In many countries, predominantly in the USA, Australia and to a growing degree in Western Europe, the complex management of mental healthcare requires quality assurance and ongoing treatment monitoring. Although routine data collection in mental healthcare is becoming more widespread, these data are rarely fed back to practitioners – let alone to patients – in a meaningful way.
Continuous monitoring of patient outcome was recommended as a means to improve quality of health services 20 years ago. Reference Ellwood1 Ten years later, Lyons et al Reference Lyons, Howard, O'Mahoney and Lish2 presented a concept on how to combine measurement with management of clinical outcomes in mental healthcare. This approach has been refined in the meantime, for example for quality management in psychotherapy. Reference Kordy and Bauer3 Feedback of patient outcome to stakeholders constitutes the prime instrument of outcome management and can be regarded as the most direct link between research and practice since outcome data are being used immediately in order to improve service provision.
Two reviews have summarised the evidence on feedback of outcome in general healthcare Reference Espallargues, Valderas and Alonso4,Reference Valderas, Kotzeva, Espallargues, Guyatt, Ferrans and Halyard5 and found some positive effects on the process of care, but none on patient health status. By focusing on specific settings, Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon6 interventions Reference Lambert, Whipple, Hawkins, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Smart7 or diagnostic groups, Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon8 the scope of reviews on the impact of outcome management in mental healthcare has been rather restricted. Thus, evidence on the effectiveness of feedback in mental healthcare is inconclusive: although Gilbody et al Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon8 could not find any randomised controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the effect of use of outcome measures in the routine treatment of people with schizophrenia, Lambert et al Reference Lambert, Whipple, Hawkins, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Smart7 stated that in out-patient psychotherapy ‘it may be time for clinicians to routinely track and formally monitor patient treatment response’. Furthermore, in many reviews, information from outcome measures for screening purposes has been mixed with continuous outcome management. Thus, there is a need for a systematic review of the effectiveness of feedback of outcome in specialist mental healthcare.
Method
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was conducted in the electronic databases Medline, PSYNDEX, PsycINFO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, the Current Controlled Trials Register, and the world wide web using Google and Google Scholar in November 2006. This search was updated in March 2008 using the same search criteria. A broad set of search terms was applied in order to achieve maximum sensitivity. Keywords entered were ‘mental disorders’ combined with ‘feedback’ and ‘treatment outcome’ as well as diverse synonyms of these search terms. A total of 1066 publications were identified in this first step. Additional hand searching was carried out using the reference lists of relevant articles and appropriate reviews. Reference Espallargues, Valderas and Alonso4,Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon6,Reference Marshall, Haywood and Fitzpatrick9,Reference Sapyta, Riemer and Bickman10 If data were missing or not apt for use in meta-analysis, authors were contacted for further information (details of the search strategy and the search terms used can be obtained from B.P.).
Inclusion criteria
English- as well as German-language publications were included in this systematic review if they examined feedback of outcome in specialist mental healthcare settings. Study participants had to be of adult age with mental health problems treated in psychiatric or psychotherapeutic settings (community, in-patient, and out-patient mental health services). Feedback was defined as providing mental healthcare professionals and/or patients with individual information on treatment outcome based on standardised measures (e.g. mental health, unmet needs). Only studies with a controlled design (not necessarily randomised) that evaluated effects of feedback interventions on patient outcome such as mental health were selected for analysis. Two of the authors (C.K. and B.P.) independently decided about study inclusion. Disagreements were resolved by discussion.
Exclusion criteria
Duplicate publications, abstracts and studies in which outcome assessment was used exclusively for routine screening or diagnosis were excluded.
Data extraction
Study characteristics, features of the feedback systems and outcome data were extracted from each included article (by C.K. and subsequently checked by B.P.) using a standard coding form developed for this review. This form included authors, publication year, study type, country, setting, patient and therapist population, unit of randomisation, inclusion and exclusion criteria, groups, feedback and effect instruments, measurement points, feedback intervention (duration, type and content of feedback, recipient, frequency and timing), outcomes assessed, as well as results and method of analysis. Furthermore, cost data (e.g. treatment duration) were noted if available.
Procedures
Data synthesis was conducted using the following two-step procedure: first, a qualitative analysis was conducted in order to provide a narrative overview. Second, a quantitative data synthesis (meta-analysis) was carried out separately for all trials with sufficient data on mental health outcome and treatment duration as end-points of the intervention. All symptoms scales applied in the studies were used as a measure of mental health outcome. If studies reported more than one scale or compound dimensions of an outcome, a single mean effect size was calculated for each study in order to avoid bias in favour of trials with multiple outcome measures.
Given our focus on differences in post-treatment outcome in controlled studies, effect sizes were calculated on the basis of (raw-) post-score analysis using the formula d =(M 1–M 2)/s.d., where M 1 and M 2 are the means of the outcome measures in the intervention (having received feedback) and control groups, and s.d. is the pooled standard deviation of the two groups' post-scores. These effect sizes were corrected in order to obtain unbiased estimators using procedures suggested by Hedges. Reference Hedges11 The direction of effect was standardised so that a positive value indicates a better outcome in the feedback condition. As larger sample sizes lead to more reliable estimators, all calculated effect sizes were weighted by the inverse of their variance. Reference Hedges and Oklin12
Some studies reported the results of more than two groups. Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13–Reference Lambert, Whipple, Smart, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Hawkins15 In these cases, effect sizes of each control group comparison were pooled, resulting in one effect size per trial. An exception was made in a study with subsequent phases Reference Bauer16 – each with an intervention and a control group – where both study phases were treated as two independent trials and effect sizes were calculated separately.
Heterogeneity between and within the selected studies was anticipated as a result of variation in settings, feedback interventions, outcome instruments, the mental disorders the participants had and mental health professionals' therapeutic orientation. Therefore, the meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model as suggested by DeSimonian & Laird Reference DerSimonian and Laird17 that considers both intra- and inter-study variability. To quantify heterogeneity, the I 2 statistic, which represents an estimation of the percentage of total variation across studies due to heterogeneity, was calculated. I 2 values below 25% indicate low heterogeneity whereas those above 75% point towards high heterogeneity. Reference Higgins, Thompson, Deeks and Altmann18
To prevent dilution of effects as a result of differences in length of follow-up periods within one trial or in comparison with the others, we calculated two separate meta-analyses: short-term for follow-up intervals up to 9 weeks after intake (predominantly at the end of therapy), and long-term for those between 3 and 12 months.
Evidence of publication bias was analysed using graphical control techniques (funnel plots) and Egger's regression test. Reference Egger, Davey Smith, Schneider and Minder19 A fail-safe number was calculated in view of the fact that non-significant studies tend to be unpublished (‘file-drawer problem’). This parameter estimates the number of studies with an effect size of zero required to nullify the overall effect size. To test the robustness of the overall effect and to prove the influence of single trials on the overall effect an exclusion sensitivity plot was calculated.
The influence of variables such as the perspective of outcome rating (self v. staff), setting and feedback modalities, including recipient, content, frequency and timing of feedback, on the effects of feedback interventions was explored via a priori defined subgroup analyses. All analyses were performed with Comprehensive Meta Analysis 2.0 for Windows and the overall effects are presented as Hedges' g with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Reference Hedges and Oklin12
Results
Search flow
The search strategy initially identified 1078 publications. After initial title and abstract screening, 68 studies were rated as potentially relevant and screened in full text. Short-listed trials that were excluded were mostly descriptive reports dealing with outcome monitoring or with theoretical aspects, development, implementation, feasibility or acceptance of feedback systems. Of the remaining trials, only 21 fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Three of them could not be retrieved even after efforts to contact the authors, one was written in a language other than English or German, and five were still in progress with no published outcome data reported.
Characteristics of included studies
Finally, 12 studies published between 2001 and 2006 met all selection criteria and were available for meta-analysis (Tables 1 and 2). Half of them were conducted in the USA, four in the UK, and two in Germany. Two studies were dissertations. Reference Bauer16,Reference Trudeau20 Sample size varied between 127 and 1374 participants. Most studies were conducted in out-patient settings such as community-based mental health services (five studies), university counselling centres (three studies), and specialist mental health units (old age psychiatry, eating disorder; two studies). Only two trials were performed in in-patient psychotherapeutic clinics. Reference Bauer16,Reference Berking, Orth and Lutz21
Table 1 Study properties

| Properties | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Location | ||
| USA | 6 | 50 |
| UK | 4 | 33 |
| Germany | 2 | 17 |
| Setting | ||
| In-patient | 2 | 17 |
| Out-patient | 10 | 83 |
| Design | ||
| Randomised controlled trial | 10 | 83 |
| Controlled trial | 2 | 17 |
| Patients | ||
| Mental illness (mixed diagnoses) | 10 | 83 |
| Old age | 1 | 8 |
| Eating disorders | 1 | 8 |
| Unit of randomisation | ||
| Patients | 7 | 58 |
| Professionals | 1 | 8 |
| Patients and professionals | 2 | 17 |
| None | 2 | 17 |
Table 2 Characteristics of the included studies and their participants

| Country and setting | Design; intervention group/control group n; follow-up time points | n | Age, years (mean) | Female, %a | Illness | Outcome measures | Feedback to | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashaye et al (2003) Reference Ashaye, Livingston and Orrell26 | UK day hospital | RCT; 1/1; 3 months | 112 | ≥65 (76.4) | 64 | Depression, dementia | HoNOS (65+), CAPE—BRS | Staff |
| Bauer (2004) Reference Bauer16 | Germany in-patient | CT; 2/2; discharge | 391 | 18-79 (34.9) | 71 | Personality disorder, depression, anxiety | SCL—11, OQ—45, IS | Clinician |
| Berking et al (2006) Reference Berking, Orth and Lutz21 | Germany in-patient | RCT; 1/1; discharge | 118 | Adults (49.4) | 62 | Depression, anxiety | FEP, VEV, CGI | Clinician |
| Brodey et al (2005) Reference Brodey, Cuffel, McCulloch, Tani, Maruish and Brodey23 | USA out-patient | RCT; 1/1; 6 weeks | 1374 | ≥18 | 75 | Depression, anxiety | SCL—11 | Clinician |
| Hawkins et al (2004) Reference Hawkins, Lambert, Vermeersch, Slade and Tuttle14 | USA out-patient | RCT; 2/1; discharge | 201 | Adults (30.8) | 68 | Mood and anxiety disorders | OQ—45 | Clinician or clinician and patient |
| Lambert et al (2001) Reference Lambert, Whipple, Smart, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Hawkins15 | USA out-patient | RCT; 1/1; discharge | 609 | 17-57 (22.2) | 70 | Personal concerns | OQ—45 | Clinician |
| Lambert et al (2002) Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13 | USA out-patient | CT; 1/1; discharge | 1020 | 17-57 (22.3) | 70 | Personal concerns | OQ—45 | Clinician |
| Marshall et al (2004) Reference Marshall, Lockwood, Green, Zajac-Roles, Roberts and Harrison27 | UK out-patient | RCT; 2/1; 12 months | 304 | Adults | — | Schizophrenia, depression | BPRS, WHO—DAS | Care coordinator |
| Schmidt et al (2006) Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22 | UK out-patient | RCT; 1/1; discharge and 6 months | 61 | Adults | 100 | Eating disorder | SEED | Patient |
| Slade et al (2006) Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24 | UK out-patient | RCT; 1/1; 7 months | 160 | 18-64 (41.2) | 22 | Schizophrenia, affective disorder | BPRS, HoNOS, TAG | Staff and patient |
| Trudeau (2001) Reference Trudeau20 | USA out-patient | RCT; 1/2; 2 and 4 months | 127 | Adults (33.9) | 72 | Mental health problems | OQ—45, RAND—36 | Clinician |
| Whipple et al (2003) Reference Whipple, Lambert, Vermeersch, Smart, Nielsen and Hawkins25 | USA out-patient | RCT; 1/1; discharge | 981 | 18-54 (22.9) | 66 | Personal concerns | OQ—45 | Clinician |
The majority of the studies (10, 83%) were RCTs, in 7 of which the unit of randomisation was the patient. The two non-randomised trials used a controlled prospective cohort design Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13 and a prospective one with sequential study phases. Reference Bauer16 Most of the studies included chose treatment as usual (TAU) for the control groups. One study compared feedback with a control condition that consisted of additional mental health assessment. Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22 In thecaseof another study that reported results of two control conditions, data abstraction was restricted to the assessment-only procedure. Reference Trudeau20
Procedures and features of the feedback systems
Characteristics of the feedback systems used are summarised in Table 3. In most studies, feedback was given continuously at 1- or 2-weekly intervals during the course of therapy. Others limited the number of feedback interventions to a maximum of two. Reference Brodey, Cuffel, McCulloch, Tani, Maruish and Brodey23,Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24 In general, standardised assessments of psychological functioning (e.g. Outcome Questionnaire–45.2, Symptom Checklist–11) or needs (e.g. Camberwell Assessment of Need for the Elderly, Camberwell Assessment of Need Short Appraisal Schedule, Cardinal Needs Schedule) were completed by participants and results were fed back to therapists or staff. Only three studies investigated the provision of a (identical or different) message to patients. Reference Hawkins, Lambert, Vermeersch, Slade and Tuttle14,Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22,Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24
Table 3 Feedback systems useda

| Measures used for feedback | Modalities of feedback | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rated by | Timingb | Frequency | Content | Features | ||
| Ashaye et al (2003) Reference Ashaye, Livingston and Orrell26 | CANE | Clinician | — | Once | Unmet needs and suitable interventions | List |
| Bauer (2004) Reference Bauer16 | OQ—45, GBB, CSC, PAE, HAQ, FLZ | Patient | Timely | Once | Phase 1: Early treatment response; | Graphs, tables, textc,d |
| HAQ, ICD—10 | Clinician | Phase 2: Additionally prognosis of treatment duration, treatment recommendation | ||||
| Berking et al (2006) Reference Berking, Orth and Lutz21 | FEP | Patient | Timely | Weekly | Progress, goal achievement | Progress graph, percentage of goal achievement |
| Brodey et al (2005) Reference Brodey, Cuffel, McCulloch, Tani, Maruish and Brodey23 | SCL—11 | Patient | Timely | Twice | Progress, extreme answers, fill-in time | Graph, tables, textc |
| Hawkins et al (2004) Reference Hawkins, Lambert, Vermeersch, Slade and Tuttle14 | OQ—45 | Patient | Delayed | Weekly | Progress, treatment recommendation | Graph, coloured progress markers, textc |
| Lambert et al (2001) Reference Lambert, Whipple, Smart, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Hawkins15 | OQ—45 | Patient | Delayed | Weekly | Progress, treatment recommendation | Graph, coloured progress markers, textc |
| Lambert et al (2002) Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13 | OQ—45 | Patient | Delayed | Weekly | Progress, treatment recommendation | Graph, coloured progress markers, textc |
| Marshall et al (2004) Reference Marshall, Lockwood, Green, Zajac-Roles, Roberts and Harrison27 | CNS | Patient | Delayed | Once | Needs, required interventions, access to intervention | Text |
| Schmidt et al (2006) Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22 | TREAT—EAT, SEED, HADS | Patient | — | Biweekly | Physical and psychological status, variables facilitating or hindering change | — |
| Slade et al (2006) Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24 | CANSAS, HAS, MANSA CANSAS, HAS, TAG | Patient Staff | Delayed | Twice | Progress, areas of disagreement | Graphs, text |
| Trudeau (2001) Reference Trudeau20 | OQ—45 | Patient | Delayed | Weekly | Progress | Graphse |
| Whipple et al (2003) Reference Whipple, Lambert, Vermeersch, Smart, Nielsen and Hawkins25 | OQ—45 | Patient | Delayed | Weekly | Progress and treatment response; | Graph, coloured progress markers, textc,f |
| CST for non-responders | ||||||
| CST based upon Haq—II, SCS, MSPSS | Patient | Delayed | — | Treatment guidelines, CST results | Text | |
Feedback mainly comprised information about current treatment status and changes over time. Thus, the basic component to illustrate treatment progress was graphical and/or numerical data, often complemented with further explanations or in some cases even with treatment recommendations. Only two studies Reference Trudeau20,Reference Berking, Orth and Lutz21 did not use any normative comparison with a reference group to evaluate individual progress in therapy.
Effect variables
A variety of outcomes were evaluated: mental health, met and unmet needs, physical impairment, social functioning, quality of life, patient satisfaction, acceptance or appraisal of feedback, as well as rates of significant clinical change and of treatment response.
Nine of the studies measured mental health status by using patient-reported generic symptom scales. Professional-rated measures of psychological functioning were used in five trials whereas three of them included both raters' perspectives. In half of the studies two or more mental health outcome questionnaires were administered (Table 2).
The parameter most frequently used in order to ascertain savings of direct costs as a result of the use of feedback was treatment duration in terms of number of treatment sessions Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13–Reference Lambert, Whipple, Smart, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Hawkins15,Reference Whipple, Lambert, Vermeersch, Smart, Nielsen and Hawkins25 or length of stay. Reference Bauer16 Only one study relied on other indicators of service use (hospital admissions and drop-out rates). Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24
Short- and long-term effects on mental health outcomes
Most of the studies included measured the impact of feedback on individuals' mental health status at the end of treatment or within 9 weeks after intake. Two of these nine trials also evaluated long-term effects. Reference Trudeau20,Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22 The remaining three studies Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24,Reference Ashaye, Livingston and Orrell26,Reference Marshall, Lockwood, Green, Zajac-Roles, Roberts and Harrison27 reported follow-up measurements only (Table 2).
In the meta-analysis of short-term outcomes, ten group comparisons with a total of 4009 participants could be included. Figure 1 shows the estimated mean effect sizes. The overall effect was d = 0.10 (95% CI 0.01–0.19) favouring the feedback intervention. Heterogeneity across studies was moderate (I 2 = 31%, P = 0.16). There was no substantial change in results (d = 0.11, 95% CI 0.02–0.20, P = 0.02) when limiting this analysis to those trials Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13–Reference Bauer16,Reference Trudeau20,Reference Whipple, Lambert, Vermeersch, Smart, Nielsen and Hawkins25 with the outcome measure used most frequently (Outcome Questionnaire–45.2). Reference Lambert, Burlingame, Umphress, Hansen, Vermeersch and Clouse28
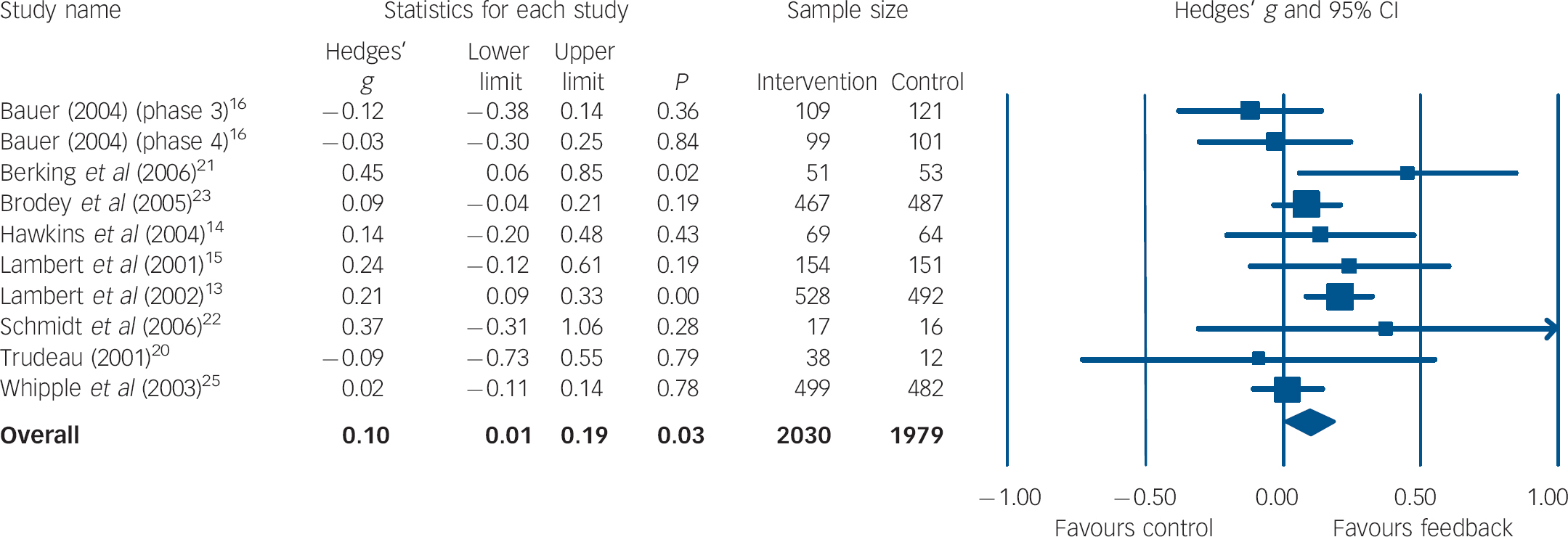
Fig. 1 Forest plot for short-term mental health outcome (random-effects model).a a. Treatment outcomes were coded as short-term if they were measured within 9 weeks after initial assessment.
For the examination of long-term effects, five trials with a total of 573 participants were included in the analysis. All except one study Reference Trudeau20 used diverse staff-rated outcome measures that were combined per trial for effect size calculations. As shown in Fig. 2 the mean weighted effect size (d = −0.06, 95% CI 0.22–0.11) was against the expected direction, but it was small and not significant. Heterogeneity between studies was very low (I 2 = 0%, P = 0.69).
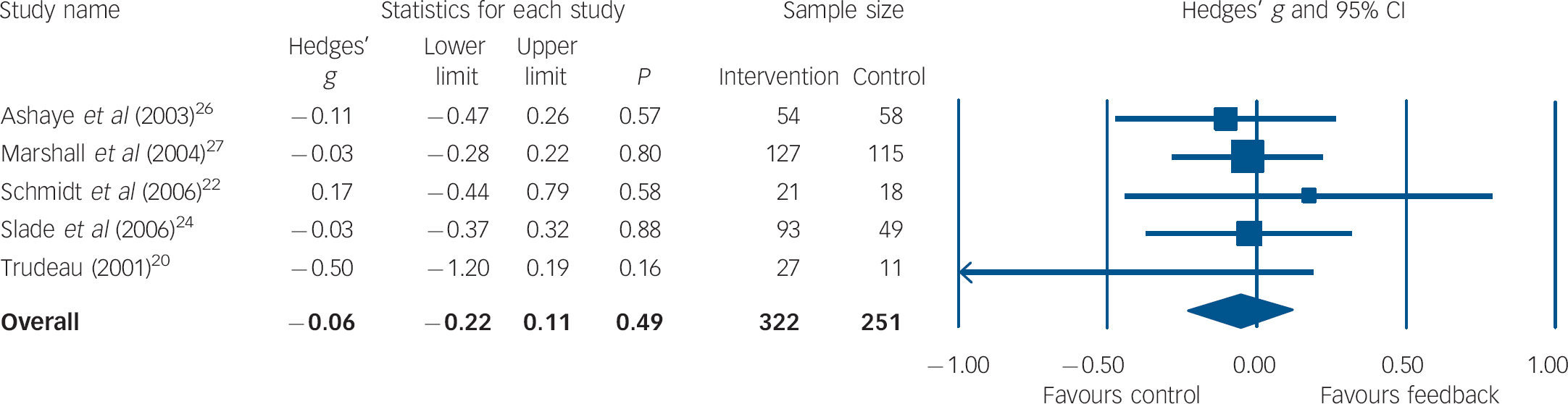
Fig. 2 Forest plot for long-term mental health outcome (random-effects model).a a. Treatment outcomes were coded as long-term if they were measured between 3 and 12 months after initial assessment.
Effects on treatment duration
Data on length of treatment as an indicator of costs were available for 981 participants from five studies (42%). Figure 3 shows the results of the pooled meta-analysis. The overall effect size was d = 0.05 (95% CI −0.05 to 0.15) with moderate heterogeneity (I 2 = 42.03%, P = 0.12).
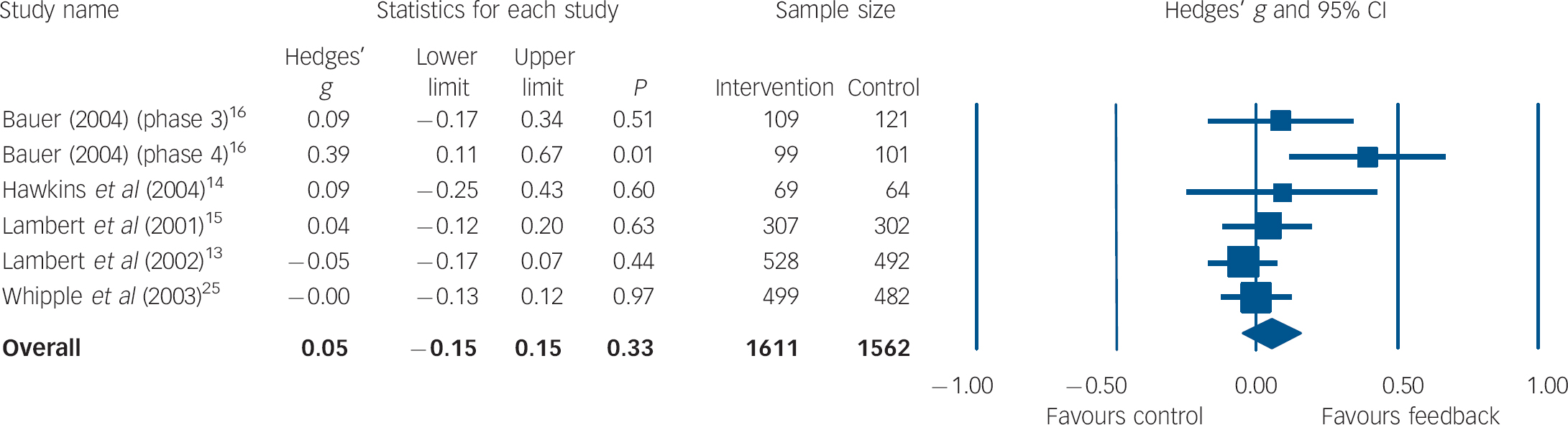
Fig. 3 Forest plot for treatment duration (random-effects model).
Moderator analyses
There were no statistically significant differences in effect sizes between any of the subgroups analysed (Table 4). However, magnitude of subgroup differences was substantial in a number of instances. Feedback was more effective if it: was given to both patients and therapists or staff (v. only to therapists/staff); was reported at least twice (v. only once); comprised information on patient progress (v. on status only). Moreover, only the latter two subgroups showed effect sizes significantly different from zero within their subgroup analysis.
Table 4 Results of subgroup analyses (random-effects model)

| Short-term mental health outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | k a | Effect size | 95% CI | P b |
| Setting | ||||
| In-patient | 3 | 0.07 | -0.23 to 0.37 | 0.65 |
| Out-patient | 7 | 0.11 | 0.04 to 0.18 | 0.00 |
| Rater of outcome | ||||
| Patient | 11 | 0.11 | 0.03 to 0.19 | 0.01 |
| Staff | 3 | 0.01 | -0.42 to 0.44 | 0.97 |
| Feedback recipient | ||||
| Therapist/staff and patient | 2 | 0.30 | -0.01 to 0.60 | 0.06 |
| Therapist/staff | 9 | 0.09 | -0.01 to 0.18 | 0.07 |
| Feedback content | ||||
| Status information | 3 | -0.04 | -0.23 to 0.14 | 0.63 |
| Progress information | 7 | 0.13 | 0.04 to 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Feedback timingc | ||||
| Timely | 4 | 0.06 | -0.04 to 0.16 | 0.23 |
| Delayed | 5 | 0.06 | -0.05 to 0.17 | 0.31 |
| Feedback frequency | ||||
| Once | 2 | -0.08 | -0.27 to 0.11 | 0.42 |
| More than once | 8 | 0.13 | 0.04 to 0.22 | 0.00 |
Heterogeneity within the clusters varied between very low and high particularly depending on number of included studies or group comparisons (I 2 ranged from 0 to 84%).
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Funnel plots for studies of short- (Fig. 4) or long-term mental health outcome as well as for studies evaluating treatment duration did not provide evidence of publication bias. Fail-safe numbers for the analyses pertaining to short-term effects showed that it would require 11 unpublished null result trials to nullify the calculated effect. Moreover, Egger's regression test was not significant (P = 0.76), suggesting no evidence of small-study bias.

Fig. 4 Funnel plot of estimated effect sizes (Hedges' g) against standard error of the trials for short-term mental health outcome.
Further sensitivity analyses revealed that the exclusion of any single study only marginally changed the overall effect sizes of all three analyses. The greatest difference in short-term outcome analysis occurred when the study of Lambert et al Reference Lambert, Whipple, Vermeersch, Smart, Hawkins and Nielsen13 was removed (d = 0.06, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.15, P = 0.14).
Discussion
Evidence base
Twelve studies fulfilling inclusion criteria for a systematic meta-analysis of the effectiveness of outcome management in mental healthcare were identified. Most of these were conducted in out-patient treatment settings in the USA or the UK. Outcome management in in-patient treatment has only been examined in Germany, which also reflects national differences in mental health service provision. Reference Becker and Vazquez-Barquero29 Sample size averaged 378 participants per study. Altogether, evidence is based upon 4540 adults, two-thirds of them female. The vast majority of study participants were people with affective disorders. However, participants' mental health problems did not always meet standard diagnostic criteria of a mental disorder, especially among student populations on which most of the research of the Lambert group is based. On the other hand, some studies focused on people with severe mental illness (e.g. Slade et al). Reference Slade, McCrone, Kuipers, Leese, Cahill and Parabiaghi24 Given that two decades have passed since the introduction of the general principles of outcome management, Reference Ellwood1 this suggests that some efforts have been made to provide systematic evidence of its effectiveness in specialist mental healthcare.
Short- and long-term effect
Results of this review of controlled studies show that feedback of outcome had a small, albeit statistically significant short-term effect on improving mental health outcomes (d = 0.10, 95% CI 0.01–0.19). This effect was found to be consistent across a variety of outcome measures as analyses limited to studies using a popular single instrument (Outcome Questionnaire–45.2) or excluding the one study with a disorder-specific scale Reference Schmidt, Landau, Pombo-Carril, Bara-Carril, Reid and Murray22 showed similar results. Furthermore, sensitivity analyses revealed that the exclusion of any single study only marginally changed the overall effect sizes of all three analyses, implying relative stability of the results. This corresponds with the calculation of fail-safe numbers indicating that at least 11 null effect trials are needed to diminish the effect. This effect size is similar to that found in other reviews on the topic, for example by Sapyta et al Reference Sapyta, Riemer and Bickman10 on various forms of feedback of client health status information (including screening information only) to health professionals (including general practitioners) in community settings (d = 0.21) or by Lambert et al Reference Lambert, Whipple, Hawkins, Vermeersch, Nielsen and Smart7 on continuous feedback of outcome in out-patient psychotherapy (d = 0.09). Bearing in mind differences in sampling and methods, such comparisons should be viewed cautiously.
It was also found that this effect did not prevail in the long run, i.e. after termination of treatment and outcome feedback, symptomatic impairment in study participants allocated to control groups was no worse than in those who had received outcome management. On the one hand, this finding suggests that outcome management has no persistent effect on improving mental health. On the other, it could also be interpreted to suggest that it might be wise to continue using outcome feedback at least to some extent after the end of treatment in order to avoid wearing off of short-term benefits. Unfortunately, a clear interpretation of this finding is difficult since long-term effects have only rarely been studied (in only five trials).
Furthermore, no advantage of outcome management was found with respect to reduction of treatment costs or cost-offset. This finding should also be interpreted with caution since only very few researchers made efforts to collect comprehensive cost data. Therefore, statistical pooling was limited to studies reporting indicators of the amount of treatment utilised.
Moderators of effect
In addition, apart from specifying the general benefit of outcome management, it is also important to identify its active ingredients. Moderator analyses showed that the effect of outcome management on individuals' short-term mental health outcome is improved if: feedback comprises information on mental health progress (v. only on status); both patient and therapist receive feedback (v. only one of them); and feedback is given frequently (v. only once). Considering the small numbers of studies and substantial heterogeneity for some clusters (I2 ranging from 0 to 84%), these results offer valuable clues but should be interpreted with caution.
Limitations
Even though the aggregated sample size of included studies would appear sufficient, the number of studies these data were drawn from was small and not particularly representative. Additionally, the number of researchers conducting this research is very small, and could introduce bias through a number of avenues. This meta-analysis has a number of further drawbacks. First, assessed studies varied considerably with regard to certain patient characteristics, most notably illness severity and comorbid disorders. The majority of trials relied on data from people with rather mild mental illness treated with out-patient psychotherapy. Second, the number of studies decreased rapidly when we tried to answer more specific questions (e.g. long-term effects, moderators). As a result of variations in study designs, measurement points had to be pooled in order to be able to examine persistence of effect. Third, except in one study, feedback was based on patient-reported outcomes whereas it might be worthwhile to also have data obtained from independent raters. Fourth, in the vast majority of the trials, the unit of randomisation was the patient, which might entail cross-contamination, Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon8 i.e. ‘real’ effects of the intervention are watered down because of a general sensitisation since one clinician receives feedback for some patients but not for others.
Implications and outlook
Psychotherapy research has put forth a number of rather refined approaches to systematically feeding back patient outcome data to clinicians and also to patients in order to improve quality of mental healthcare, e.g. patient-focused research, Reference Lambert, Hansen and Finch30 expected treatment response Reference Lueger, Howard, Martinovich, Lutz, Anderson and Grissom31 or computer-assisted quality management. Reference Kordy, Hannöver and Richard32 All these outcome management systems heavily rely on professionals' endorsement and use of standardised outcome measures. Although there is a trend towards increased use of such instruments among psychologists in clinical practice, Reference Hatfield and Ogles33 psychiatrists have hardly picked up on this development. Reference Gilbody, House and Sheldon34 A reason for this might be doubts about the benefits of outcome management among clinicians.
This review might contribute to reducing such doubts at least to some extent, since it has shown that feedback of outcome improves symptomatic impairment in people with mental illness treated in various specialist mental health services. Even though overall effect size was modest, some single studies yielded impressive effects. However, the evidence base is hardly sufficient to adequately analyse crucial more specific questions such as differential effectiveness in certain subgroups (e.g. by diagnosis). Nevertheless, this review provides some clues on issues that should be taken into account when implementing outcome management in routine practice, i.e. to feedback outcome continuously and regularly to both clinicians and patients, and to provide information on treatment progress.
Future research might pick up on these clues in order to move beyond trying to answer the question of a general effect of outcome management in mental healthcare. One direction should be to conduct much-needed comprehensive cost-effectiveness analyses based upon sound estimates of costs of feedback (staff, equipment, space and other resource costs), direct and indirect costs and treatment outcome. Most importantly, active ingredients of outcome management should be scrutinised in more detail in order to arrive at feedback systems tailored to the needs of specific subgroups of people with mental illness, but also to the requirements of clinicians who, at least during kick-off, are asked to devote substantial amounts of extra effort to make outcome management work.
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their knowledgeable and helpful comments.











eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.