Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 November 2024
There are different classes of pulsating stars in the H-R diagram. While many of those classes are undisputed, some remain a mystery such as the objects historically called ‘Maia variables’. Whereas the presence of such a class was suggested seven decades ago, no pulsational driving mechanism is known that could excite short-period oscillations in these late B to early A-type stars. Alternative hypotheses that would render the reports of variability of those stars erroneous have been proposed such as incorrect effective temperatures, binarity or rapid rotation, but no certain conclusions have been reached yet. Therefore, the existence of these variables as a homogeneous class of pulsating star is still under discussion. Meanwhile, many new candidates of these variables have been claimed especially by using photometric observations of space telescopes. In this study, we examined 31 objects that are alleged members of this hypothetical group and carried out detailed spectroscopic and photometric analyses to test the proposed hypotheses for their cause of variability. The 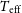 $T_\textrm{eff}$,
$T_\textrm{eff}$, 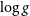 $\log g$,
$\log g$, 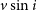 $v \sin i$, and chemical abundances of the targets were determined and the TESS photometric data were examined. As a result, we found that most of these targets are located inside the
$v \sin i$, and chemical abundances of the targets were determined and the TESS photometric data were examined. As a result, we found that most of these targets are located inside the 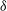 $\delta$ Scuti,
$\delta$ Scuti, 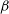 $\beta$ Cephei, or SPB star instability strips, a few show evidence for binarity and others for rapid rotation. We give arguments that none of the apparently rapid pulsations in our targets is caused by a star outside any known instability strip. By extrapolation, we argue that most stars proposed as pulsators outside well-established instability domains are misclassified. Hence there is no sufficient evidence justifying the existence of a class of pulsating stars formerly known as the ‘Maia variables’.
$\beta$ Cephei, or SPB star instability strips, a few show evidence for binarity and others for rapid rotation. We give arguments that none of the apparently rapid pulsations in our targets is caused by a star outside any known instability strip. By extrapolation, we argue that most stars proposed as pulsators outside well-established instability domains are misclassified. Hence there is no sufficient evidence justifying the existence of a class of pulsating stars formerly known as the ‘Maia variables’.
To send this article to your Kindle, first ensure no-reply@cambridge.org is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about sending to your Kindle. Find out more about saving to your Kindle.
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox.
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive.