Article contents
Toxocara canis infection worsens the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 September 2022
Abstract
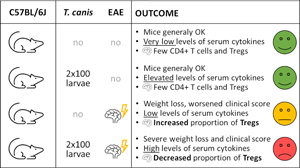
Toxocara canis, a gastrointestinal parasite of canids, is also highly prevalent in many paratenic hosts, such as mice and humans. As with many other helminths, the infection is associated with immunomodulatory effects, which could affect other inflammatory conditions including autoimmune and allergic diseases. Here, we investigated the effect of T. canis infection on the course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Mice infected with 2 doses of 100 T. canis L3 larvae 5 weeks prior to EAE induction (the Tc+EAE group) showed higher EAE clinical scores and greater weight loss compared to the non-infected group with induced EAE (the EAE group). Elevated concentrations of all measured serum cytokines (IL-1α, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A, IFN-γ and TNF-α) were observed in the Tc+EAE group compared to the EAE group. In the CNS, the similar number of regulatory T cells (Tregs; CD4+FoxP3+Helios+) but their decreased proportion from total CD4+ cells was found in the Tc+EAE group compared to the EAE group. This could indicate that the group Tc+EAE harboured significantly more CD4+ T cells of non-Treg phenotype within the affected CNS. Altogether, our results demonstrate that infection of mice with T. canis worsens the course of subsequently induced EAE. Further studies are, therefore, urgently needed to reveal the underlying pathological mechanisms and to investigate possible risks for the human population, in which exposure to T. canis is frequent.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 1
- Cited by



