Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 October 2019
The Milky Way’s (MW) satellite population is a powerful probe of warm dark matter (WDM) models as the abundance of small substructures is very sensitive to the properties of the WDM particle. However, only a partial census of the MW’s complement of satellite galaxies exists because surveys of the MW’s close environs are incomplete both in depth and in sky coverage. We present a new Bayesian analysis that combines the sample of satellites recently discovered by the Dark Energy Survey (DES) with those found in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) to estimate the total satellite galaxy luminosity function down to Mv = 0. We find that there should be at least 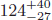 $124_{ - 27}^{ + 40}$ (68% CL, statistical error) satellites as bright or brighter than Mv = 0 within 300 kpc of the Sun, with only a weak dependence on MW halo mass. When it comes online the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope should detect approximately half of this population. We also show that WDM models infer the same number of satellites as in ΛCDM, which will allow us to rule out those models that produce insufficient substructure to be viable.
$124_{ - 27}^{ + 40}$ (68% CL, statistical error) satellites as bright or brighter than Mv = 0 within 300 kpc of the Sun, with only a weak dependence on MW halo mass. When it comes online the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope should detect approximately half of this population. We also show that WDM models infer the same number of satellites as in ΛCDM, which will allow us to rule out those models that produce insufficient substructure to be viable.