Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Xu, Jingshi
and
Zhu, Jinlai
2018.
Estimates of bilinear pseudodifferential operators associated to bilinear Hörmander classes in Besov and Triebel–Lizorkin spaces with variable exponents.
Journal of Inequalities and Applications,
Vol. 2018,
Issue. 1,
Yang, Sibei
and
Yang, Dachun
2019.
Atomic and maximal function characterizations of Musielak–Orlicz–Hardy spaces associated to non-negative self-adjoint operators on spaces of homogeneous type.
Collectanea Mathematica,
Vol. 70,
Issue. 2,
p.
197.
Almeida, Víctor
Betancor, Jorge J.
Dalmasso, Estefanía
and
Rodríguez-Mesa, Lourdes
2019.
New Trends in Applied Harmonic Analysis, Volume 2.
p.
45.
Zhuo, Ciqiang
and
Yang, Dachun
2019.
Variable weak Hardy spaces WH
L
p(·)(ℝ
n
) associated with operators satisfying Davies–Gaffney estimates.
Forum Mathematicum,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 3,
p.
579.
Zhuo, Ciqiang
and
Yang, Dachun
2020.
Variable Besov Spaces Associated with Heat Kernels.
Constructive Approximation,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 3,
p.
479.
Zhang, Junqiang
and
Liu, Zongguang
2020.
Some estimates of Schrödinger type operators on variable Lebesgue and Hardy spaces.
Banach Journal of Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 14,
Issue. 2,
p.
336.
Almeida, Víctor
Betancor, Jorge J.
Dalmasso, Estefanía
and
Rodríguez-Mesa, Lourdes
2020.
Local Hardy Spaces with Variable Exponents Associated with Non-negative Self-Adjoint Operators Satisfying Gaussian Estimates.
The Journal of Geometric Analysis,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 3,
p.
3275.
Zhang, Junqiang
and
Yang, Dachun
2021.
Isomorphisms of variable Hardy spaces associated with Schrödinger operators.
Acta Mathematica Scientia,
Vol. 41,
Issue. 1,
p.
39.
Jian, Tan
2022.
Meyer-Coifman type Hardy spaces with variable exponents and their dual spaces.
SCIENTIA SINICA Mathematica,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 9,
p.
1073.
Seghier, Souad Ben
and
Saibi, Khedoudj
2022.
Herz-type Hardy spaces with variable exponents associated with operators satisfying Davies–Gaffney estimates.
Proceedings - Mathematical Sciences,
Vol. 132,
Issue. 1,
Liu, Xiong
Sun, Chunyou
and
Yang, Sibei
2022.
Variable Hardy Spaces on Non-tangentially Accessible Domains and Their Applications to Div-Curl Lemma.
The Journal of Geometric Analysis,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 12,
Liu, Xiong
Yang, Dachun
and
Yang, Sibei
2022.
Variable Hardy spaces associated with Schrödinger operators on strongly Lipschitz domains with their applications to regularity for inhomogeneous Dirichlet problems.
Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo Series 2,
Vol. 71,
Issue. 3,
p.
925.
Tan, Jian
2023.
Weighted Variable Hardy Spaces Associated with Para-Accretive Functions and Boundedness of Calderón–Zygmund Operators.
The Journal of Geometric Analysis,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 2,
Bownik, Marcin
and
Wang, Li‐An Daniel
2023.
A partial differential equation characterization of anisotropic Hardy spaces.
Mathematische Nachrichten,
Vol. 296,
Issue. 6,
p.
2258.
He, Y.
2023.
Variable Hardy–Lorentz spaces associated with operators satisfying Davies–Gaffney estimates on metric measure spaces of homogeneous type.
Acta Mathematica Hungarica,
Vol. 170,
Issue. 1,
p.
209.
Tan, Jian
2023.
A new approach for hardy spaces with variable exponents on spaces of homogeneous type.
Filomat,
Vol. 37,
Issue. 23,
p.
7719.
Qin, Gaigai
and
Fu, Xing
2024.
Weighted boundedness of fractional integrals associated with admissible functions on spaces of homogeneous type.
Fractional Calculus and Applied Analysis,
Vol. 27,
Issue. 5,
p.
2718.
Lin, Xiaosheng
Yang, Dachun
Yang, Sibei
and
Yuan, Wen
2024.
Hardy Spaces Associated with Non-negative Self-adjoint Operators and Ball Quasi-Banach Function Spaces on Doubling Metric Measure Spaces and Their Applications.
Communications in Mathematics and Statistics,
Lin, Xiaosheng
Yang, Dachun
Yang, Sibei
and
Yuan, Wen
2025.
Maximal Function and Riesz Transform Characterizations of Hardy Spaces Associated with Homogeneous Higher Order Elliptic Operators and Ball Quasi-Banach Function Spaces.
Constructive Approximation,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Chichoune, Romaissa
Mokhtari, Zouhir
and
Saibi, Khedoudj
2025.
Weighted variable Besov space associated with operators.
Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo Series 2,
Vol. 74,
Issue. 1,
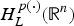 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ associated with L. By means of variable tent spaces, the authors establish the molecular characterization of
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ associated with L. By means of variable tent spaces, the authors establish the molecular characterization of 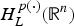 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$. Then the authors show that the dual space of
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$. Then the authors show that the dual space of 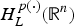 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ is the bounded mean oscillation (BMO)-type space
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ is the bounded mean oscillation (BMO)-type space 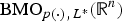 ${\rm BM}{\rm O}_{p(\cdot ),{\kern 1pt} L^ * }({\open R}^n)$, where L* denotes the adjoint operator of L. In particular, when L is the second-order divergence form elliptic operator with complex bounded measurable coefficients, the authors obtain the non-tangential maximal function characterization of
${\rm BM}{\rm O}_{p(\cdot ),{\kern 1pt} L^ * }({\open R}^n)$, where L* denotes the adjoint operator of L. In particular, when L is the second-order divergence form elliptic operator with complex bounded measurable coefficients, the authors obtain the non-tangential maximal function characterization of 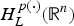 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ and show that the fractional integral L−α for α∈(0, (1/2)] is bounded from
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ and show that the fractional integral L−α for α∈(0, (1/2)] is bounded from 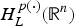 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ to
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ to 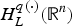 $H_L^{q(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ with (1/p(·))−(1/q(·))=2α/n, and the Riesz transform ∇ L−1/2 is bounded from
$H_L^{q(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ with (1/p(·))−(1/q(·))=2α/n, and the Riesz transform ∇ L−1/2 is bounded from 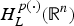 $H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ to the variable Hardy space Hp(·)(ℝn).
$H_L^{p(\cdot )} ({\open R}^n)$ to the variable Hardy space Hp(·)(ℝn).