Article contents
Another plea for ‘best practice’ in molecular approaches to trematode systematics: Diplostomum sp. clade Q identified as Diplostomum baeri Dubois, 1937 in Europe
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 07 January 2022
Abstract
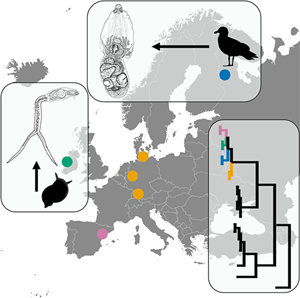
DNA sequence data became an integral part of species characterization and identification. Still, specimens associated with a particular DNA sequence must be identified by the use of traditional morphology-based analysis and correct linking of sequence and identification must be ensured. Only a small part of DNA sequences of the genus Diplostomum (Diplostomidae) is based on adult isolates which are essential for accurate identification. In this study, we provide species identification with an aid of morphological and molecular (cox1, ITS-5.8S-ITS2 and 28S) characterization of adults of Diplostomum baeri Dubois, 1937 from naturally infected Larus canus Linnaeus in Karelia, Russia. Furthermore, we reveal that the DNA sequences of our isolates of D. baeri are identical with those of the lineage Diplostomum sp. clade Q , while other sequences labelled as the ‘D. baeri’ complex do not represent lineages of D. baeri. Our new material of cercariae from Radix balthica (Linnaeus) in Ireland is also linked to Diplostomum sp. clade Q. We reveal that D. baeri is widely distributed in Europe; as first intermediate hosts lymnaeid snails (Radix auricularia (Linnaeus), R. balthica) are used; metacercariae occur in eye lens of cyprinid fishes. In light of the convoluted taxonomy of D. baeri and other Diplostomum spp., we extend the recommendations of Blasco-Costa et al. (2016, Systematic Parasitology 93, 295–306) for the ‘best practice’ in molecular approaches to trematode systematics. The current study is another step in elucidating the species spectrum of Diplostomum based on integrative taxonomy with well-described morphology of adults linked to sequences.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 14
- Cited by



