No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the Riemann P Equation with Integral Exponent differences
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2009
Extract
The differential equation in question is of the second order and has three regular singular points. It is usually denoted by
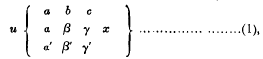
where a, b, c are the singular points, a, a′ etc. the exponents at those singularities. The solution when no one of the numbers α – α′, β – β′, γ – γ′ is an integer or zero is well known; all types of solution are expressible in terms of the hypergeometric functions.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Edinburgh Mathematical Society 1924
References
* (a) Gesammelte Werke VI, 184–202.
(b) Journal für Math. 56 (1859). 149–165.Google Scholar
* Quart. J. of Math. 39 (1908) 107.Google Scholar
† The notation ![]() is best reserved for the functions of §4 which, for λ=0, reduce to associated Legendre Functions.
is best reserved for the functions of §4 which, for λ=0, reduce to associated Legendre Functions.
* When λ = 0, these functions become the associated Legendre functions.


