Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 October 2020
Recent laboratory studies have shown that PAH cations dehydrogenate to give charged molecules consisting of only carbon atoms. Our experiments using ion-trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry show that a key group of photodissociation fragments from the coronene cation 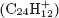 $({{\rm{C}}_{24}}{\rm{H}}_{12}^ + )$ are carbon clusters of
$({{\rm{C}}_{24}}{\rm{H}}_{12}^ + )$ are carbon clusters of 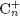 ${\rm{C}}_n^ +$ composition. Density functional theory calculations shed light onto potential dissociation pathways leading up to the main
${\rm{C}}_n^ +$ composition. Density functional theory calculations shed light onto potential dissociation pathways leading up to the main 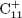 ${\rm{C}}_{11}^ +$ and
${\rm{C}}_{11}^ +$ and 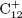 ${\rm{C}}_{12}^ +$ clusters, and highlight the importance of pentagon formations in the carbon backbone of the precursor molecule in generating certain fragments.
${\rm{C}}_{12}^ +$ clusters, and highlight the importance of pentagon formations in the carbon backbone of the precursor molecule in generating certain fragments.