than once according to parental or self-report. Lifetime suicide attempt status was based on both adolescent and adult assessments. Suicide attempts were defined as acts of self-injury with at least some level of suicidal intent.
Ideation. Suicidal ideation (lifetime) was a three-level composite index based on current suicidal thoughts (Scale for Suicide Ideation); lifetime suicidal thoughts in adulthood (DIS: ‘Have you ever thought of suicide?’) and pre/adolescent suicidal ideation. Individuals were classified into non-ideator (score 0), transient ideator (score 1) and persistent ideator (score 2–3) groups.
Personality pathology. The Diagnostic Assessment of Personality Pathology instrument assesses 18 personality traits, 7 of which are related to constructs studied in relation to suicidal behaviours. Reference Livesley, Jang and Vernon10 These include affective instability, anxiousness, conduct problems, cognitive–perceptive dysregulation, identity problems, insecure attachment and stimulus-seeking (α values 0.85–0.93).
Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. The Barratt Impulsiveness Scale is a 30-item instrument assessing trait impulsivity by enquiring about general ways of acting/thinking across situations (α=0.81). Reference Barratt, Spence and Izard11
Childhood physical abuse. We selected a subset of 14 questions evaluating the presence and frequency of severe/very severe physical aggression, abuse and injuries perpetrated by each parent against the respondent as a child. Reference Straus, Hamby, Boney-McCoy and Sugarman12
Childhood sexual abuse. The Childhood Sexual Abuse Scale measures incidents of sexual violence to age 18 years. Reference Felitti, Anda, Nordenberg, Williamson, Spitz, Edwards, Koss and Marks13 We selected items evaluating abusive acts involving physical contact – fondling or sexual (vaginal, anal, oral) – perpetrated by family members, school peers or staff, short-term or long-term romantic acquaintances, or strangers.
Stressful life events. Stressful life events in the past year included atypical/severe stressful events related to finances, school/work, death of a close person, illness/serious injury to self/others, parental separation/divorce, and partner/children difficulties.
Social support. The Social Support Scale measures perceived support by friends and family using 15 statements assessed with Likert scales (α=0.88). Reference Turner14
Data analyses
Univariate analyses
We first used χ2 analysis of variance (ANOVA), correcting for the number of tests (P=0.0015, 34 tests), to preselect variables for inclusion in multivariate analyses. We investigated four domains implicated in the risk of suicide attempts: socio-demographic (early socio-economic adversity, adult income and gender); psychiatric (adolescent/adult mood/anxiety diagnoses, adolescent disruptive disorder and adult nicotine, alcohol and drug dependence/misuse, adolescent/adult comorbidity and lifetime suicidal ideation); experiential (social support and stressful events); and personality traits (childhood disruptiveness, childhood/adult anxiousness; adult impulsivity, affective instability, conduct problems, cognitive–perceptive dysregulation, identity problems, insecure attachment, stimulus-seeking traits and adolescent self-esteem).
Multivariate analyses
Participants who had experienced childhood abuse were classified into three non-overlapping groups according to the type of abuse – contact sexual abuse, physical abuse, or both – and compared with their non-abused peers. Binary logistic regression was used to identify both the correlates of lifetime suicide attempt histories and odds of suicide attempts and suicidal ideas in the three abuse groups relative to the non-abuse control group. These analyses were adjusted for disruptive subsample membership (as disruptiveness is related to the impulsive–aggressive dimension linked to suicidality) and for gender, given the well-known gender differences in abuse and suicidality rates. Reference Beautrais3
We used the Nagelkerke R 2 to estimate the proportion of the total variance explained in our dependent variable (history of suicide attempts). We also used the Hosmer–Lemeshow test, a χ2-based goodness-of-fit test, to investigate the null hypothesis predicting that the identified model fits the data well. A P-value greater than 0.05 indicates that model predictions are not significantly different from the observed values, failing to reject the null hypothesis.
We first performed main effect analyses investigating univariately significant variables first within and then across the four risk domains using a threshold of P>0.05. We then tested first-order moderators affecting the relationship of lifetime suicide attempts and suicidal ideation: gender (physical-abuse group); abuser identity, abuse frequency and abuse severity (sexual-abuse group). Analyses were performed with and without weights. Cook's test identified one outlier (Cook's indicator=2.41) in the sexual-abuse group, which was excluded from our final analyses. We also addressed multicollinearity by centring continuous variables. Finally, we examined the latter for normality (a probability–probability plot revealed a modest departure from normality for the trait of conduct problems) and for linearity (ANOVA tests of linearity suggested non-significance of non-linear components at P<0.05).
Results
Contact sexual abuse in childhood was reported by 9.9% (men 2.7%, women 18.0%; χ2 1=146.40, P=0.0005), physical abuse by 20.6% (men 26.3%, women 14.3%; χ2 1=9.46, P=0.002) and both by 8.2% (men 4%, women 12.8%; χ2 1=43.36, P=0.0005) of our participants. The least severe type of contact sexual abuse, involving touch, was, at 49%, the most frequent. Threats and force were reported in 22% and 30% of the remaining sexual abuse cases respectively. In a third of the sexual abuse cases the abuser was a family member, and in about two-thirds the abuse occurred on multiple occasions.
Our prediction that the percentage of individuals reporting a history of non-fatal suicidal behaviours would be higher among those who had been abused, especially those reporting both abuse types, Reference Windle, Windle, Scheidt and Miller15 was largely met (Table 1). Overall, histories of suicide attempts (χ2 3=102.07, P=0.0005) and ideation (χ2 3=69.17, P=0.0005) were more frequently reported in the abused group than in the non-abused group. Moreover, we observed a dose-dependent relationship in the total sample: the non-abused group had a lower prevalence of lifetime suicide attempts (6.0%) than the physical abuse (11.7%), sexual abuse (14.8%) and both abuse types (32.2%) groups. At 25.4%, the prevalence of lifetime suicidal ideation in the non-abused group was also lower than in the physical abuse (36.6%), sexual-abuse (49.6%) and both abuse types (58.1%) groups. In models adjusted for gender and disruptive group membership, those reporting both types of abuse had a 5–14 times greater risk for the four subtypes of suicide attempts and 3–6 times greater odds of suicidal ideas. The sexual-abuse group had higher odds of repeated and late-onset suicide attempts and both types of suicidal thoughts compared with the physical-abuse group. Inspection of gender-stratified odds ratios suggests that the gradient in most suicidal behaviours is confined to the female subsample.
Table 1 Relationship between history of childhood abuse, and suicidal ideation or attempts
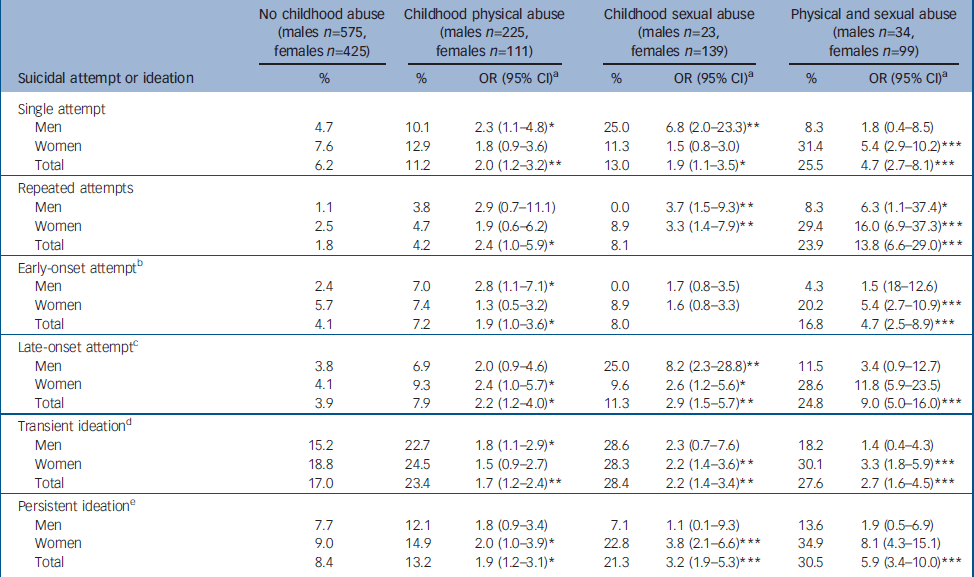
| No childhood abuse (males n=575, females n=425) | Childhood physical abuse (males n=225, females n=111) | Childhood sexual abuse (males n=23, females n=139) | Physical and sexual abuse (males n=34, females n=99) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suicidal attempt or ideation | % | % | OR (95% CI)a | % | OR (95% CI)a | % | OR (95% CI)a |
| Single attempt | |||||||
| Men | 4.7 | 10.1 | 2.3 (1.1-4.8)* | 25.0 | 6.8 (2.0-23.3)** | 8.3 | 1.8 (0.4-8.5) |
| Women | 7.6 | 12.9 | 1.8 (0.9-3.6) | 11.3 | 1.5 (0.8-3.0) | 31.4 | 5.4 (2.9-10.2)*** |
| Total | 6.2 | 11.2 | 2.0 (1.2-3.2)** | 13.0 | 1.9 (1.1-3.5)* | 25.5 | 4.7 (2.7-8.1)*** |
| Repeated attempts | |||||||
| Men | 1.1 | 3.8 | 2.9 (0.7-11.1) | 0.0 | 3.7 (1.5-9.3)** | 8.3 | 6.3 (1.1-37.4)* |
| Women | 2.5 | 4.7 | 1.9 (0.6-6.2) | 8.9 | 3.3 (1.4-7.9)** | 29.4 | 16.0 (6.9-37.3)*** |
| Total | 1.8 | 4.2 | 2.4 (1.0-5.9)* | 8.1 | 23.9 | 13.8 (6.6-29.0)*** | |
| Early-onset attemptb | |||||||
| Men | 2.4 | 7.0 | 2.8 (1.1-7.1)* | 0.0 | 1.7 (0.8-3.5) | 4.3 | 1.5 (18-12.6) |
| Women | 5.7 | 7.4 | 1.3 (0.5-3.2) | 8.9 | 1.6 (0.8-3.3) | 20.2 | 5.4 (2.7-10.9)*** |
| Total | 4.1 | 7.2 | 1.9 (1.0-3.6)* | 8.0 | 16.8 | 4.7 (2.5-8.9)*** | |
| Late-onset attemptc | |||||||
| Men | 3.8 | 6.9 | 2.0 (0.9-4.6) | 25.0 | 8.2 (2.3-28.8)** | 11.5 | 3.4 (0.9-12.7) |
| Women | 4.1 | 9.3 | 2.4 (1.0-5.7)* | 9.6 | 2.6 (1.2-5.6)* | 28.6 | 11.8 (5.9-23.5) |
| Total | 3.9 | 7.9 | 2.2 (1.2-4.0)* | 11.3 | 2.9 (1.5-5.7)** | 24.8 | 9.0 (5.0-16.0)*** |
| Transient ideationd | |||||||
| Men | 15.2 | 22.7 | 1.8 (1.1-2.9)* | 28.6 | 2.3 (0.7-7.6) | 18.2 | 1.4 (0.4-4.3) |
| Women | 18.8 | 24.5 | 1.5 (0.9-2.7) | 28.3 | 2.2 (1.4-3.6)** | 30.1 | 3.3 (1.8-5.9)*** |
| Total | 17.0 | 23.4 | 1.7 (1.2-2.4)** | 28.4 | 2.2 (1.4-3.4)** | 27.6 | 2.7 (1.6-4.5)*** |
| Persistent ideatione | |||||||
| Men | 7.7 | 12.1 | 1.8 (0.9-3.4) | 7.1 | 1.1 (0.1-9.3) | 13.6 | 1.9 (0.5-6.9) |
| Women | 9.0 | 14.9 | 2.0 (1.0-3.9)* | 22.8 | 3.8 (2.1-6.6)*** | 34.9 | 8.1 (4.3-15.1) |
| Total | 8.4 | 13.2 | 1.9 (1.2-3.1)* | 21.3 | 3.2 (1.9-5.3)*** | 30.5 | 5.9 (3.4-10.0)*** |
Identification of correlates and moderators of suicide attempts
Our hypotheses regarding the correlates of suicide attempts focused on four domains. Because high social support buffers the impact of stress and guards against social isolation (two important triggers of suicidal behaviours), we expected social support and stressful life events Reference Straus16 to represent significant correlates of suicide attempts. These expectations were not met in any of our abuse groups. Second, among socio-demographic factors, as expected, Reference Beautrais3 female gender was associated with suicide attempts in the group who experienced both types of abuse, as was one of the four aspects of early socio-economic adversity (paternal education: physical-abuse group OR=0.71, 95% CI 0.58–0.88). In contrast to previous research, neither adult income nor the remaining three components of early socio-economic adversity were related to suicide attempts. Reference Beautrais, Wells, McGee and Oakley Browne17,Reference King, Schwab-Stone, Flisher, Greenwald, Kramer, Goodman, Lahey, Shaffer and Gould18
Our hypothesis that suicidal ideation Reference O'Boyle and Brandon19 might be of relevance for suicide attempts was met in all three abuse groups (sexual abuse OR=6.7, 95% CI 2.6–17.2; physical abuse OR=5.8, 95% CI 2.9–11.7; both OR=4.5, 95% CI 2.1–9.6). In terms of psychiatric diagnoses, in contrast to previous research evidence, Reference O'Boyle and Brandon19 we were unable to confirm the involvement of adolescent mood and anxiety disorders or adult substance misuse. Reference Kessler, Borges and Walters20 The opposite was true for disruptive disorder, an important correlate of suicide attempts in our physical-abuse group (OR=3.1, 95% CI 1.1–9.1) (Table 2).
Table 2 Correlates of suicide attempts in participants reporting childhood physical abuse
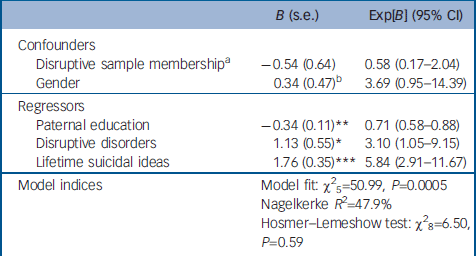
| B (s.e.) | Exp[B] (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Confounders | ||
| Disruptive sample membershipa | -0.54 (0.64) | 0.58 (0.17-2.04) |
| Gender | 0.34 (0.47)b | 3.69 (0.95-14.39) |
| Regressors | ||
| Paternal education | -0.34 (0.11)** | 0.71 (0.58-0.88) |
| Disruptive disorders | 1.13 (0.55)* | 3.10 (1.05-9.15) |
| Lifetime suicidal ideas | 1.76 (0.35)*** | 5.84 (2.91-11.67) |
| Model indices | Model fit: χ2 5=50.99, P=0.0005 | |
| Nagelkerke R 2=47.9% | ||
| Hosmer—Lemeshow test: χ2 8=6.50, P=0.59 | ||
Fourth, we predicted significant contributions of several personality traits related to emotional dysregulation and impulsive-aggression, Reference Brezo, Paris and Turecki4 given their involvement in essential aspects of functioning: self-perception (identity problems and self-esteem), Reference Dinwiddie, Heath, Dunne, Bucholz, Madden, Slutske, Bierut, Statham and Martin21 interpretation (cognitive–perceptive dysregulation), interaction (submissiveness, disruptiveness, insecure attachment, social avoidance and suspiciousness) and reaction to social environments (passive-aggressivity, affective instability, anxiousness). Two of these traits – childhood aggression/disruptiveness (sexual-abuse group OR=1.4, 95% CI 1.1–1.8; both abuse types OR=4.6, 95% CI 1.1–18.2) and adolescent/adult conduct problems (both abuse types OR=1.1, 95% CI 1.01–1.2) – made significant contributions (Tables 3 and 4).
Table 3 Correlates of suicide attempts in participants reporting childhood sexual abusea
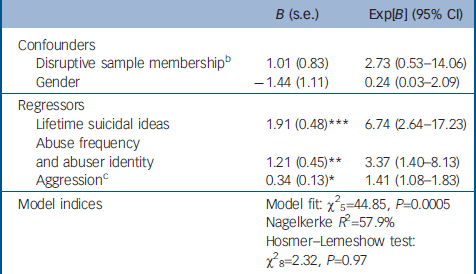
| B (s.e.) | Exp[B] (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Confounders | ||
| Disruptive sample membershipb | 1.01 (0.83) | 2.73 (0.53-14.06) |
| Gender | -1.44 (1.11) | 0.24 (0.03-2.09) |
| Regressors | ||
| Lifetime suicidal ideas | 1.91 (0.48)*** | 6.74 (2.64-17.23) |
| Abuse frequency and abuser identity | 1.21 (0.45)** | 3.37 (1.40-8.13) |
| Aggressionc | 0.34 (0.13)* | 1.41 (1.08-1.83) |
| Model indices | Model fit: χ2 5=44.85, P=0.0005 | |
| Nagelkerke R 2=57.9% | ||
| Hosmer—Lemeshow test: χ2 8=2.32, P=0.97 | ||
Table 4 Correlates of suicide attempts in participants reporting both sexual and physical abuse in childhooda
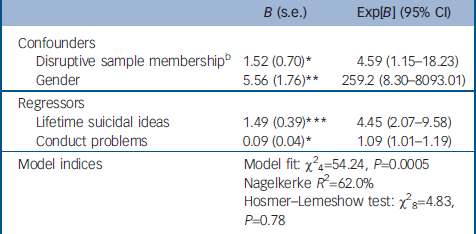
| B (s.e.) | Exp[B] (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Confounders | ||
| Disruptive sample membershipb | 1.52 (0.70)* | 4.59 (1.15-18.23) |
| Gender | 5.56 (1.76)** | 259.2 (8.30-8093.01) |
| Regressors | ||
| Lifetime suicidal ideas | 1.49 (0.39)*** | 4.45 (2.07-9.58) |
| Conduct problems | 0.09 (0.04)* | 1.09 (1.01-1.19) |
| Model indices | Model fit: χ2 4=54.24, P=0.0005 | |
| Nagelkerke R 2=62.0% | ||
| Hosmer—Lemeshow test: χ2 8=4.83, P=0.78 | ||
Evidence for gender-based moderation of the risk of suicide attempts and suicidal ideation, especially in people experiencing childhood physical abuse, has been offered before. Reference Windle, Windle, Scheidt and Miller15,Reference D'Eramo, Prinstein, Freeman, Grapentine and Spirito22 In our study, however, gender did not act as a moderator of the relationship of suicidal ideation and suicide attempts in the physical-abuse group.
On the basis of previous research suggesting that severe childhood sexual abuse – that involving fathers or stepfathers, or repeated abuse – may be strongly associated with suicide attempts, Reference Hebert, Parent, Daignault and Tourigny23 we also tested evidence of moderation by three sexual abuse characteristics: abuser identity, abuse frequency and abuse severity. Although none of the hypothetical moderating effects was significant, we did observe an interaction between abuse frequency and abuser identity (OR=3.4, 95% CI 1.4–8.1). Abuse frequency had a conditional effect on suicide attempts, and was, in turn, moderated by abuser identity. Repeated sexual abuse had a stronger association with suicide attempts than did onetime abuse (Fig. 1). Relative risk increased with the degree of relatedness between the child and the abuser: compared with participants reporting no history of childhood abuse, those abused by a non-related person (RR=2.3), a member of their extended family (RR=3.4) or a member of their immediate family (RR=5.0) had progressively higher likelihoods of reporting suicide attempts.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first community-based study examining abuse characteristics as moderators of suicide attempt risk in adults with a history of childhood physical abuse, contact sexual abuse, or both. This stratification helped us to overcome the classification problems frequently encountered in maltreatment studies, Reference Kinard24 and enabled us to identify protective, risk and moderating influences that may explain differences in suicide attempt risk across abuse sub-populations.

Fig. 1 Interaction of abuse frequency and abuser identity.
Distribution of suicidal behaviours
For the most part, participants with no history of childhood abuse had the lowest odds of non-fatal suicidal behaviours, and those reporting physical abuse, sexual abuse or both abuse types respectively had progressively higher odds of such behaviours. The existence of such a gradient has been suggested previously. Reference Beitchman, Inglis and Schachter25 Stratification by gender further revealed that the gradient may be specific to female suicide attempters and ideators, corroborating evidence for gender-specific psychiatric consequences across abuse types. Reference Thompson, Kingree and Desai26 This heterogeneity might be related to gender-specific gene–environment interactions, neurobiological changes, coping responses to childhood abuse and differential exposure levels to childhood trauma. Reference Teicher, Andersen, Polcari, Navalta and Kim27
Correlates and moderators of suicide attempts
Our primary hypothesis regarding Axis I disorders was supported only in adults reporting physical abuse in childhood. Satisfying criteria for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder and/or oppositional-defiant disorder tripled the likelihood of a positive suicide attempt history. Disruptive disorder symptoms, especially in those reporting physical abuse, have already been linked to suicidal behaviours. Reference Renaud, Brent, Birmaher, Chiappetta and Bridge28 We were, however, unable to test if this association was mediated by substance use disorders, as previously suggested. Reference Renaud, Brent, Birmaher, Chiappetta and Bridge28 This possibility seems unlikely in our sample, as substance misuse was not related to suicide attempts. Anxiety and mood disorders were similarly not significant, either because their contribution was limited to shared variance with suicidal ideation or because they are not important intermediaries between childhood abuse and suicide attempts.
Interestingly, we found that externalising personality traits assessed at different life stages may be of relevance to suicide attempts. Conduct problems – self-reported tendencies to engage in acts of vandalism or theft, alcohol intoxication, and bullying or threats of violence – contributed to the variance in suicide attempts in our group with both types of abuse. Furthermore, disruptive–aggressive personality traits in childhood were significant in both the combined-abuse group and the sexual-abuse group. These traits are related to impulsivity–aggression, a putative mediator of suicide risk. Reference Turecki29 Similar traits have been implicated across age and gender groups. Reference King, Schwab-Stone, Flisher, Greenwald, Kramer, Goodman, Lahey, Shaffer and Gould18
Explanations for the involvement of externalising tendencies – impulsive–aggressive personality traits and disruptive disorders – are likely to involve interplays of abusive environments and genes. For example, externalising behaviour is predicted by high-intensity family conflict, a situation more likely to arise in abusive households. Reference Hebert, Tremblay, Parent, Daignault and Piché30 Childhood abuse itself may influence the development of impulsivity and aggression, Reference Brown, Cohen, Johnson and Smailes31 although its precise role is unknown. Our data demonstrated that aggression at age 6 years (our earliest personality measure) was most relevant, among those who had attempted suicide, in participants who reported the most severe childhood abuse type (both physical and sexual). Additionally, relative to sexually abused children, those experiencing both physical and sexual abuse were more likely to report abuse by family members rather than by unrelated persons, further supporting the notion of compound family adversity in abusive households. Ultimately, abuse in children may be not only involved in the aetiology of externalising tendencies but also a negative reinforcer of such tendencies through reactive gene–environment correlations: in other words, externalising behaviours may provoke negative reactions by adults and peers, leading to social difficulties, an important motivator of suicide attempts.
Unlike externalising tendencies, which exhibited some abuse specificity, suicidal thoughts made consistent contribution across abuse types in our study. Persistent suicidal ideation made suicide attempts 5–6 times more likely in those with a history of childhood abuse. Its relationship with suicide attempts was additive rather than moderated by gender and abuse characteristics, in contrast to our hypotheses. Suicidal thoughts, however, may be mediators between suicide attempts and maladaptive coping responses related to abuse.
Our exploration of the effect of childhood sexual abuse characteristics indicated that the impact of abuse frequency on suicide attempts depended on the identity of the abuser. Repeated abuse was, generally, more strongly associated with suicide attempts than was one-time abuse. Furthermore, sexual abuse by a member of the immediate family – father, stepfather or brother, for example – carried the greatest risk, whereas abuse perpetrated by an extended family member (uncle, cousin) or an unrelated individual (an acquaintance, romantic partner or stranger) carried intermediate and weaker risks respectively. There are at least two plausible explanations for this pattern. First, abuse by a father or stepfather is considered especially traumatic, Reference D'Eramo, Prinstein, Freeman, Grapentine and Spirito22 possibly because such abuse is more likely to occur in families with multiple problems and also because these families cannot provide safe and healing conditions following abuse. Second, abuse by close family members, who are expected to be among our main, lifelong sources of support, may have long-term consequences on the development of healthy attachment patterns necessary for mental health. Reference Allen and Farmer32
Although we examined possible protective influences of adolescent self-esteem, social support, and childhood and adult environments, only paternal education was found to have such effect. Low parental education has already been recognised as a risk factor for childhood abuse. Reference Straus16 We found it also to be strongly correlated with socio-economic status (r=0.58, P=0.0005), another factor positively related to mental health and exposure to abuse. Reference Beitchman, Inglis and Schachter25 Better-educated parents might provide a more stable and healthy environment, one that would lower the likelihood of abuse taking place or reduce its impact. They might, furthermore, be less likely to use corporal punishment and similar disciplinary methods. When facing challenging situations themselves, educated parents might also model more adequate coping behaviours rather than resort to suicidal gestures and/or externalising behaviours.
In summary, the three abuse groups have both shared and distinct correlates of suicide attempts across diverse risk domains. Additional longitudinal studies need to examine childhood abuse in relation to the onset and developmental course of psychosocial problems, addressing moderating and mediating influences involving characteristics of abusive acts, the person abused, and the abuser.
Alternative methodological explanations of observed findings must also be noted. Our study population included self-reported abuse victims, excluding individuals who repressed memories of such events or chose not to report them. Nevertheless, we found those self-reporting abuse to be at higher risk of attempting suicide than those reporting no childhood abuse. Furthermore, not having information on the proportion of those who had received psychosocial interventions following abuse disclosure, we were unable to control for the possible confounding effects of such interventions. The lack of external validation of abusive experiences and attachment security, possibility of measurement error, and the small number of sexually abused male participants who had attempted suicide also merit consideration. We also note a modest departure from normality of the trait of conduct problems, although logistic regression is believed to be relatively robust to such departures.
To address the suboptimal psychometric properties of the suicidal ideation and intent scales – possibly attributable to translation problems – we used multiple instruments to assess suicidality. Still, more information is needed on the means used at self-injury. These limitations notwithstanding, our findings confirm the association between suicide attempts and childhood abuse, and involvement of both additive and interactive influences.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Alexandre Bureau for his valuable comments on the manuscript. The study was supported in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (grant MOP 151060).








eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.