Article contents
Resampling-Based Inference Methods for Comparing Two Coefficients Alpha
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2025
Abstract
The two-sample problem for Cronbach’s coefficient αC\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\alpha _C$$\end{document}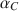 , as an estimate of test or composite score reliability, has attracted little attention compared to the extensive treatment of the one-sample case. It is necessary to compare the reliability of a test for different subgroups, for different tests or the short and long forms of a test. In this paper, we study statistical procedures of comparing two coefficients αC,1\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\alpha _{C,1}$$\end{document}
, as an estimate of test or composite score reliability, has attracted little attention compared to the extensive treatment of the one-sample case. It is necessary to compare the reliability of a test for different subgroups, for different tests or the short and long forms of a test. In this paper, we study statistical procedures of comparing two coefficients αC,1\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\alpha _{C,1}$$\end{document}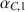 and αC,2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\alpha _{C,2}$$\end{document}
and αC,2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\alpha _{C,2}$$\end{document}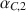 . The null hypothesis of interest is H0:αC,1=αC,2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$H_0 : \alpha _{C,1} = \alpha _{C,2}$$\end{document}
. The null hypothesis of interest is H0:αC,1=αC,2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$H_0 : \alpha _{C,1} = \alpha _{C,2}$$\end{document}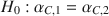 , which we test against one-or two-sided alternatives. For this purpose, resampling-based permutation and bootstrap tests are proposed for two-group multivariate non-normal models under the general asymptotically distribution-free (ADF) setting. These statistical tests ensure a better control of the type-I error, in finite or very small sample sizes, when the state-of-affairs ADF large-sample test may fail to properly attain the nominal significance level. By proper choice of a studentized test statistic, the resampling tests are modified in order to be valid asymptotically even in non-exchangeable data frameworks. Moreover, extensions of this approach to other designs and reliability measures are discussed as well. Finally, the usefulness of the proposed resampling-based testing strategies is demonstrated in an extensive simulation study and illustrated by real data applications.
, which we test against one-or two-sided alternatives. For this purpose, resampling-based permutation and bootstrap tests are proposed for two-group multivariate non-normal models under the general asymptotically distribution-free (ADF) setting. These statistical tests ensure a better control of the type-I error, in finite or very small sample sizes, when the state-of-affairs ADF large-sample test may fail to properly attain the nominal significance level. By proper choice of a studentized test statistic, the resampling tests are modified in order to be valid asymptotically even in non-exchangeable data frameworks. Moreover, extensions of this approach to other designs and reliability measures are discussed as well. Finally, the usefulness of the proposed resampling-based testing strategies is demonstrated in an extensive simulation study and illustrated by real data applications.
Keywords
- Type
- Original Paper
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © 2017 The Psychometric Society
Footnotes
The work of Markus Pauly and Maria Umlauft was supported by the German Research Foundation project DFG-PA 2409/3-1.
Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11336-017-9601-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
References
- 4
- Cited by


