Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2025
Model selection from a set of candidate models plays an important role in many structural equation modelling applications. However, traditional model selection methods introduce extra randomness that is not accounted for by post-model selection inference. In the current study, we propose a model averaging technique within the frequentist statistical framework. Instead of selecting an optimal model, the contributions of all candidate models are acknowledged. Valid confidence intervals and a χ2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal}\usepackage{amsmath}\usepackage{wasysym}\usepackage{amsfonts}\usepackage{amssymb}\usepackage{amsbsy}\usepackage{mathrsfs}\usepackage{upgreek}\setlength{\oddsidemargin}{-69pt}\begin{document}$$\chi ^2$$\end{document}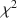 test statistic are proposed. A simulation study shows that the proposed method is able to produce a robust mean-squared error, a better coverage probability, and a better goodness-of-fit test compared to model selection. It is an interesting compromise between model selection and the full model.
test statistic are proposed. A simulation study shows that the proposed method is able to produce a robust mean-squared error, a better coverage probability, and a better goodness-of-fit test compared to model selection. It is an interesting compromise between model selection and the full model.
Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1007/s11336-018-9624-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.