Ageing is accompanied by a progressive loss of lean tissue mass. Sarcopenia is used to define age-related loss in skeletal muscle mass estimated to affect 30% of people older than 60 years and >50% of those older than 80 years. The magnitude of change in lean tissue mass with ageing is referenced to race- and gender-specific healthy young adults(Reference Baumgartner, Koehler and Gallagher1). Accurate reference body compositional data is therefore required to diagnose and investigate the prevalence of sarcopenia, its impact on health and function and to evaluate the effect of dietary and lifestyle intervention. The UL Body Composition Study(2) is a prospective study that seeks to establish age- and gender-specific reference ranges for whole-body and segmental body composition based on a representative sample of the Irish population residing within the UL community. The present paper reports on the whole body and segmental distribution of lean tissue mass for men and women aged 18–30 years.
With ethical approval (ULREC 08/07) and informed, written consent height, weight and body composition was measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA; iDXA™; GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, Bucks., UK) on 497 men and 392 women aged 18–30 years. Total body lean tissue mass was segmented into appendicular (legs+arms) lean tissue mass and expressed relative to stature squared generating an appendicular lean tissue mass index (ALTMI; Table 1).
Table 1. Anthropometric and body composition of young adult men and women.
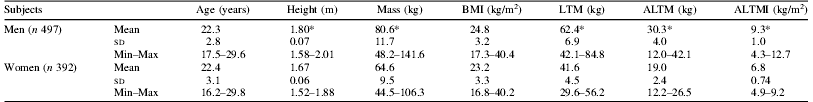
Min–Max, minimum–maximum. *P<0.05 men v. women.
The data revealed predicted sex-specific differences in the mean values for percentage total body fat (♀31.1% v. ♂18.6%) and lean tissue (♀64.6 v. ♂77.4%) mass. Significant difference between the sexes was also evident in the appendicular lean tissue mass and remained when the lean tissue mass in the arms and legs was normalised to stature squared in order to account for the difference in for skeletal size.
The functional capacity of an individual, i.e. general mobility and the ability to perform activities of daily living, is determined primarily by the appendicular lean tissue mass(Reference Cruz-Jentoft, Baeyens and Bauer3). Thus, a guideline criterion of sarcopenia has been defined as an appendicular lean tissue mass index (ALTMI) value of less than −2 sd below the sex-specific mean for ALTMI in a healthy, younger adult(Reference Baumgartner, Koehler and Gallagher1). Based on the data from the present study, a criterion reference for sarcopenia in the Irish adult population would be an ALTMI value less than 7.3 kg/m2 in men and less than 5.24 kg/m2 in women.



