Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Jorgensen, Terrence D.
Pornprasertmanit, Sunthud
Schoemann, Alexander M.
and
Rosseel, Yves
2012.
Béland, Sébastien
and
Michelot, Florent
2020.
Une note sur le coefficient oméga (ω) et ses déclinaisons pour estimer la fidélité des scores.
Mesure et évaluation en éducation,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 3,
p.
103.
Sijtsma, Klaas
and
Pfadt, Julius M.
2021.
Rejoinder: The Future of Reliability.
Psychometrika,
Vol. 86,
Issue. 4,
p.
887.
Ren, Fen
and
Wang, Kexin
2022.
Modeling of the Chinese Dating App Use Motivation Scale According to Item Response Theory and Classical Test Theory.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 21,
p.
13838.
Widaman, Keith F.
and
Revelle, William
2022.
Thinking thrice about sum scores, and then some more about measurement and analysis.
Behavior Research Methods,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 2,
p.
788.
Flores-Kanter, Pablo Ezequiel
and
Mosquera, Mariano
2023.
How do you Behave as a Psychometrician? Research Conduct in the Context of Psychometric Research.
The Spanish Journal of Psychology,
Vol. 26,
Issue. ,
Xiao, Leifeng
and
Hau, Kit-Tai
2023.
Performance of Coefficient Alpha and Its Alternatives: Effects of Different Types of Non-Normality.
Educational and Psychological Measurement,
Vol. 83,
Issue. 1,
p.
5.
Wang, Miyan
Chen, Xiaohong
Yang, Yuwei
Wang, Haiyan
Yan, Yan
Huang, Xiaoying
Bi, Yanli
Cao, Wensha
and
Deng, Guoxue
2023.
Effect evaluation of case-based learning with situated cognition theory on competence training for student nurses in pediatric surgery.
Heliyon,
Vol. 9,
Issue. 2,
p.
e13427.
Gutiérrez-Aguilar, Olger
Cervantes-Bolaños, Samuel
Verano-Barrientos, César
Apaza-Jiménez, Luis
Gonzales-Condori, Jonathan
and
Tomaylla-Quispe, Ygnacio
2023.
The Privacy of Information and its Relationship with the Trust of Services in Social Networks on Smartphones in University Students.
p.
1.
Kehl-Floberg, Kristen E.
Marks, Timothy S.
Edwards, Dorothy F.
and
Giles, Gordon M.
2023.
Conventional clock drawing tests have low to moderate reliability and validity for detecting subtle cognitive impairments in community-dwelling older adults.
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience,
Vol. 15,
Issue. ,
Xiao, Leifeng
and
Hau, Kit-Tai
2023.
Accuracy and Sensitivity of Coefficient Alpha and Its Alternatives with Unidimensional and Contaminated Scales.
Applied Measurement in Education,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 1,
p.
31.
Flores-Kanter, Pablo Ezequiel
Alesandrini, Claudia
and
Alvarado, Jesús M.
2023.
Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale: Evidence of Construct Validity in Argentinians.
Behavioral Sciences,
Vol. 13,
Issue. 3,
p.
198.
Lakiss, Nour
2023.
Digital Economy and the Green Revolution.
p.
139.
Kadi, Melissa
Bourion-Bédès, Stéphanie
Bisch, Michael
and
Baumann, Cédric
2023.
A Structural Validation of the Brief COPE Scale among Outpatients with Alcohol and Opioid Use Disorders.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
Vol. 20,
Issue. 3,
p.
2695.
CLEOPHAS, MARIA DAS GRAÇAS
MARQUES, MURILO S.
and
BARBOSA, MARCIA CRISTINA
2023.
Self-perceived competences by future chemistry teachers in Brazil.
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências,
Vol. 95,
Issue. suppl 1,
Malkewitz, Camila Paola
Schwall, Philipp
Meesters, Christian
and
Hardt, Jochen
2023.
Estimating reliability: A comparison of Cronbach's α, McDonald's ωt and the greatest lower bound.
Social Sciences & Humanities Open,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 1,
p.
100368.
Koutná, Martina
Havrdová, Egle
Netík, Jan
and
Pour, Marek
2024.
Evaluation of a Parenting Program for Disadvantaged Families in the Czech Republic.
Research on Social Work Practice,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 1,
p.
84.
Araújo-Neto, Fernando de Castro
Prado, Fernanda Oliveira
Dosea, Aline Santana
Fonseca, Francielly Lima da
Araújo, Dyego Carlos Souza Anacleto de
Brito, Giselle de Carvalho
Mesquita, Alessandra Rezende
and
Lyra-Jr, Divaldo Pereira de
2024.
Assessment of Professionalism in Pharmacists and Pharmacy Students: Scoping Review of Instruments and Validity Evidence.
American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education,
Vol. 88,
Issue. 8,
p.
100733.
Corbelli, Giuseppe
Levantini, Valentina
Muratori, Pietro
Senese, Vincenzo Paolo
Bravaccio, Carmela
Pisano, Simone
Catone, Gennaro
and
Paciello, Marinella
2024.
Assessing Callous-Unemotional Traits Across Early Adolescence: Further Evaluation of Short Versions.
Child Psychiatry & Human Development,
Cho, Eunseong
2024.
Beyond alpha and omega: The accuracy of single-test reliability estimators in unidimensional continuous data.
Behavior Research Methods,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 6,
p.
6299.
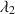 , μ2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\mu _{2}$$\end{document}
, μ2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\mu _{2}$$\end{document}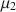 , congeneric reliability and the Gilmer-Feldt coefficient are more accurate than coefficient alpha. 6) The name omega should not be used to refer to a specific reliability estimator.
, congeneric reliability and the Gilmer-Feldt coefficient are more accurate than coefficient alpha. 6) The name omega should not be used to refer to a specific reliability estimator.

