The consumption of high-fat foods fried in oil that has undergone repeat cycles of heating contributes a notable proportion to UK dietary fat intake (Reference Henderson, Gregory and Irving1,Reference Nelson, Erens and Bates2). High-fat meals have been found to impair endothelial function(Reference Vogel, Corretti and Plotnick3), which is believed to be mediated via an oxidative stress mechanism(Reference Bae, Bassenge and Kim4); however, few studies have examined the postprandial effects of thermally-oxidised fats commonly used in the UK for repeated deep-frying(Reference Hall5).
The present study was designed to investigate the postprandial effects of commercially-used fresh oil and re-used deep-fried oil (palm oleic–mid-oleic sunflower oil blend) on endothelium-dependent vasodilation, which was determined using brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation (FMD). Nineteen healthy male subjects (aged 18–40 years) were fed test meals containing 50 g fat in a randomised cross-over design. The test fats were fresh or re-used deep-fried oil (10 d frying at 180°C with five batches of potato chips per d) containing 7.2% and 23.8% (v/v) polar compounds respectively and 1.0 meq/kg and 4.4 meq/kg peroxides respectively. Plasma TAG and NEFA concentrations and FMD were determined fasting and 3 h postprandially.
Following the fresh oil the postprandial increase in plasma TAG was significantly higher compared with that following the fried oil. There was a significant meal effect (P=0.04) for FMD but post-hoc analysis revealed no significant differences between meals at 3 h and no significant differences in the 3 h postprandial change in FMD.
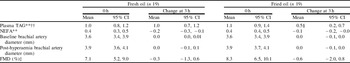
Time effect (ANOVA): **P<0.01. Meal×time interaction (ANOVA): ††P<0.01. Meal effect (ANOVA): ‡P<0.05. Mean value was significantly different from that for fresh oil (paired t test on mean change): §P<0.05.
The lower postprandial TAG response following the fried oil is likely to be a consequence of degradation of TAG to other lipid fractions. Existing evidence demonstrates an association between postprandial lipaemia and impaired FMD(Reference Vogel, Corretti and Plotnick3), but in the current study the greater TAG response following the fresh oil did not result in a significant impairment in FMD compared with the fried oil. This finding suggests that other mechanisms, such as increased oxidative stress, may have also influenced postprandial endothelial function. This outcome merits further research into the interaction between deep-fried oils, oxidative stress and endothelial function.
Special thanks to K McNeill and B Jiang, Cardiovascular Division, King's College London, St Thomas' Hospital, London, UK and Jo Bruce, ADM-PURA, Erith, UK.


