The correlation between recessions and suicide is one of the best characterised statistical relationships in demographic history. Reference Stuckler, Basu, Suhrcke, Coutts and McKee1 In 1897, Durkheim wrote, ‘It is a well-known fact that economic crises have an aggravating effect on suicidal tendency’. Reference Durkheim2 In North America and Europe, two regions most affected by the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression, suicides have risen markedly.
Method
To calculate excess suicides in Europe (2008-2010) and Canada (2008-2009), we estimate, taking 2007 as our pre-recession baseline, the unadjusted difference between the baseline suicide rate and the suicide rate for each year after the recession began. These estimates are conservative because background secular trends were declining prior to the onset of the economic downturns. Estimates of the excess suicides in the USA were taken from a previous study using state-level data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Further details of our methods for calculating excess suicides can be found in the online supplement.
Results
Internationally comparable suicide data from the World Health Organization (WHO) European Health for All database, shows that following the Great Recession nearly all European societies have experienced rising suicide rates. As shown in Fig. 1, prior to the onset of recession in 2007, suicide rates had been falling in Europe. Subsequently, this downward trend reversed, rising by 6.5% by 2009 and remaining elevated through 2011. This increase corresponds to an additional 7950 suicides above what would be expected on past trends between 2007 and 2010 (see online supplement). Canada too experienced a reversal, as suicides rose by 4.5% (about 240 suicides more than expected) between 2007 and 2009. In the USA, where suicides had been on an upward trajectory, the rate of increase accelerated, with an increase over and above past trends of 4.8%, totalling about 4750 excess suicides between 2007 and 2010. Reference Reeves, Stuckler, McKee, Gunnell, Chang and Basu3 However, those few industrialised countries outside of these regions, such as New Zealand, that have escaped unscathed from the financial crisis have avoided a rise in suicides. These conservative figures suggest that, in total, there have been at least 10 000 more economic suicides than would have been expected in the European Union, Canada and the USA since the Great Recession began in 2007. But are these suicides an inevitable accompaniment of economic hardship?
One clue that, in theory, increased suicides during an economic crisis are avoidable is seen in the marked cross-national variations in countries affected by the current recession. Despite large recessions, some countries experienced no change in suicides, whereas in others suicides rose in step with worsening economies. In general, we observed four main suicide patterns: (a) accelerating rate of previous increase in suicides: USA and Poland; (b) increase from stable trends: Canada; (c) reversal of downward suicide trends: Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, The Netherlands, Portugal, Poland, Romania, Slovenia, Spain and UK; (d) no significant change: Austria and Sweden (missing data and small populations mean that Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, Luxembourg, Malta, and the Slovak Republic are not reported).
Another clue that increases in such suicides can be averted stems from the observation that not everyone is equally affected. Although underlying suicide rates do vary, it is noteworthy that the scale of the increase associated with an economic crisis does too. Rates rose in both men and women but these increases are about fourfold greater among men, widening the pre-existing gap in suicide rates. Between 2008 and 2010, had the change in the male suicide rate not exceeded that among females there would have been 2380 fewer deaths in Europe (see online supplement). This concentration of the increase in working-age men, which is consistent with an extensive body of theory and previous empirical research, Reference Lewis and Sloggett4 also suggests these findings are not due to data artefacts. Although comparisons of suicide rates among countries must be treated with some caution, albeit often overstated, in part because of cultural factors and coding practices (which may, in fact, understate the rise), any such bias should be non-differential with respect to changes within countries and over short periods of time. Reference Birt, Bille-Brahe, Cabecadas, Chishti, Corcoran and Elgie5 Thus, it is implausible that any change in coding rules would selectively affect only one gender and at particular ages.
It is important to check whether these increases are a potential artefact of small numbers. Taking the USA as an example, we found that the acceleration in the suicide rate was a statistically significant departure from the time trend prior to the recession (β = 0.51 (95% CI 0.28-0.75) rise in suicide rate per 100 000 population per year). Reference Reeves, Stuckler, McKee, Gunnell, Chang and Basu3 Thus, these stark variations are likely to be real; revealing the potential of preventing suicides associated with economic crises.
Suicide rates may vary across nations because the depth and nature of recessions also varies. Economic shocks can worsen mental health and, potentially, lead to suicide, through three major pathways. First, job loss is an independent risk factor for increased risk of depression and suicide. Reference Lewis and Sloggett4 Suicide is ∼2.5 times more likely among the unemployed compared with the employed (total odds ratio (OR) = 2.6). Reference Lewis and Sloggett4 Indebtedness, itself a consequence of unemployment, is another, independent risk factor for depression and suicide. Longitudinal data from the UK show that those free from mental health problems at baseline who had financial difficulties were 1.33 times more likely to experience mental illness than those who did not, after controlling for age, gender, marital status, family type, employment status and other socioeconomic measures. Reference Skapinakis, Weich, Lewis, Singleton and Araya6 Third, debt and unemployment leading to foreclosure on mortgages are associated with depression and anxiety-related disorders. Reference Pevalin7 Those who have had their houses repossessed are 1.6 times more likely to experience mental illness than those who have not. Reference Pevalin7 Due to the nature of the recession, unemployment, debt and housing insecurity have risen in Europe and North America increasing suicide risk. Yet, some European countries seem to have avoided this association. For example, in Austria the suicide rate has not increased despite rising unemployment during the recession (online Fig. DS1). Further, our analysis of suicides in the USA suggested that unemployment only explained a small proportion of the variance in suicide rates. Consequently, there is still a large residual not explained by economic shocks. Reference Reeves, Stuckler, McKee, Gunnell, Chang and Basu3
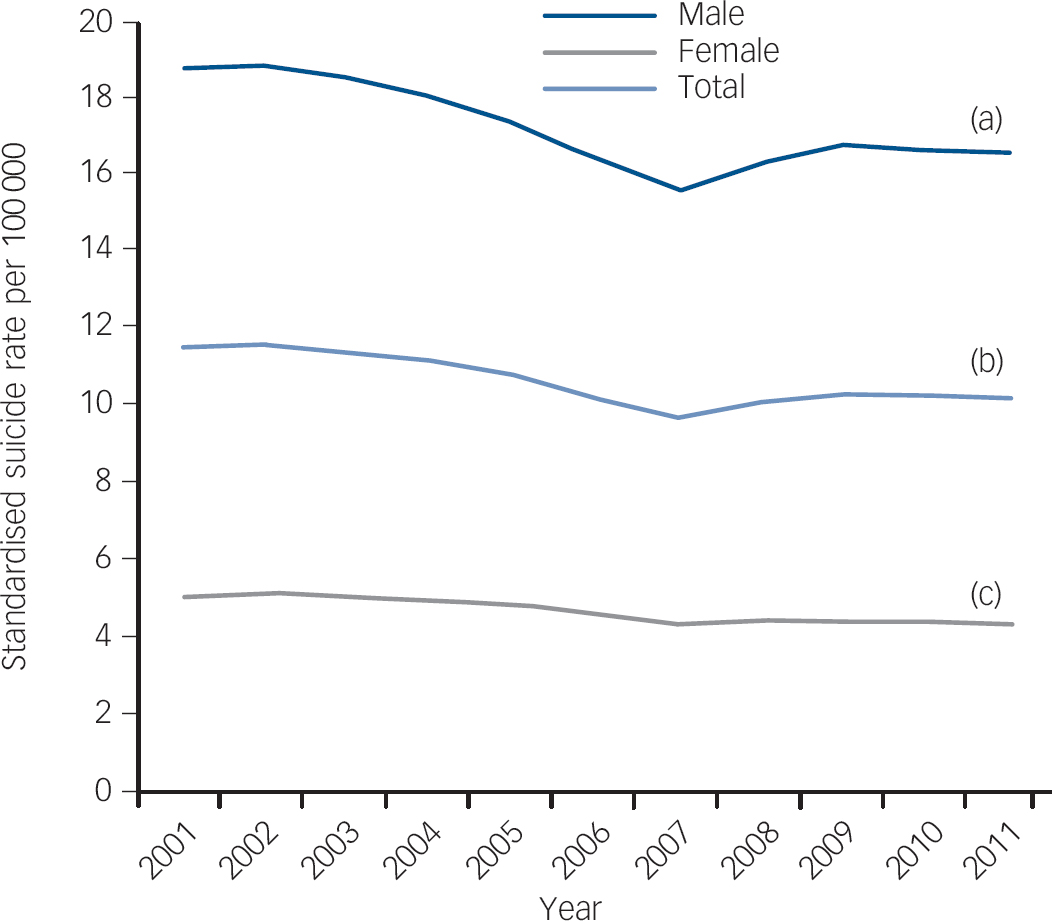
Fig. 1 European Union age-standardised suicide rate for the total population (b), and for males (a) and females (c), 2001-2011.
Discussion
If we accept that these suicides could have been prevented, what could have been done? Looking to recent history, two countries have previously broken this link: Sweden, between 1991 and 1992, and Finland, between 1990 and 1993, both experienced substantial rises in unemployment concurrent with reductions in suicide. Reference Stuckler, Basu, Suhrcke, Coutts and McKee1 In the present recession, Sweden again exhibited no marked increase in total suicide rates. Three factors may increase mental health resilience during economic shocks. One is access to secondary prevention. The majority of suicides occur among persons with clinical depression. Reference Gunnell, Saperia and Ashby8 Effective treatment, such as antidepressants, may moderate the impact of economic shocks on suicide by controlling depression associated with financial uncertainty. Yet, thus far, there is little individual-level evidence to substantiate a protective role of antidepressants against suicide; the most comprehensive meta-analysis to date finds no evidence of a beneficial effect. Reference Gunnell, Saperia and Ashby8 Nonetheless, prescription rates have appeared to rise markedly in some countries during the recent recession, such as the UK where the rate of increase in prescribing accelerated from an 11% rise between 2003 and 2007 to a 19% rise between 2007 and 2010.
Another potentially protective intervention is helping the newly unemployed to return to work. Active labour market programmes, which assist the unemployed find work while providing other forms of support, reduce the impact of unemployment on suicide. Reference Stuckler, Basu, Suhrcke, Coutts and McKee1 In European recessions in 1970-2007, we estimated that each US$100 per capita of investment in active labour market programmes reduced the association of unemployment with suicide by 0.4%. Reference Stuckler, Basu, Suhrcke, Coutts and McKee1
Third, greater gender equality in the workplace may attenuate the mental health risks of economic shocks. Reference Bambra, Pope, Swami, Stanistreet, Roskam and Kunst9 In highly masculine environments, where male identity is bound up with work, job loss poses greater status threat. Conversely, where women’s labour force participation rates are lower, the threat or experience of unemployment may less significantly affect women’s mental health. More research is needed to understand how gender norms and family structures affect vulnerability to economic change. Reference Bambra, Pope, Swami, Stanistreet, Roskam and Kunst9
There is also a need to better understand how to prevent economic shocks from worsening mental health. For now, the evidence that some societies have successfully de-coupled economic shocks from adverse mental health outcomes reveals the hope that it will be possible to eliminate the association of economic shocks with a rise in suicidality. At a time of deep retrenchments in health systems, particularly in mental health services, voices of psychiatrists must not remain silent. The medical community must first be informed about macro-economic policies that affect the health of their patients. They can - and, according to the medical code of ethics, have a duty to - contribute to the mental health of populations, as practitioners but also advocates of evidence-based prevention. Recessions will continue to hurt, but need not cause self-harm.




eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.