- PN
parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition (PN) line sepsis is a common complication in hospitalised patients receiving PN. Studies in Europe have shown that rates of bloodstream infections related to indwelling venous lines can vary from 22·5% to a staggering 66% of cases(Reference Ronveaux, Jans and Suetens1, Reference Raymond and Aujard2). Hospitalised patients receiving PN are often critically ill and making a confident, expedient diagnosis of PN line sepsis can be difficult. Early clinical suspicion, investigation, diagnosis and treatment are necessary to ensure that these unwell patients do not deteriorate quickly. Appropriate management of the PN line is necessary, along with appropriate microbiological input to help confirm the diagnosis.
Aetiology
A PN line can become infected in a number of ways: (1) poor aseptic technique when inserting the line; (2) migration of organisms along the line; (3) poor aseptic technique and line care when using the line; (4) contaminated infusions; (5) haematogenous spread from distant foci of infection(Reference Bouza, Burillo and Munoz3).
Clinical diagnosis
Clinical suspicion must be raised when a patient on PN becomes unwell and/or pyrexial. Sepsis related to the PN line does not always cause a rise in serum inflammatory markers of infection such as white cell count or C-reactive protein, meaning that more emphasis is placed on microbiological techniques to confirm the diagnosis. Often the PN line suspected of causing sepsis is removed and sent to microbiology. Unfortunately only about 20% of lines removed are found to have been infected, meaning that there was no need to remove the line and the patient is likely to require insertion of another(Reference Ryan, Abel and Abbott4–Reference Linares, Dominguez and Martin6). This has led to the development of line-conserving techniques to diagnose infection.
Non-line-conserving techniques
The most common techniques used to confirm line infection following removal of the line are a qualitative procedure, Maki's semi-quantitative procedure, quantitative endoluminal cultures after flushing, and sonication.
The qualitative procedure involves culturing the tip of the PN line for organisms. This is the simplest technique but is not used often due to a relative lack of specificity at around 75%(Reference Michel, Marsh and McMichan7). The accuracy of this technique is affected by the fact that a line may be colonised by organisms without causing sepsis in the patient. Clinical correlation must be used when interpreting results using this technique.
Maki's semi-quantitative procedure was first described in 1977. It is still used as the international reference. It involves rolling the line tip on an agar plate and culturing it. An arbitrary number of colony forming units set at >15 is used to indicate a positive culture(Reference Maki, Weise and Sarafin8). A high specificity of >75% has been reported with this technique.
Quantitative cultures of fluid repeatedly flushed through the PN line lumen have also been used to help with diagnosing infection. This has the advantage of including organisms within the line lumen rather than just those on the outside of the tip(Reference Cleri, Corrado and Seligman9). Again an arbitrary number of colony forming units of organisms is set as a positive result. This technique is not used in everyday practice because of the large workload it would generate.
Sonication is a newer method that was developed in the 1990s. This technique involves bathing the line in the culture broth and subjecting it to high-frequency ultrasound. The broth is then diluted and cultured using the normal technique for qualitative procedure. Using ultrasound it is able to improve the diagnostic specificity, but requires extra equipment and time and as such is not practical for everyday use(Reference Sherertz, Raad and Belani10).
Line-conserving techniques
It would be preferable to confirm line infection before removing the line, and therefore a number of techniques have been developed which leave the line in place until infection is confirmed. Usually if there is serious suspicion of line infection, these techniques are used and PN is stopped until the result is obtained. The most common techniques are intraluminal brushing, semi-quantitative swabs from the external line and differential quantitative blood cultures.
Intraluminal brushing was first tried in 1989. This technique involves using a specially designed wire brush and passing it down the line suspected of being infected. The theory is that the organisms on the fibrin sheath on the inside of the line become caught up on the bristles of the brush which is then removed and sent for culture(Reference Tighe, Kite and Fawley11). The results were initially good, but concerns about the risks of the technique led to it being discarded as a popular method of diagnosing infection(Reference Markus and Buday12). Side effects included cardiac arrhythmias from inserting the wire brush too far or the risk of endocarditis caused by dislodging infection from the line and sending emboli to the valves.
Taking simple microbiology swabs from the external portion of the line has proved to be effective, although this is not able to diagnose all infections(Reference Raad, Baba and Bodey13). This involves using simple culture swabs to swab the area where the line hub enters the skin. It is not exact as not all line infections are found at this part of the line and all infections under the skin or on the line tip are missed by this technique.
Differential blood cultures involve drawing blood for culture both from the PN line suspected of sepsis and from a distal, peripheral site and comparing the two. If the concentration of organisms in the two cultures is the same, then the line is unlikely to be the source of the infection. If the concentration is higher in the line cultures, then it is likely to be infected. A ratio of between 5:1 and 10:1 is accepted as positive. It is not always possible to perform this technique as the PN lines are often made of a very soft material that collapses when suction is applied, meaning that drawing back blood from the line is not always possible(Reference Capdevila, Planes and Palomar14, Reference Douard, Arlet and Longuet15). The line tip may also become covered by a fibrin sheath that prevents aspiration of blood.
Defining parenteral nutrition line sepsis
It is clear from the literature that no clear definition of PN line-related sepsis exists.
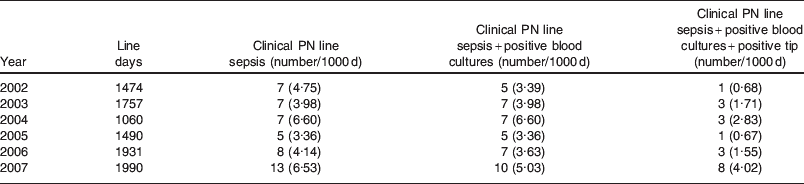
Depending on which definition is used, a patient may or may not be formally diagnosed as having PN line-related sepsis. The definitions used in clinical practice and in the published literature exist as a spectrum. At one end the simplest definition is a clinical suspicion of PN line-related sepsis where pyrexia is associated with the use of PN and this subsides on stopping the PN and no other source is found. This can obviously include many false-positive cases and lead to an over-diagnosis of PN line sepsis. At the other end of the spectrum, a diagnosis may only be made once positive blood cultures and a positive line tip are found in the presence of clinical suspicion. This is not always possible to achieve, leading to many cases being unfairly discounted leading to an under-representation of the true incidence. Different units may apply these different diagnostic criteria to diagnose line sepsis. It is therefore very difficult to accurately estimate what the actual incidence of sepsis is and how each unit is performing compared to the national average. It is accepted in the literature that rates should be corrected as number of events per 1000 line days to standardise each unit's rate of sepsis. If national audit is to be carried out in this area, a nationally accepted standardised definition must be agreed on. Table 1 shows how the incidence of PN line sepsis can be altered, depending on what definition is used in a large unit in Glasgow(Reference McWhirter, Ferguson and McKee16). The numbers are shown as the actual numbers of cases with the number of cases per 1000 line days shown in brackets.
Table 1. Rates of parenteral nutrition (PN) line-related sepsis varying by definition from Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Conclusion
Improvement in the education of those involved in the management of these patients combined with good quality input from microbiologists is vital to improving the care of these patients. This could include increased teaching of doctors at the medical school or foundation training stage into the issues surrounding line infection and line care. Improved awareness among nursing staff about the importance of good line care is also essential.
Acknowledgements
There are no conflicts of interest. No funding was received for this article.



