In public health nutrition, sustainability refers to the ability to maintain food system capacity to support the nutritional health needs of current and future populations while protecting the ecological systems that produce food. The FAO defines sustainable diets as those that are ‘protective and respectful of biodiversity and ecosystems, culturally acceptable, accessible, economically fair and affordable; nutritionally adequate, safe and healthy; while optimizing natural and human resources’( 1 ).
Traditionally, sustainability has been largely overlooked in public health nutrition activities as they have tended to focus on addressing relatively short-term nutritional needs of populations and framed these needs mainly within a biological health context. Yet, it is an immutable fact that we live in a world of physical limits. We cannot create an infinite supply of land, water, nutrients and fossil-fuel energy resources to drive food systems indefinitely, nor can we continue to withstand the excessive losses and waste of food, or the resources used to produce it. Current threats to sustainability are presenting unprecedented risks to public health nutrition globally. These risks necessitate that sustainability be positioned as integral to public health nutrition research, teaching, policy and professional practice.
Historically, there have been threats to sustainability and consequent risks to public health nutrition. The differences now are that the threats are more substantial, complex and evolving rapidly. For example, the World Meteorological Organization( 2 ) reports that 2014 was the hottest year on record, inevitably affecting food production. Moreover, the WHO( 3 ) reports that in 2014 39 % of the world’s adult population was overweight or obese, a situation that is not only the major contributing factor to the global burden of disease( Reference Lim, Vos and Flaxman 4 ), but also the excessive food consumption with which it is associated represents an unnecessary use of finite resources and production of greenhouse gas emissions (GHGE).
Our dietary behaviours and the way we have developed and operate food systems are contributing to the disruption of ecological systems that are crucial to sustainability. The consequences of this disruption are profound and include adverse impacts on food security, nutritional quality, variety, safety and ultimately public health nutrition; not to mention the quality of lives of those producing the food, especially in resource-poor settings. The need for action is critical – action to remove the causes of the problems, build resilience to the problems and treat the symptoms of the problems.
A diversity of UN agencies, national governments, non-government organizations, philanthropists and private-sector groups are calling for policies to redesign food systems to help promote healthy and sustainable diets. Notably, the Zero Hunger Challenge, delivered by UN Secretary General Ban Ki Moon at the close of Rio+20, positions sustainable food systems at the centre of its five pillars( 5 ). In 2014, the FAO/WHO Second International Conference on Nutrition devoted nine of its sixty recommendations to actions for sustainable food systems promoting healthy diets( 6 ). The Final Report of the previous Special Rapporteur on the Right to Food, Olivier DeSchutter, has sustainable food systems, sustainable diets and sustainable consumption and production as an overarching theme( 7 ). Later this year the Sustainable Development Goals will be released( 8 ) and they will underpin national and global public policy (including food policy) activities in the post-2015 development agenda.
Public health nutritionists are well placed to play a central role in helping to understand food system-related sustainability problems and their causes, investigate and provide evidence to identify solutions, and act to inform policy and practice. But building a shared understanding of problem causation and evidence-informed solutions is complex and faces many challenges. There is uncertainty about the what, how and why to think about the relationship between sustainability and public health nutrition. There is a lack of models, tools and evidence of what works and what is needed in public health nutrition to mitigate sustainability challenges. There is a lack of consensus and political will to act in the face of perceived competing agendas between promoting healthy and sustainable diets and promoting economic growth. Framing the concept of healthy food in terms of sustainability, and linking environmental concerns to public health nutrition, may implicate the intergenerational concepts of justice and global health equality as normative criteria for public health nutrition policy, but this is at odds with the current focus on individual nutrition-related behaviour and health.
A special issue on sustainability
This special issue was conceived as an opportunity to provide expert analyses of concepts, ideas and empirical studies associated with sustainability and public health nutrition. It is the latest contribution by the journal in providing leadership in sustainability and public health nutrition over the past decade. Ten years ago, Public Health Nutrition published a supplement on the New Nutrition Science project, which proposed a new direction built around reforming nutrition science through the integration of biological, social and environmental dimensions( Reference Cannon and Leitzmann 9 ). Five years ago an editorial in the journal called on readers to consider the idea of developing ‘food supply guidelines for industry and governing agencies to improve the supply and sustainability of foods available for people to eat’( Reference Yngve and Tseng 10 ).
Sustainability and public health nutrition is a broad and rapidly evolving research area. It is unrealistic to attempt to comprehensively cover all aspects in one issue of the journal. Nevertheless, after the journal issued its call for submissions for the special issue in early 2014, it was exciting to witness the breadth of innovative studies available for consideration. Following an extensive review process, twenty-two high-quality papers from around the world were accepted and are included in this special issue. These papers cover a diversity of topics and their analyses range from a systemic appraisal of policy processes through to an assessment of individual behaviours. A coherent structure for the issue has been achieved by grouping papers in accordance with a social ecological model of public health (in this context ‘ecological’ refers to multilevel interactions and not the science of ecology). A social ecological model is based on the premise that the determinants of behaviours such as healthy and sustainable diets are embedded in social systems and environmental contexts.
There are a number of social ecological models available; for the purposes of this special issue we adapted Story et al.’s( Reference Story, Kaphingst and Robinson-O’Brien 11 ) ecological framework of the multiple levels of analysis of the influences on what people eat, to group research papers. The four levels of analysis as depicted in Fig. 1 are: (i) macro-level environments; (ii) physical environments; (iii) social environments; and (iv) individual factors. We supplement this framework with a category representing broad systems approaches that highlight interactions and feedback loops across levels.
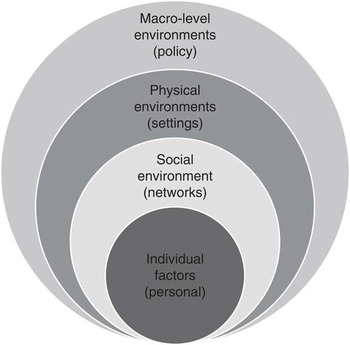
Fig. 1 Levels of analysis for grouping research papers (adopted from Story et al.( Reference Story, Kaphingst and Robinson-O’Brien 11 ))
Macro-level environments
The macro-level environments level of analysis refers to those activities that exert a powerful societal-wide influence on what people eat and include public policies and food marketing. Setting the scene for this section, and the special issue as a whole, is the paper by Berry et al., who conducted a quasi-historical approach from meetings and reports from international and global food security and nutrition forums to investigate the position of the concept of sustainability within the context of food security( Reference Berry, Dernini and Burlingame 12 ). The authors draw attention to the 1996 Rome Declaration on World Food Security which defined food security in three basic dimensions: availability, accessibility and utilization. In 2009, at the World Summit on Food Security, a fourth dimension was added: stability/vulnerability, reflecting a food system’s ability to withstand shocks. The authors recommend adding sustainability as a fifth dimension, citing dual benefits for advancing food security and sustainability causes.
The idea of integrating a sustainability dimension into nutrition policies and nutrition reference standards is gaining momentum around the world. Two separate papers present case studies of the successful integration of sustainability considerations into national dietary guidelines for Qatar( Reference Seed 13 ) and Brazil( Reference Monteiro, Cannon and Moubarac 14 ). Each provides an overview of the sustainability criteria used and shares insights and lessons learned about how and why the integration of sustainability into national dietary guidelines was achieved in their respective countries.
Yet, there remains resistance to the integration of a sustainability dimension into nutrition policy. In their analysis of a national food and nutrition policy in Australia, Trevena et al. explain that despite agreement that sustainability was a policy priority, differences in how actors from civil society and those representing corporate interests framed its meaning and its ‘solution’ resulted in a lack of shared vision to advance the concept( Reference Trevena, Kaldor and Downs 15 ). One approach that would help shed light on the competing frames towards the causes of sustainability problems and their policy solutions is the policy formulation tool described in the paper by Lawrence et al.( Reference Lawrence, Friel and Wingrove 16 ). The tool is designed for strategically informing policy activities to promote healthy and sustainable diets. It consists of two complementary components: (i) a conceptual framework of the environment–public health nutrition relationship to characterize and conceptualize the food system problem; and (ii) an ‘Orders of Food Systems Change’ schema to identify, assess and propose policy options to redesign food systems.
Physical environments
In the context of this special issue, the physical environments level of analysis grouped those papers that investigated the changing of practices in hospital, public kitchen and educational institutional settings, as well as community-based interventions. Ranke et al. evaluated the outcomes of the Balanced Menus Challenge in which participating US hospitals reduce meat purchases by 20 %, then invest the savings into purchasing sustainably produced meat( Reference Ranke, Mitchell and St. George 17 ). The study demonstrates that hospitals in the Maryland/Washington, DC region can reduce meat purchasing and increase the amount of sustainably produced meat purchased and served. Sørensen et al. evaluated two comparative methods for measuring organic food procurement for public kitchens: one based on the use of procurement invoices and the other on self-reported procurement( Reference Sørensen, Lassen and Løje 18 ). They report that both measurement methods were valid with a high significant correlation coefficient found between the two methods and measurements relevant for the baseline status.
Davis et al. investigated school gardens as a setting for promoting healthy and sustainable diets( Reference Davis, Spaniol and Somerset 19 ). In their review of thirteen studies that have examined the impact of garden-based programmes on dietary behaviours in kindergarten through 8th grade students, they found evidence of some increased vegetable intake and improved attitudes towards willingness to taste, prepare and cook fruit and vegetables. This finding was further supported by Munroe et al., who report that an online, interactive intervention for full-time students (18–24 years) attending a public university in the USA was effective in motivating college students to adopt ‘green eating’ behaviours( Reference Monroe, Lofgren and Sartini 20 ).
Black and her team describe the development and application of the School Food Environment Assessment Tools as a novel scoring system to assess the integration of healthy and environmentally sustainable food initiatives in thirty-three elementary and secondary schools in Vancouver( Reference Black, Velazquez and Ahmadi 21 ). The authors report that the assessment tools and proposed indicators offer a practical approach for researchers, policy makers and school stakeholders to assess school food system environments, identify priority areas for intervention and track relevant changes over time. Changes in the practices of elementary schools participating in the US National School Breakfast Program to reduce food waste were investigated in an article by Blondin et al. published in the June 2015 issue of this journal( Reference Blondin, Djang and Metayer 22 ). The authors report that menu changes as well as efforts to use leftover food productively reduced waste and improved the Program’s economic, environmental and nutritional impact.
Wilkins and her team explored the influence of participation in community-supported agriculture (CSA) on vegetable exposure, vegetable intake during and after the CSA season, and preference related to locally produced vegetables acquired directly from CSA growers( Reference Wilkins, Farrell and Rangarajan 23 ). The authors conclude that dietary patterns supported through CSA participation can promote preferences and consumer demand that support local production and seasonal availability. Bertmann and colleagues explored the feasibility of a workplace farmstand programme in Sarpy County (Omaha), Nebraska, USA, through the utilization of an online ordering system, to build awareness for local food systems, encourage community participation and increase local fruit and vegetable availability( Reference Bertmann, Fricke and Carpenter 24 ). They report that this workplace farmstand pilot study helped to establish a sustained producer–employer relationship. In a similar setting, Jilcott-Pitts and her colleagues examined barriers to and facilitators of shopping at farmers’ markets in Pitt County, eastern North Carolina, USA and associations between shopping at farmers’ markets and self-reported dietary behaviours and BMI( Reference Jilcott Pitts, Wu and Demarest 25 ). The authors identify barriers to shopping at farmers’ markets and highlight the need to increase awareness of existing markets to increase high-risk-group participants’ use of farmers’ markets.
Social environment
The social environment level of analysis refers to interactions with family, friends and others through mechanisms such as social norms. The sole paper within this level of analysis was Kuhnlein’s investigation into how Indigenous Peoples understand how to enhance use of their food systems to promote sustainability( Reference Kuhnlein 26 ). She concludes that promoting the use of local traditional food biodiversity is an essential driver of food system sustainability, not only for Indigenous Peoples, but also as a contribution to global consciousness more broadly. This paper invites a debate about the need to reconceptualize solutions for the problem of sustainability by questioning the dominant models of social organization and avoiding a one-size-fits-all approach that risks alienating many populations with particular social and cultural heritages.
Individual factors
Investigating the role of individual knowledge, attitudes and behaviours in sustainability was a popular research topic in the special issue. Several investigations focused on animal and red meat production and consumption. Marlow et al. conducted a comparative analysis of the use of water, energy, pesticides and fertilizer to produce commodities for two dietary patterns that vary in plant and animal product content using ‘real world’ data from California( Reference Marlow, Harwatt and Soret 27 ). Their findings contribute to a body of literature indicating that diets containing more animal products, particularly beef, require substantially more water, energy, fertilizer and pesticides than those containing less animal products. In related research, Temme and colleagues evaluated dietary GHGE for Dutch children and adults aged 7–69 years( Reference Temme, Toxopeus and Kramer 28 ). They too report that meat consumption was the main contributor to GHGE. An interesting non-meat finding was that, while many such studies exclude beverages, they included them and found that due to high consumption, dairy and soft drinks (girls, boys and women) and alcoholic drinks (men) were the next leading dietary sources of GHGE.
Clonan et al. investigated the relationship between red and processed meat consumption, purchasing behaviours and attitudes towards perceived impact on health, animal welfare and the environment in an area of the UK( Reference Clonan, Wilson and Swift 29 ). They report that human health and animal welfare are more common motivations to avoid red and processed meat than environmental sustainability. It is not clear how much the lower priority on environment reflects lack of knowledge v. relatively low concern, and there was population diversity in these attitudes. Regardless, the research suggests there may be benefits for the environment from encouraging positive attitudes to animal welfare; developing omni standards which incorporate health, production and animal welfare; and strengthening education and communication about environmental impacts.
Innovative solutions to the problem of meat overconsumption have broadened the focus from ‘less or no meat’ to ‘include alternative protein sources’. In vitro meat has been suggested as a dietary alternative to conventional meat. While such innovative food science solutions to sustainability threats are being developed rapidly, their impact will depend on acceptability. Laestadius and Caldwell’s qualitative analysis of online comments, for instance, finds that some endorse the environmental and public health benefits of in vitro meat, but overall there is a current negative public perception of the meat as unnatural, risky and unappealing( Reference Laestadius and Caldwell 30 ). Their conclusion is that for those wishing to promote in vitro meat, communications and regulatory strategies may help build public trust.
Whereas ruminant animal products are implicated as a threat to sustainability, these products can be highly nutritious; e.g. lean red meat and some dairy products. In an effort to understand these trade-offs, Temme et al. modelled the impact of diets with less or no meat and dairy products on the nutrient intakes of 2–6-year-olds in the Netherlands( Reference Temme, Bakker and Seves 31 ). They report that under a partial substitution of current behaviours, there were both health and environmental benefits, but a full vegan scenario may require extra attention to assure adequate nutrition for young girls.
Metrics for assessing the sustainability of different aspects of dietary behaviour were investigated in two papers. Luckett and his colleagues analysed national household consumption data to evaluate the applicability of the Nutritional Functional Diversity score to describe the contribution of biodiversity to sustainable diets in Malawi( Reference Luckett, DeClerck and Fanzo 32 ). Their analysis demonstrates the score was an effective indicator for identifying populations in Malawi with low nutritional diversity and examining the relative roles of markets, agricultural extension and home production in achieving nutritional diversity in that country. Massett and colleagues compared how two different functional units (units for calculating environmental indicators), 100 g and 100 kcal (420 kJ), affected the associations between three sustainability dimensions: (i) GHGE; (ii) nutritional quality; and (iii) price( Reference Masset, Vieux and Darmon 33 ). They conclude that the choice of functional unit was influential, but that neither functional unit would be ‘best’ to identify foods more likely to be included in sustainable dietary patterns. They suggest alternative options such as a functional unit integrating sustainability and nutritional criteria, or classifying foods based on their position in sustainable dietary patterns.
Systems approaches
In addition to the four levels of analysis covered in Story et al.’s framework, there is a need for broad systems engagement that not only spans levels but, more importantly, focuses on the interrelationships and feedback loops among them. James and Friel synthesize evidence from a three-year mixed-methods research project to determine points of intervention in Australian-based urban food systems to improve systems’ climate resilience, equity and healthiness( Reference James and Friel 34 ). Their investigation identifies the interconnectedness of food system sectors; improving environmental sustainability, equity and population health requires a coordinated focus on the whole system. They present areas for action, emphasizing that there are strengths and limitations for sustainability in every food system sector and in both local and industrial subsystems of the food system.
Discussion
Collectively, the investigations in the papers in this special issue cover all levels of ecological analysis. The papers contribute to and reaffirm a body of work showing, among many findings, the importance to the achievement of healthy and sustainable diets of: integrating sustainability considerations into nutrition policy and reference standards such as dietary guidelines; changing procurement practices and educational opportunities in institutional settings; appreciating that socio-cultural approaches are also essential to intervening effectively for sustainability; promoting certain dietary behaviours such as moderating red meat consumption; and coordinating community-based interventions across sectors and stakeholders.
Insofar as the investigations presented in this special issue are representative of sustainability and public health nutrition research agendas more broadly, there are research gaps in the literature that need attention. Most of the studies were conducted in high- and middle-income country contexts and further research about achieving a healthy and sustainable diet in rapidly urbanizing low-income countries is required. Also, the papers as a whole do not equally represent the different levels of analysis. A large number of the papers address the concept of sustainability with a focus on information exchange and favouring an ‘individual responsibility’ model as normative for promoting behaviour change towards healthy and sustainable diets. Another significant area of research focused on physical environment interventions. By contrast there is just one paper within each of social environments and systems approaches levels of analysis.
Interventions addressing individual factors and physical environments are necessary cornerstones for dietary reform but on their own are insufficient to bring about the large-scale social and system changes needed to fully respond to sustainability challenges. The field has matured to the point where additional breadth and depth are required: more research taking account of the full food system including interactions and feedback loops; greater investment is needed in research examining the role of factors including culture, equity, food marketing and industry power in food system sustainability; and additional focus on the intersections between nutrition and the biophysical environment including agriculture. Additionally research-related priorities now include communicating the impressive evidence base about what constitutes a healthy and sustainable diet, as well as translating this evidence into policy and interventions to support and encourage populations, business and farmers in putting this evidence into practice. There needs to be an element of ‘choice editing’ for policy in this area. For example, why label some goods on shelves as more sustainable and sell them for a premium? Should not all our food be sustainable? What would it take to enable that shift, while preserving both food affordability for all and incomes for food system workers? The danger is that sustainable food becomes the preserve of the rich and rich nations who can afford it. For these reasons it is necessary to think of ecological sustainability as a global resource.
A call for policy research and action from public health nutritionists
Building support for policies to support healthy and sustainable diets is never just a matter of evidence. In public health and preventive medicine there is a long history of interventionist public health policy. The powerful influences are the corporate interests and neo-liberal economics above and beyond public health nutrition and sustainability. Policy capacity needs to be strengthened with public health nutrition advocates becoming savvier around policy development, combined with building new skills and ways of engaging with policy action( Reference Forest, Denis and Brown 35 ). An expanded skill set will be needed to support activities that provide balance to government and industry perspectives. The traditional focus on producing evidence to inform policy will need to be complemented with skills in the critical analysis of policy-making processes as well as a commitment to leadership and social responsibility to support the development of policies to promote healthy and sustainable diets. To enable researchers to participate in such work, there is additionally a need for shifts in academic advancement structures and for foundation funding to both encourage the investment of time and provide training to researchers to improve their ability to engage productively.
Conclusion
Sustainability is now a priority issue for public health nutrition. The number of researchers engaged and the broad scope of the investigations presented in this special issue bear testament to the increasing attention towards sustainability and public health nutrition research. Indeed, a substantial amount of research, policy and practice work in this field already has been undertaken by the profession as a whole and we look forward to this escalating into the future. Interdisciplinary collaborations with fields having complementary expertise in sustainability present important opportunities to advance the science and avoid reinventing wheels. We trust that this special issue will make a strong positive contribution to this escalation by stimulating understanding and provoking deeper thought about policies and interventions to act on the significant and urgent sustainability challenges confronting public health nutrition.



