Romantic couples often struggle in situations in which the partners argue about financial issues, how to spend time together, family responsibilities, and bad habits. Indeed, relationship conflict is inevitable with no risks of damaging if they are adequately addressed (Overall, Reference Overall2020). However, ironically, people often respond destructively to their loved ones in times of conflict, and such destructive responses become one of the most challenging relationship problems (Overall & McNulty, Reference Overall and McNulty2017). While the potential (inter) personal consequences of conflict resolution are well-known (e.g., Overall, Reference Overall2020), identifying, clearly, the conditions that promote direct destructive (vs. constructive) conflict-resolution strategies is crucial to help individuals build healthier and happier relationships.
To shed light on this issue, recent research has indicated that power dynamics are essential when negotiating conflict (Pietromonaco et al., Reference Pietromonaco, Overall, Beck and Powers2020). Yet, surprisingly, relatively little theoretical or empirical work has focused on the influence that power differences have on relationship partners and their conflict-resolution responses. Because people often feel the need to influence others to achieve a desirable solution when goals and needs conflict in relationships (Overall et al., Reference Overall, Hammond, McNulty and Finkel2016; Rusbult & van Lange, Reference Rusbult and van Lange2003), the present work investigates whether the ability or capacity to influence the partner’s ideas—namely power within the relationship—plays an important role in determining the type of response used during romantic conflicts. Building on the power and close relationship literature, the current research sought to (a) uncover if powerful people (rather powerless) are more willing to use a direct destructive (vs. constructive) response to their partner during romantic conflict discussions; and if so, (b) untangle the conditions under what powerful people may use a destructive response during romantic conflicts.
Power in Relationships as Determining of Conflict Resolution
Although in many romantic relationships partners strive for equality, asymmetries in levels of dependence commonly result in one partner perceiving to have more relative power than the other across different types of interactions (e.g., Simpson et al., Reference Simpson, Farrell, Oriña, Rothman, Mikulincer, Shaver, Simpson and Dovidio2015). According to the Principle of Least Interest (Kelley & Thibaut, Reference Kelley and Thibaut1978), the partner in a relationship who is less invested or interested in continuing the relationship has relatively more power to influence their partner in their favor because is less affected by their partner’s actions (i.e., has less to lose if the relationship ended) and thus, is more independent of him/her. Therefore, in line with previous literature, holding power in relationships includes both being more independent of the partner as well as being more able to influence the partner to reach desired outcomes (Overall et al., Reference Overall, Hammond, McNulty and Finkel2016; Simpson et al., Reference Simpson, Farrell, Oriña, Rothman, Mikulincer, Shaver, Simpson and Dovidio2015). These power dynamics may have important consequences when negotiating conflicts. In particular, because powerful people are relatively more independent of others, they have the option to decide between displaying constructive or destructive responses during a romantic discussion (Foulk et al., Reference Foulk, Chighizola and Chen2020; Rusbult & Zembrodt, Reference Rusbult, Johnson and Morrow1986). Constructive responses refer to an attempt to maintain the relationship via cooperative or prosocial behaviors such as seeking help, explaining one’s point of view, and suggesting solutions to problems. Destructive responses allow a relationship to atrophy or end it via oppositional behaviors such as being selfish, coercive, or ending the relationship (Rusbult et al., Reference Rusbult, Johnson and Morrow1986).
In line with Kipnis’s (Reference Kipnis1972) early proposition that power corrupts, we propose that powerful, as compared to powerless individuals, may be more likely to respond to their partner via opposition (rather than cooperative) behaviors—that is, using direct destructive conflict resolution. We draw our assumptions from diverse theoretical perspectives on power and close relationships—such as the approach-inhibition theory (Keltner et al., Reference Keltner, Gruenfeld and Anderson2003), and the interdependency theory (Kelley & Thibaut, Reference Kelley and Thibaut1978). Despite their differences, these theoretical models share the assumption that people high in power are less dependent from others, basically because they have the potential to influence and retaliate against others by delivering punishments and withholding rewards. This makes them less vulnerable to potential threats and thus, individuals may directly engage in courses of action that advance their aims rather than broader partner or relationship’s interest. Stated differently, elevated power seems to evoke a focus on personal benefits or desires and hinders power-holders from behaving in favor of relationships welfare (Case et al., Reference Case, Conlon and Maner2015; Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee2003). Supporting this view, traditional research has demonstrated that holding power reduces perspective-taking (Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Magee, Inesi and Gruenfeld2006), compassion (van Kleef et al., Reference van Kleef, Oveis, van Der Löwe, LuoKogan, Goetz and Keltner2008), social affiliative motives (Case et al., Reference Case, Conlon and Maner2015), willingness to help strangers (Lammers et al., Reference Lammers, Galinsky, Gordijn and Otten2012) and, sacrifice in romantic relationships (Riguetti et al., Reference Riguetti, Luchies, van Gils, Slotter, Witcher and Kumashiro2015). Likewise, importantly, a higher power relative to others increases dehumanization (Gwinn et al., Reference Gwinn, Judd and Park2013), abusive behaviors (Cislak et al., Reference Cislak, Cichocka, Wojcik and Frankowska2018), and intimate partner violence (Martín-Lanas et al., Reference Martín-Lanas, Osorio, Anaya-Hamue, Cano-Prous and de Irala2019). Together, this theoretical and empirical reasoning guided us to suggest power as a factor that determines individuals’ destructive rather than constructive responses in times of conflict. Yet, to our knowledge, no prior research has specifically analyzed whether greater power guides individuals’ conflict-resolution responses within relationship interactions in a close relationship context. This link is particularly important in romantic relationships because they are a highly interdependent context where people are also communally oriented and should care or feel responsible about each other’s needs and well-being (Clark & Mills, Reference Clark, Mills, Van Lange, Kruglanski and Higgins2012). In fact, romantic relationships cannot survive long terms if people always act in a dysfunctional manner (Karremans & Smith, Reference Karremans and Smith2010). Therefore, albeit the antisocial view of power may predominate the power literature, powerful individuals might not invariably behave destructively in any conflictual situation (Foulk et al., Reference Foulk, Chighizola and Chen2020). Additionally exploring how relationship power may interlock with the other situational and relational factors provides refined insights (Tost & Johnson, Reference Tost and Johnson2019). In this line, the current investigation expands prior research by testing whether higher power is associated with destructive rather constructive responses in a conflictual situation towards their romantic partner, testing the moderating roles of conflict seriousness and the inclusion of the partner in their self.
Untangling when Power Does Promote Destructive Responses in Romantic Relationships
Considering power heightens goal pursuit during relevant situation contexts (Guinote, Reference Guinote2007), we suggest that variables that constrain those interests during romantic conflicts may prompt individuals’ destructive rather constructive responses to face such conflicts. The seriousness of the conflict—a contextual factor that may affect people’s responses and behaviors by highlighting their own needs (Deutsch et al., Reference Deutsch, Coleman and Marcus2011)—could, firstly, explain under what circumstances powerful individuals may use destructive responses to face conflicts. Evidence has shown that how severely someone interprets the conflict influences how they will react to it (Garrido-Macías et al., Reference Garrido-Macías, Valor-Segura and Expósito2020). Specifically, the perception of conflict as severe increases the demand for solutions, the need to vent frustration, and the use of direct oppositional responses during the conflict (Overall & McNulty, Reference Overall and McNulty2017; Rusbult et al., Reference Rusbult, Johnson and Morrow1986). For example, McNulty and Rusell (Reference McNulty and Russell2010) explained that the discussion of severe relationship problems increases the use of direct oppositional behaviors to effectively resolve problems; conversely, when problems are minor, the use of this response is likely to be perceived as unnecessary. Why would the seriousness of the conflict specifically affect the responses of powerful people? Given its fundamental role in structuring social interactions, conflict might exacerbate the effects of some dimensions of interdependence, for example, relationship power (Rusbult & van Lange, Reference Rusbult and van Lange2003). When the conflict of interest is strong and relevant situations arise, powerful individuals experience important demands that may outweigh their resources, resulting in a greater threat to their position and therefore their goal fulfillment (Scholl, de Wit, et al., Reference Scholl, de Wit, Ellemers, Fetterman, Sassenberg and Scheepers2018). In other words, power-holders might suspect others’ withdrawal of cooperation and fear of losing power (Mooijman et al., Reference Mooijman, van Dijk, van Dijk and Ellemers2019). As not every conflict of interest implies a power imbalance (and vice versa), this suggests that the confluence of both factors may render social interactions particularly troubling from a relationship perspective. Indeed, previous work has shown that when threats to power are high, restoring power has priority, leading to a cascade of defensive responses that aim at protecting individuals from harm (Bukowski et al., Reference Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote, Kofta, Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote and Kofta2017; Deng et al., Reference Deng, Zheng and Guinote2018; Weiss et al., Reference Weiss, Michels, Burgmer, Mussweiler, Ockenfels and Hofmann2020). Thus, we suggest that the higher the perceived degree of conflict, the more the power-holder sees reasons to suspect the possibility of their own goals could be blocked and thus, they might respond to perceived constraints upon their power by increasing negative or antisocial behaviors to get their way during interpersonal conflicts (Carpenter, Reference Carpenter2017; Deng et al., Reference Deng, Zheng and Guinote2018; Foulk et al., Reference Foulk, Chighizola and Chen2020). As a result of these dynamics, we predicted that the perception of having power would be associated with an increase in destructive responses during romantic conflicts (and a decrease in constructive ones), to the extent that people identify romantic conflict as severe.
Secondly, going beyond the previous postulation, different levels of relationship motivations may also differentially affect conflict-resolution responses. Drawing from an interdependence theory framework, individuals goals could be composed by others needs besides the personal ones (Rusbult & van Lange, Reference Rusbult and van Lange2003). Indeed, prior research has shown that romantic relationship partners may have mostly a communal relationship in which individuals’ main goal might be to make happy their partner or take care of their relationship welfare and maintenance, beyond their self-interests (Clark & Mills, Reference Clark, Mills, Van Lange, Kruglanski and Higgins2012). In this line, the conflict resolution of powerful partners may also depend on the degree to which individuals perceived their partner as a central part of their self-concept and thus, include their partner into their conception of the self (IOS; Aron et al., Reference Aron, Aron and Smollan1992). Evidence in interpersonal contexts has shown that when individuals have a high IOS, they are motivated to act constructively, in favor of this person or relationship’s needs, moving their own personal need to the background (Scholl, Sassenberg, et al., Reference Scholl, Sassenberg, Ellemers, Scheepers and de Wit2018). Conversely, having low feelings of connectedness does not promote each partner’s awareness of the other’s needs (Rusbult et al., Reference Rusbult, Verette, Whitney, Slovik and Lipkus1991). Why would IOS affect the conflict responses of powerful people? As outlined above, powerful individuals should better respond in an important situation, especially to what is accessible during these situations (Guinote, Reference Guinote2007). When the other person is close to the powerful one and thus, likely to be included in their self (Aron et al., Reference Aron, Aron and Smollan1992), power should heighten pursuit of relationship-maintenance goals and the powerful person could behave and communicate constructively according to the relationship’s needs (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Lee-Chai and Bargh2001; Scholl, Sassenberg, et al., Reference Scholl, Sassenberg, Ellemers, Scheepers and de Wit2018). Conversely, when the identification is low, the personal self should be salient and individuals probably behave destructively for the relationship, focusing on their personal goals. Accordingly, previous researches have shown that power induces prosocial behaviors when people feel––or are induced to feel––closely connected to the other person (DeMarree et al., Reference DeMarree, Briñol and Petty2014; Gordon & Chen, Reference Gordon and Chen2013; Karremans & Smith, Reference Karremans and Smith2010). However, following a traditional view of power, other studies suggest that powerful people tend to be less committed and connected to their relationships, and thus engage in destructive responses for the relationship (Chen et al., Reference Chen, Lee-Chai and Bargh2001; Lammers et al., Reference Lammers, Galinsky, Gordijn and Otten2012; Riguetti et al., Reference Riguetti, Luchies, van Gils, Slotter, Witcher and Kumashiro2015). Because not all romantic relationships are characterized by the same level of feelings and motivation of connectedness which drives force for engaging in pro-relationship behavior (Rusbult et al., Reference Rusbult, Verette, Whitney, Slovik and Lipkus1991), we suggest that the higher perceived power relative to the romantic partner would be associated with an increase in destructive (not constructive) conflict resolution to the extent that the partner is not considered a central part of their self-concept.
The Current Research
In the present research, three studies were conducted to test the general hypothesis that power would be positively associated with destructive responses and negatively associated with constructive responses to face conflicts (Hypothesis 1). We further examined under what circumstances the perception of power would be associated with conflict resolution, that is, whether the effects of power were moderated by the seriousness of the conflict and IOS. We expected that power would result in greater destructive and lower constructive responses when (a) the conflict was severe rather than mild (Hypothesis 2), (b) one had a low rather than high IOS (Hypothesis 3).
STUDY 1
Method
Sample
Participants were 347 Spanish individuals (207 women) who were involved at least 6 months in a romantic relationship. Originally, 400 participated in the study but 53 were excluded because they did not follow the instructions properly. Participants’ mean age was 22.91 years (SD = 8.79). On average, they reported being involved in a romantic relationship for 4.47 years (SD = 6.97), and 19.6% lived together. A sensitive power analysis was conducted using the linear multiple regression R 2 increase tested in G*Power (Faul et al., Reference Faul, Erdfelder, Buchner and Lang2009) to determine our ability to detect the contribution of interactions between power, seriousness, and IOS. Sensitivity analysis suggests that with this sample (N = 347, α = .05), we have the ability to detect small effect sizes (f 2 ≥ 0.034) with a power level of .80.
Measures and Procedure
Participants were recruited through an incidental sampling procedure in different public locations (e.g., local transportation stations) in a southeast Spanish city. Specifically, a trained evaluator requested the participants’ collaboration and informed them of the estimated study’s duration (approximately 15 min) and the agreement with the principles of confidentiality and anonymity regarding their responses. After signing an informed consent form, participants who affirmed being involved in a romantic relationship were asked to complete the questionnaire booklet individually and voluntarily. First, they were asked to indicate to what extent they have power in their romantic relationship using the Spanish adaptation of the Sense of Power Scale (e.g., “I can make my partner listen to me”; Anderson et al., Reference Anderson, John and Keltner2012; Willis et al., Reference Willis, Carretero-Dios, Rodríguez-Bailón and Petkanopoulou2016), composed by 8 items rated on a 7-point Likert scale (1 = totally disagree, 7 = totally agree); Cronbach’s alpha =. 73. Then, individuals were asked to conceptualize their own experiences of relationship closeness using an adapted Spanish version of the Inclusion of the other in the self (IOS) scale (Aron et al., Reference Aron, Aron and Smollan1992; Gómez et al., Reference Gómez, Brooks, Buhrmester, Vázquez, Jetten and Swann2011). This pictorial scale includes five sets of two circles in which one of the circles represents the “self” of the participant and the other circle represents their “partner”. Each set depicts the circles with different degrees of overlap (1 = totally independent, 5 = almost completely overlapping). Therefore, participants had to indicate which model most closely represented their relationship. Next, individuals were asked to vividly describe, in writing, a conflict situation that they had experienced with their intimate partner. After writing about this incident, they were asked to complete another short questionnaire about this conflict situation. Specifically, participants rated the severity of the conflict described using 4 items (e.g. “At the time of the incident you described above, how trivial or severe was the problem?”; Rusbult et al., Reference Rusbult, Johnson and Morrow1986; Valor-Segura et al., Reference Valor-Segura, Expósito and Moya2014) on a 6-point Likert Scale (1 = not all severe, 6 = extremely severe); Cronbach’s alpha = .89. Then, participants were asked to report how they responded to the described conflict situation with their partner using the Adaptation of the Accommodation in Romantic Couples Scale (ARCS) to the Spanish Population. This measure was composed by 27 items rated on a 9-point Likert scale (1 = I did not do that, 9 = I showed that type of behavior; Valor-Segura et al., Reference Valor-Segura, Garrido-Macías and Lozano2020) that included a direct “destructive” conflict resolution subscale (e.g. “When I am very upset with my partner I think about terminating our relationship”; α = .91) and the direct “constructive” conflict resolution subscale (e.g. “When things aren’t going well between us, I suggest changing things in the relationship to solve the problem”; α = .75). Once participants filled the questionnaire, they were fully debriefed and thanked.Footnote 1
Results and Discussion
Statistical Analysis Strategy
Descriptive statistics and correlations for all variables are displayed in Table 1. Hierarchical regression analyses were performed to test the predictive contribution of power, the seriousness of the conflict, IOS, and their interactions terms to destructive and constructive responses, using SPSS Version 21. Specifically, sociodemographicFootnote 2 factors were entered in Step 1 (method: Enter); power (standardized), seriousness (standardized), and IOS (standardized) were included in Step 2 (method: Enter); and the two-way interactions of Power × Seriousness, Pwer × IOS, and Seriousness × IOS were incorporated in Step 3 (method: Enter) of the regression model.Footnote 3 When the expected interactions emerged, we performed simple slopes analyses to interpret the interactions for high (+1SD) and low (−1SD) conflict seriousness and IOS.
Table 1. Mean, Standard Deviations, and Correlations for the Main Variables in Each Study

Note. IOS = Inclusion of the Other in the Self; Higher scores on continuous variables indicate greater standing on the variable (e.g., greater Power).
a In Study 3, a dichotomy measure of power was used (0 = powerless; 1 = powerful).
b In Studies 2 and 3, a dichotomy measure of seriousness was used (0 = mild; 1= severe).
* p < .05.
** p < .001.
Key Analyses
As Table 2 displays, power was related to destructive responses; that is participants were more likely to respond destructively as they reported perceiving increasing amounts of power in the relationship. Moreover, as expected, the effect of power on destructive responses was moderated by the seriousness of the conflict, as well as, by IOS. Simple slope analyses (Figure 1) revealed that power was not associated with destructive responses in the case of mild conflict situations (−1 SD), β = .13, t = 1.78, p = .077, 95% CI [−0.01, 0.26]. Conversely, this association emerges in the case of severe conflict situations (+1 SD), β = .30, t = 5.16, p < .001, 95% CI [0.17, 0.51]. Likewise, as Figure 2 shows, power was not associated with destructive responses for people high (+1 SD) in IOS, β = −.01, t = −0.01, p = .993, 95% CI [−0.15, 0.15], but this association emerges for people low (−1SD) in IOS, β = .27, t =3.44, p = .001, 95% CI [0.11, 0.42]. Therefore, the more power a person perceives in their relationship, the more destructively respond in a conflict situation when the conflict was severe, or they were lowly identified with their partner (low IOS).
Table 2. Moderated Multiple Regression Analysis of Destructive & Constructive Responses as a Function of Power, Conflict’s Seriousness, and IOS (Study 1)

Note. N = 347; IOS = Inclusion of the Other in the Self; SE = standard error; CI = confidence interval. Higher scores on continuous variables indicate greater standing on the variable (e.g., greater Power). CI that does not include 0 indicates statistically meaningful associations.
* p < .05.
** p < .01.
*** p < .001.
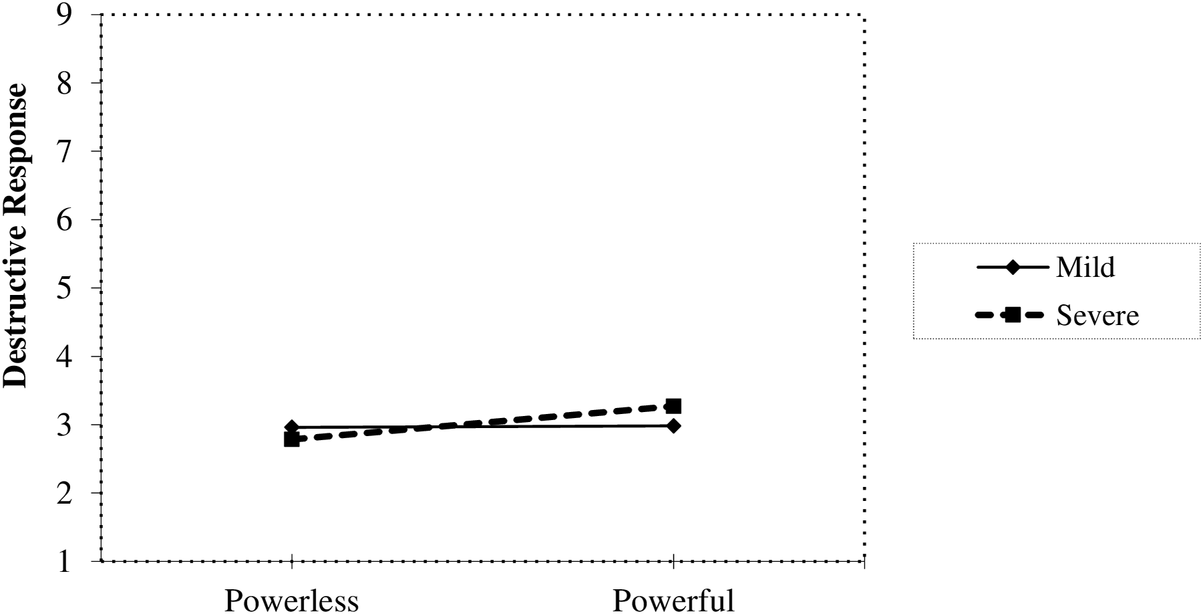
Figure 1. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Seriousness of the Conflict Predicting Destructive Conflict Resolution. Study 1 (N = 347).

Figure 2. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Inclusion of the Other in the Self (IOS) Predicting Destructive Conflict Resolution. Study 1 (N = 347).
For constructive responses, there was no significant main effect of power and no significant second order interaction of power and the seriousness of the conflict, and power and IOS.
In sum, the findings provide preliminary evidence that powerful individuals are more likely to respond destructively (not constructively) if the conflict was severe and to the extend participant had a low IOS; this does not occur during mild conflicts if they have a high level of IOS. Despite our results confirm that severe incidents would facilitate the power-holders’ destructive responses as an attempt to defend their own interests (Bukowski et al., Reference Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote, Kofta, Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote and Kofta2017; Deng et al., Reference Deng, Zheng and Guinote2018), previous research has shown that, in general, people with high power perceive less conflict given their relative independence to others (Weiss et al., Reference Weiss, Michels, Burgmer, Mussweiler, Ockenfels and Hofmann2020). Therefore, Study 2 aimed to replicate the previous findings and extend them by experimentally inducing the seriousness of the conflict to make most salient an important conflict situation in which aims and desires may be strongly threatened.
STUDY 2
Method
Sample
Participants were 221 Spanish individuals (115 women) who were involved at least 6 months in a romantic relationship. Originally, 240 participated in the study but 19 were excluded because they did not follow the instructions properly. Participants’ mean age was 34.72 years (SD = 11.09). On average, they reported being involved in a romantic relationship for 10.91 years (SD = 10.57), and 58.8% lived together. As in the previous study, the sensitive power (Faul et al., Reference Faul, Erdfelder, Buchner and Lang2009) suggests that with this sample (N = 221, α = .05), we have the ability to detect small effect sizes (f 2 ≥ 0.055) with a power level of .80.
Measures and Procedure
Participants were recruited following the same procedure as in Study 1. They provided informed written consent and then, individually, completed the questionnaire in which they, first, rated their perceived power (α = .86) and IOS as in Study 1. Next, individuals were asked to vividly describe, in writing, a conflict situation that they had experienced with their intimate partner. However, in this case, the conflict experienced with the partner was manipulated depending on it seriousness (mild or severe). Specifically, participants were randomly assigned to complete a priming essay—adapted from Valor-Segura et al. (Reference Valor-Segura, Expósito and Moya2014)—intended to elicit conflicts of different seriousness (mild or severe). Their task instructions were: “Please recall a particular incident in your relationship in which you experienced a [mild/severe] conflict or discussion. Please describe this situation—what happened, how you felt, and so forth”. After writing about the assigned incident, they were asked to complete another short questionnaire about this conflict situation. Specifically, to check the effectiveness of the manipulation, participants were asked to rate the severity of the conflict described using 1 item (e.g., “How severe do you consider the previous discussion that you described?”) rated on a 6-point Likert Scale (1 = not severe, 6 = extremely severe). Then, as in Study 1, participants were asked to report their conflict-resolution responses: destructive (α = .91) and constructive (α = .84). Once participants filled the questionnaire, they were provided with information about the study.1
Results and Discussion
Statistical Analysis Strategy
Descriptive statistics and correlations for all variables are displayed in Table 1. To verify the effectiveness of the experimental manipulation a Student’s t-test with the experimental condition (mild vs. severe conflict) as the independent variable and “perceived seriousness” as the outcome variable was conducted. Then, as in Study 1, we performed hierarchical regression analyses to test the predictive contribution of power (standardized), the seriousness of the conflict (0 = mild, 1 = severe), IOS (standardized), and their interactions terms to destructive and constructive responses.
Manipulation Check
The results yielded statistically significant differences depending on condition t = −13.43, p < .001, d = −1.82. As expected, participants in the severe condition (M = 4.55, SD = 1.27) reported having described a conflict more severe that did participants in the mild condition (M = 2.40, SD = 1.09).
Key Analyses
As Table 3 displays, there was no significant main effect of power on destructive responses. However, as expected, the effect of power on destructive responses was moderated by the seriousness of the conflict, as well as, by IOS. Simple slope analyses (Figure 3, Panel A) revealed that power was not associated with destructive responses in the case of mild conflict situations (−1 SD), β = −.04, t = −0.41, p = .680, 95% CI [−0.13, 0.08]. Conversely, this association emerges in the case of severe conflict situations (+1 SD), β = .38, t = 4.35, p < .001, 95% CI [0.26, 0.69]. Likewise, as Figure 4 shows, although power was not associated with destructive responses for people high (+1 SD) in IOS, β = −.01, t = −0.01, p = .993, 95% CI [−0.15, 0.15], this association emerges for people low (−1 SD) in IOS, β = .16, t = 1.96, p = .052, 95% CI [0.00, 0.35]. Therefore, the more power a person perceive in their relationship, the more destructively respond in a conflict situation when the conflict was severe, or they were lowly identified with their partner (low IOS).
Table 3. Moderated multiple regression analysis of Destructive & Constructive Responses as a function of Power, Conflict’s Seriousness, and IOS (Study 2)

Note. N = 221; IOS = Inclusion of the Other in the Self; SE = standard error; CI = confidence interval. Higher scores on continuous variables indicate greater standing on the variable (e.g., greater Power). CI that does not include 0 indicates statistically meaningful associations.
* p < .05.
** p < .01.
*** p < .001.

Figure 3. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Seriousness of the Conflict Predicting Destructive (Panel A) and Constructive (Panel B) Conflict Resolution. Study 2 (N = 221).

Figure 4. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Inclusion of the Other in the Self (IOS) Predicting Destructive Conflict Resolution. Study 2 (N = 221).
For constructive responses, there was a significant main effect of power; that is participants were less likely to communicate constructively if they were the power-holder in the relationship. Moreover, as expected, the effect of power on constructive responses was moderated by the seriousness of the conflict. Simple slope analyses (Figure 3, Panel B) revealed that power did not led to constructive responses in the case of mild conflict situations, β = .06, t = 0.59, p = .556, 95% CI [−0.12, 0.21]. Conversely, this association emerges in case of severe conflict situations, β = −.44, t = −5.02, p < .001, 95% CI [−0.72, −0.31]. Lastly, the effect of power on constructive responses was not moderated by IOS.
In sum, Study 2 corroborated the findings of Study 1. Powerful individuals are more likely to respond destructively (and not constructively) during a severe conflict and to the extend participant had a low IOS; this does not occur during a mild conflict or if they have a high level of IOS. Despite these findings provide strong external validity because were found regarding self-reported past conflicts, the data precludes any conclusions about causality. To resolve this issue, in Study 3, besides the seriousness of the conflict, power was manipulated using a well-established experiential priming procedure (Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee2003).
STUDY 3
Method
Sample
Participants were 160 Spanish individuals (82 women) who were involved at least 6 months in a romantic relationship. Participants’ mean age was 27.69 years (SD = 9.93). On average, they reported being involved in a romantic relationship for 6.19 years (SD = 8.14), and 40.9% lived together. As previous studies, the sensitivity analysis suggests that with this sample (N = 160, α = .05), we have the ability to detect small effect sizes (f 2 ≥ 0.077) with a power level of .80.
Measures and Procedure
Participants were recruited following the same procedure as in Studies 1 and 2. They provided informed written consent, and then, individually completed the questionnaire in which they first rated their IOS. Next, individuals were asked to vividly describe, in writing, a conflict situation that they had experienced with their intimate partner in which the seriousness of the conflict (mild or severe) and the participants’ power (powerless or powerful) were manipulated. Specifically, participants were randomly assigned to complete an essay in which the first priming intended to elicit conflicts of different seriousness (situations that could be described as mild or severe) as in Study 2, and the second priming intended to elicit either feeling of low or high power. For the second aim, we used an experiential priming procedure—adapted from a manipulation of power by Galinsky et al. (Reference Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee2003), and previously used in the literature by Laurin et al., (Reference Laurin, Fitzsimons, Finkel, Carswell, vanDellen, Hofmann, Lambert, Eastwick, Fincham and Brown2016)—which manipulates people’s relative perception of power in a specific situation. Specifically, participants were divided into two conditions. In the powerless condition, the task instructions were: “Please recall a [mild/severe] incident in your relationship [in which your partner had power over you]. By power, we mean a situation in which your partner had control of your ability to get something you wanted, or was in a position to evaluate you. Please describe this situation in which you did not have power—what happened, how you felt and so forth”. In the powerful condition, the task instructions were: “Please recall a [mild/severe] incident in your relationship [in which you had power over your partner]. By power, we mean a situation in which you controlled the ability of your partner to get something they wanted or were in a position to evaluate him/her. Please describe this situation in which you had power—what happened, how you felt, and so forth”. After writing about this incident, they were asked to complete another short questionnaire about this conflict situation. Specifically, to check the effectiveness of the conflict’ seriousness and power manipulations, participants were asked to rate the severity of the conflict described using 1 item (e.g., “How severe do you consider the previous discussion that you described?”) rated on a 6-point Likert Scale (1 = not severe, 6 = extremely severe); and to what extend they had power during the conflict described using 1 item (e.g., “Do you think that you had control and influence on the discussion previously described with your partner?”) rated on a 6-point Likert Scale (1 = no control and influence, 6 = much control and influence). Then, as in Study 1 and 2, participants were asked to report their conflict-resolution responses: destructive (α = .92) and constructive (α = .75). Once participants filled the questionnaire, they were provided with information about the study.1
Results and Discussion
Statistical Analysis Strategy
Descriptive statistics and correlations for all variables are displayed in Table 1. To verify the effectiveness of the experimental manipulations two Student’s t-test were conducted with the seriousness (mild vs. severe conflict) and power (powerless vs. powerful) experimental condition as the independent variables and perceived seriousness and power, respectively, as the outcomes variable. Then, as in Studies 1 and 2, we performed hierarchical regression analyses to test the predictive contribution of power (0 = powerless, 1 = powerful), the seriousness of the conflict (0 = mild, 1 = severe), IOS (standardized), and their interactions terms to destructive and constructive responses.
Manipulation Checks
The results yielded statistically significant differences depending on seriousness condition (t = −5.52, p < .001, d = −0.88), and power condition (t = −7.53, p < .001, d = −1.23). Participants in the severe condition (M = 4.34, SD = 1.59) reported having described a conflict more severe that did participants in the mild condition (M = 3.01, SD = 1.43). Moreover, participants in the powerful condition (M = 4.59, SD = 1.22) reported having described a conflict in which they feel more power that did participants in the powerless condition (M = 3.01, SD = 1.36).
Key Analyses
As Table 4 displays, power was related to destructive responses; that is participants were more likely to respond destructively as they reported perceiving increasing amounts of power in the relationship. Moreover, as expected, the effect of power on destructive responses was moderated by the seriousness of the conflict and IOS. Simple slope analyses (Figure 5, Panel A) revealed that power was not associated with destructive responses in the case of mild conflict situations (−1 SD), β = .20, t = 1.79, p = .077, 95% CI [−0.04, 0.67]. Conversely, this association emerges in the case of severe conflict situations (+1 SD), β = .49, t = 4.89, p < .001, 95% CI [0.63, 1.50]. Likewise, as Figure 6 shows, although power was not associated with destructive responses for people high (+1 SD) in IOS, β = .14, t = 1.15, p = .256, 95% CI [−0.18, 0.65], this association emerges for people low (−1SD) in IOS, β = .43, t = 4.36, p < .001, 95% CI [0.52, 1.40]. Therefore, replicating previous results, the more power a person perceives in their relationship, the more destructively respond in a conflict situation when the conflict was severe, or they were lowly identified with their partner (low IOS).
Table 4. Moderated Multiple Regression Analysis of Destructive & Constructive Responses as a Function of Power, Conflict’s Seriousness, and IOS (Study 3)

Note. N = 160; IOS = Inclusion of the Other in the Self; SE = standard error; CI = confidence interval. Higher scores on continuous variables indicate greater standing on the variable (e.g., greater IOS). CI that does not include 0 indicates statistically meaningful associations.
* p < .05.
** p < .01.
*** p < .001.

Figure 5. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Seriousness of the Conflict Predicting Destructive (Panel A) and Constructive (Panel B) Conflict Resolution. Study 3 (N = 160).

Figure 6. The Interaction among Perceived Power and the Inclusion of the Other in the Self (IOS) Predicting Destructive Conflict Resolution. Study 3 (N = 160).
For constructive responses, there was a significant main effect of power; that is participants were less likely to respond constructively if they were the power-holder in the relationship. Moreover, as expected, the effect of power on constructive responses was moderated by the seriousness of the conflict. Simple slope analyses (Figure 5, Panel B) revealed that power did not led to constructive responses in the case of mild conflict situations and, β = −.04, t = −0.37, p = .711, 95% CI [−0.51, 0.35]. Conversely, this association emerges in case of severe conflict situations, β = −.30, t = −2.79, p = .007, 95% CI [−1.07, −0.18]. Lastly, the effect of power on constructive responses was not moderated by IOS. In sum, Study 3 corroborated that powerful individuals are more likely to respond destructively (not constructively) during a severe conflict, and to the extend participant had a low IOS; this does not occur during a mild conflict or if they have a high level of IOS.
Internal Mini Meta-Analysis
To determine the strength, reliability, and robustness of our conclusions, we conducted an internal mini meta-analysis to test our hypotheses across studies per the recommendations of Goh et al. (Reference Goh, Hall and Rosenthal2016).
Statistical Analysis Strategy
First, we carried on a mini meta-analysis of the main effect of perceived power on destructive and constructive responses across the three studies. Second, we tested if the associations between perceived power and destructive or constructive responses are moderated by seriousness and IOS. Next, we conducted the mini meta-analysis using the effect sizes for the relation between power and destructive or constructive responses for participants high and low in moderation variables (e.g., 1 SD above and below the mean of conflict seriousness and IOS). We used fixed effects in which the correlations (a measure of effect size) were calculated from the sample size along to the t-value of the multiple regressions. Positive correlations indicate that a higher level of power is associated with a higher level of destructive/constructive responses, whereas negative correlation associated a higher level of power with a lower level of destructive/constructive responses. Analyses were conducted using the most recent version of the mini meta-analysis Excel template created by Goh et al. (Reference Goh, Hall and Rosenthal2016).
Results
Main Effect of Power on Destructive/Constructive Responses (Hypothesis 1)
Result revealed that power was positively related to destructive responses (r = .17, p < .001, CI [0.10, 0.24]), and negatively related constructive responses (r= −.13, p < .001, CI [−0.19, −0.05]).
Moderation of Power by the Seriousness of the Conflict (Hypothesis 2)
Results revealed that the interaction effect of power with seriousness was positively related to destructive responses (r = .14, p < .001, CI [0.07, 0.21]), and negatively related constructive responses (r= −.16, p = .033, CI [−0.31, −0.01]). Specifically, power was positively associated to destructive responses (r = .37, p < .001, CI [0.27, 0.45]) and negatively related to constructive responses (r = −.27, p < .001, CI [−0.36, −0.16]) among severe conflicts, but not during mild conflicts (r = .08, p = .087, CI [−0.02, 0.19] and r = .01, p = .929, CI [−0.09, 0.11], respectively).
Moderation of Power by IOS (Hypothesis 3)
Results revealed that the interaction effect of power with IOS was related to destructive responses (r = .15, p < .001, CI [0.08, 0.22]). However, no association emerged between the interaction effect of power with IOS and constructive responses (r= −.04, p = .316, CI [−0.12, 0.19]). Specifically, power was positively associated to destructive responses (r = .20, p < .001, CI [0.13, 0.27]) among low IOS individuals, but not in high IOS individuals (r = .03, p = .115, CI [−0.04, 0.11]).Footnote 4
General Discussion
Existing studies suggest that having (or lacking) power has many effects on people and their actions (Cho & Keltner, Reference Cho and Keltner2020; Deng et al., Reference Deng, Zheng and Guinote2018; Willis & Rodriguez-Bailon, Reference Willis and Rodríguez-Bailón2010). However, until now, the role of power as the main factor that promotes individuals’ conflict resolution responses in romantic contexts and the conditions that stimulate power-holders’ responses have seldom been explored. Across three studies, the primary findings of this research showed that power was positively associated with destructive responses and negatively associated with constructive responses. Bolstering work on the approach-inhibition theory of power (Keltner et al., Reference Keltner, Gruenfeld and Anderson2003) and interdependency theory (Kelley & Thibaut, Reference Kelley and Thibaut1978), results suggest that the perception of power is associated with increased freedom and independence from others, which in turn can promote individuals to prioritize self-interest over the relationship’s earnings, as reveals their destructive responses (Case et al., Reference Case, Conlon and Maner2015; Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee2003; Cho & Keltner, Reference Cho and Keltner2020). Therefore, these findings extend prior research that shows the negative consequences of social power for interpersonal relations (e.g., Case et al., Reference Case, Conlon and Maner2015; Cislak et al., Reference Cislak, Cichocka, Wojcik and Frankowska2018; Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee2003; Keltner et al., Reference Keltner, Gruenfeld and Anderson2003; Lammers et al., Reference Lammers, Galinsky, Gordijn and Otten2012; Riguetti et al., Reference Riguetti, Luchies, van Gils, Slotter, Witcher and Kumashiro2015; Willis & Rodriguez-Bailon, Reference Willis and Rodríguez-Bailón2010), and provide evidence that the psychological perception of power could also emerge as an important factor that guides people’s destructive responses towards their loved ones in times of conflict.
The second, perhaps most noteworthy, finding from this research is that the perception of having power is associated with greater destructive and lower constructive responses to the extent that the conflict was severe and participants had a low IOS. We provide evidence that powerful individuals do not invariably behave destructively in a conflictual situation instead, these findings advance the close relationship literature by identifying the particular conditions under destructive responses can be triggered in powerful individuals (Foulk et al., Reference Foulk, Chighizola and Chen2020). Specifically, as we have shown, these oppositional responses may be particularly relevant in situations of severe conflict, which presumably endanger their important personal goals (Carpenter, Reference Carpenter2017). Following Guinote’s (Reference Guinote2007) situated focus theory of power, these results suggest that power-holders, who are better at distinguishing potential threats to their personal goals, might be particularly oriented to the fulfillment of those goals using destructive responses probably in a direct attempt to control their partners, thereby maintaining and even imposing their own powerful position, needs, and desires (Bukowski et al., Reference Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote, Kofta, Bukowski, Fritsche, Guinote and Kofta2017; Deng et al., Reference Deng, Zheng and Guinote2018; Scholl, de Wit, et al., Reference Scholl, Sassenberg, Ellemers, Scheepers and de Wit2018). Therefore, our findings confirm that given its fundamental role in structuring social interactions, the perception of conflict can exacerbate the effects of power (Weiss et al., Reference Weiss, Michels, Burgmer, Mussweiler, Ockenfels and Hofmann2020).
Beyond the seriousness of the conflict, because romantic relationships are characterized by higher levels of communal strength (Clark & Mills, Reference Clark, Mills, Van Lange, Kruglanski and Higgins2012), we additionally considered that the effect observed thus far may be due to individuals’ goals and to what extend their partner is included in their prior needs and goals. Interestingly, our results indicated that when powerful individuals who, according to the self-concept expansion model (Aron et al., Reference Aron, Aron and Smollan1992) do not include other into the self, seem less concerned with others’ needs—in short, they communicate destructively with others. We thus propose that the low IOS or the perception of disconnection between a person and his or her partner may make powerful people move their personal interests rather than relational goals to the foreground. When this happens and individuals’ personal goals are highlighted, either because their IOS with the partner is low and they respond more to personal goals or because such goals are prioritized or threatened by a severe conflict, power-holder may increase their tendency to think, feel, and act in typically powerful ways to restore their control position, according to the classic power literature (Galinsky et al., Reference Galinsky, Magee, Inesi and Gruenfeld2006; Kipnis, Reference Kipnis1972). In the short-run, this could be functional because conflicts may vanish quickly and powerful individuals may get their goals (Overall, Reference Overall2020). However, in the long run, serious problems could remain unaddressed (Overall & McNulty, Reference Overall and McNulty2017). For example, on a stable basis, powerful partners may continue problematic behavior that may adversely impact the relationship quality (Overall, Reference Overall2020). Thus, scientists and therapists should understand which mechanisms could change this destructive pattern. Our findings provide critical evidence that power dynamics in relationships are contingent on the seriousness of the conflict and the levels of partner’s inclusiveness. Marital therapy interventions could use this information to provide skills regarding behavioral patterns that will be more helpful versus detrimental in resolving the challenges of social life. For instance, individuals could analyze targeting issues related to the perception of threat and disconnection between a person and his or her partner when severe relationship problems appear, and whether their response may be more or less effective at navigating interpersonal interactions. Future studies could complement these findings and analyze whether individual differences (e.g., attachment styles), adherence to certain social norms (e.g., traditional gender beliefs), and partner’s responsiveness could also shape how individuals respond to relationship conflicts.
Finally, some limitations of the current research should be acknowledged when interpreting results. First, the sample of our studies was withdrawn from the young general population. Because previous studies have revealed that there is a developmental shift in the way that conflict is handled in later life (e.g., older couples perceive conflict as less stressful and cope with them more proactively; Neubauer et al., Reference Neubauer, Smyth and Sliwinski2019), future studies using a larger sample composed by a representative participants’ selection of each cohort from the general population should corroborate our finding in more detail. Second, albeit the findings regarding past conflict situations have strong external validity, the use of retrospective bias could also trigger all sorts of memory biases. Hence, power and the seriousness of the conflict were manipulated, thereby allowing us to exercise more control over our findings and minimize other causal pathways. However, to gain convergent validity, utilizing different methodologies may be useful in future studies. Third, in the present research, the sizes of some effects presented are small. This might be due we conceptualized power based on a general person’s perceived ability to control decisions and outcomes in a relationship. Future studies may benefit from testing our predictions at a couple level to calculate the power each partner has in a specific domain and their relative influence across domains (Farrell et al., Reference Farrell, Simpson and Rothman2015). Lastly, previous research has shown that direct destructive conflict communication have negative consequences in relationships when it was stable, but is less harmful when partners’ negative-direct behavior varied across time (Overall, Reference Overall2020). Thus, the identification of variability versus stability as a consequential feature of social behavior could offer fruitful directions for examining how power and personal or contextual factors shape interpersonal patterns such as romantic conflicts. Despite these limitations, we should highlight that the utilization of samples of adults involved in established romantic relationships and the replication of results across studies are notable strengths of this research.
It is an irony of life that the people we love the most, such as our romantic partners, are also the people towards which we display destructive behaviors in times of conflict. A key contribution of this research stems from introducing relative power as a factor to determine such conflict-resolution strategies and the underlying circumstances that explain when this happens. The seriousness of the conflict and IOS thus may be necessary to understand individuals’ conflict-resolution responses and may help marital intervention researchers develop specialized intervention strategies for couples based on their relationships characteristics and dynamics. We also expect that this research will open up interesting avenues for future work on the psychosocial mechanisms that emerge from close relationship interactions and the ways in which they can help people to constructively cope with conflict in the context of romantic relationships.












