Chronic disease has been traditionally attributed to risk factors in adulthood; however, current orthodoxy suggests that the true origins of such diseases are initiated much earlier in life from inappropriate nutritional circumstances arising during the formative years(Reference Barker, Erikson, Forsen and Osmond1). The present study was undertaken to examine current maternal attitudes towards the importance of paediatric diet in relation to adult diseases and to determine the extent to which attitudinal differences between subgroups in the population exist.
A non-randomised postal follow-up survey to the DIT–Coombe Hospital Infant Feeding Study was carried out, involving the recruitment of 209 mothers from a pool sample of 520 mothers in the previous study(Reference Tarrant, Younger, Sheridan-Periera and Kearney2) (response rate 46.7%). Quantitative data were obtained from a cross-sectional questionnaire ranking maternal attitudes towards infant diet on a five-point Likert scale(Reference Nayak and Erinjeri3) (from strongly disagree to strongly agree) of perceived importance.
In general, a higher percentage of respondents (64) had a cumulative positive view of the relationship between paediatric diet and disease risk. Of the mothers >70% expressed a strong positive attitude towards the influence of early childhood diet and the risk of being overweight, poor growth and development, unhealthy food preference, osteoporosis, diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease. In comparison, cancer, eczema and food allergies were viewed positively overall but the extent to which individuals most strongly agreed with each fell to <50%. The majority had a negative opinion (either disagreed strongly or tended to disagree) of the importance of paediatric diet in mental health problems. According to one-way ANOVA analysis, attitudinal differences in mean scores (P<0.05) were observed in mothers according to age at time of birth, education level, accommodation status and health insurance status, as well as the timing of weaning (Table).
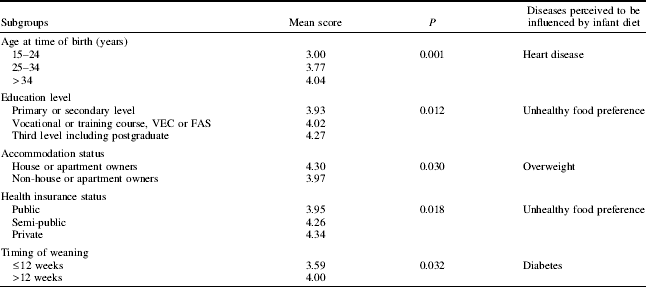
VEC, Vocational Education Committee; FAS, Training and Employment Authority.
The results indicate that mothers who are younger and less educated, as well as those who wean their child before 12 weeks after birth should be targeted for further health education on the specific benefits of infant diet, which may in turn contribute towards relieving the strain of chronic disease on society.


