No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Enhancement of Thermonuclear Reaction Rate due to Strong Screening
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 August 2015
Extract
The enhancement factor for the rate of thermonuclear reactions which involve two kinds of nuclei with charges Zi and Zj in the strong-screening regime is given for general cases of surrounding nuclear plasmas by the formula, exp[1.25Γij −0.095τij(3Γij/τij)2]. Here, Γij = 2ZiZje2/(ai+aj)T; ai = [3Zi/4πΣkZknk]1/3; τij = [(27π2/4)(2μijZi2Zj2e4Th2)]1/3; μij is the reduced mass for the two reacting nuclei Zi and Zj; and nk is the number density of nuclei Zk. The calculation is based on the recent results of Monte Carlo computations for binary ion mixtures, which have shown that the screening functions hij(r) at intermediate distances [0.5 ≤ r/[(ai+aj)/2] ≤ 1.6] can be expressed to a good degree of accuracy by
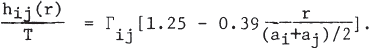
Application to the calculation of carbon ignition in the carbon-oxygen core of a highly evolved star is discussed. The carbon ignition temperature is found to be single-valued as a function of the density in contrast to the work of Graboske.
- Type
- Session 7: Supernova Explosions Leading to the Formation of Neutron Stars and Black Holes
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Reidel 1981


