Article contents
Effects of multiple stressors on northern leopard frogs in agricultural wetlands
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 March 2021
Abstract
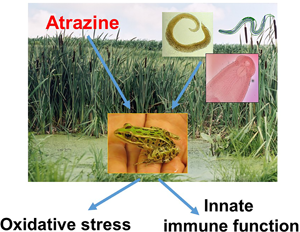
Natural and anthropogenic stressors, including parasites and pesticides, may induce oxidative stress in animals. Measuring oxidative stress responses in sentinel species that are particularly responsive to environmental perturbations not only provides insight into host physiology but is also a useful readout of ecosystem health. Newly metamorphosed northern leopard frogs (Lithobates pipiens), a sentinel species, were collected from agricultural and non-agricultural wetlands exposed to varying concentrations of the herbicide atrazine. Significant effects of certain parasites' abundance and their interaction with atrazine exposure on frog oxidative stress were identified. Specifically, increased protein levels were detected in frogs infected with echinostome metacercariae. In addition, the nematode Oswaldocruzia sp. was significantly associated with increased thiol concentration and catalase activity. Significant parasite × atrazine interactions were observed for atrazine exposure and the abundance of Oswaldocruzia sp. on thiol, as thiol concentrations increased with parasite abundance at low atrazine localities and decreased in high atrazine wetlands. In addition, a significant interaction between the abundances of Oswaldocruzia sp. and gorgoderid trematodes on thiol concentrations was observed. These findings demonstrate that studies of oxidative stress on animals in natural ecosystems should account for the confounding effects of parasitism, particularly for amphibians in agricultural landscapes.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 10
- Cited by



