No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 August 2017
The most direct method of determining distances to galactic sources outside the Solar System is the measurement of annual parallaxes. Using as an example astrometric observations of the quasars 3C345 and NRAO512 which are separated by ∼ 0°.5 at the sky, we show that under certain conditions, annual parallaxes of galactic radio sources can be determined with VLBI with an accuracy of 50 μas (standard error). This accuracy is about tenfold higher than any annual parallax accuracy ever obtained with optical astrometry.
The, so far, most direct method of determining distances to extragalactic sources combines VLBI measurements of a supernova's angular expansion velocity with optical spectroscopic measurements of the supernova's radial expansion velocity. We have estimated the distance to SN1979C in M100 in the Virgo cluster to be 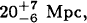 a lower bound on the distance to SN1980K in NGC6946 to be 5 Mpc, and H0 to be
a lower bound on the distance to SN1980K in NGC6946 to be 5 Mpc, and H0 to be 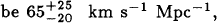 with the uncertainties intended to represent standard errors.
with the uncertainties intended to represent standard errors.