No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Non-thermal radio emission from dark matter annihilation processes in simulated Coma like galaxy clusters
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 29 January 2021
Abstract
Taking secondary particles produced from dark matter (DM) annihilation process to the origin of the extended diffuse radio emission observed in galaxy clusters, we studied both their morphology and radio spectral profile using simulated Coma like galaxy clusters. We have considered a neutralino annihilation channel dominated by 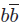 $b\overline b $
species with a branching ratio of 1 and neutralino mass of 35 GeV with annihilation cross-section of 1×10-26 cm3 s-1. The radio emission maps produced for the two simulated galaxy clusters which are based on the MUsic SImulation of galaxy Clusters (MUSIC) dataset reveal the observed radio halo morphology showing radio emission both from the central regions of the cluster and substructures lying out off cluster centre. The flux density curve is in a good agreement for ν ≤ 2 GHz with the obsevational values for the Coma cluster of galaxies showing a small deviation at higher frequencies.
$b\overline b $
species with a branching ratio of 1 and neutralino mass of 35 GeV with annihilation cross-section of 1×10-26 cm3 s-1. The radio emission maps produced for the two simulated galaxy clusters which are based on the MUsic SImulation of galaxy Clusters (MUSIC) dataset reveal the observed radio halo morphology showing radio emission both from the central regions of the cluster and substructures lying out off cluster centre. The flux density curve is in a good agreement for ν ≤ 2 GHz with the obsevational values for the Coma cluster of galaxies showing a small deviation at higher frequencies.
- Type
- Contributed Papers
- Information
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union , Volume 15 , Symposium S356: Nuclear Activity in Galaxies Across Cosmic Time , October 2019 , pp. 385 - 387
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of International Astronomical Union


