Article contents
Nonadiabatic observables in β Cephei star models
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 May 2016
Extract
Results of the recent stability surveys (Dziembowski and Pamyatnykh 1993; Gautschy and Saio 1993) leave no doubts that the opacity mechanism is responsible for oscillations observed in β Cephei stars. The linear nonadiabatic analysis used to determine the instability domains in the HR diagram, yields also quantities that may be compared with observations. These nonadiabatic observables are evaluated from the complex eigenfunctions y(r) and f(r) describing variations of the radial displacement and the bolometric flux, respectively. Both y and f are very nearly constant within the stellar atmosphere. The eigenfunctions describing the horizontal displacement and variations of thermodynamical quantities may be expressed in terms of y and f. Since the linear eigenfunctions may be arbitrarily normalized, there are only two real independent observables. We may choose them to be 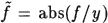 and ψ = arg(f/y). Using static atmosphere models, with the inertial term included in the effective gravity, we may evaluate amplitude ratios and phase differences for integrated changes in directly measured parameters (Dziembowski 1977, Stamford and Watson 1981, Watson 1988).
and ψ = arg(f/y). Using static atmosphere models, with the inertial term included in the effective gravity, we may evaluate amplitude ratios and phase differences for integrated changes in directly measured parameters (Dziembowski 1977, Stamford and Watson 1981, Watson 1988).
- Type
- 1. Pulsation and Rotation
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Kluwer 1994
References
- 1
- Cited by


