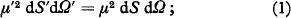No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 April 2016
The classical theorems on the intensity of radiation (e.g. Milne) depend on the geometry of rectilinear ray trajectories in uniform media. In particular, the theorem concerning the specific intensity I in a medium specified by an isotropic refractive index μ—that, where there are no gains due to emission or losses due to absorption or scattering, the quantity I/μ2 = constant—is proved by assuming that the medium consists of a series of regions of constant refractive index at whose plane interfaces the coefficients of reflection are zero. For these the geometry of the trajectories (Figure 1) is such that, by Snell’s law,