Article contents
Metformin improves the therapeutic efficacy of low-dose albendazole against experimental alveolar echinococcosis
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 October 2021
Abstract
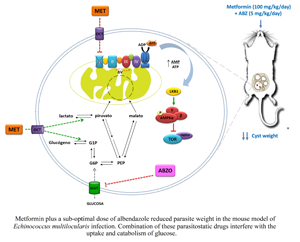
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is a severe disease caused by Echinococcus multilocularis. Its chemotherapeutic treatment is based on benzimidazoles, which are rarely curative and cause several adverse effects. Therefore, it is necessary to develop alternative and safer chemotherapeutic strategies against AE. It has previously been shown that metformin (Met) exhibits considerable in vivo activity on an early-infection model of AE when administered at 50 mg kg−1 day−1 for 8 weeks. Here, the challenge is heightened by a 2-fold increase in parasite inoculum or by starting the treatment 6 weeks post-infection. In both cases, only the combination of Met (100 mg kg−1 day−1) together with a sub-optimal dose of albendazole (ABZ) (5 mg kg−1 day−1) led to a significant reduction in parasite weight compared to the untreated group. Coincidentally, drug combination showed the highest level of damage in E. multilocularis metacestodes. Likewise, Met alone or combined with ABZ led to a decrease in parasite glucose availability, which was evidenced as a lower intracystic glucose concentration. Therefore, the results demonstrate that combination therapy with Met and ABZ offers an alternative to improve the efficacy and reduce the toxicity of the high-dose ABZ monotherapy currently employed.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 9
- Cited by



