Introduction
Currently, parasitic gastrointestinal nematodes (GINs) of medical and veterinary importance are primarily controlled using anthelmintic drugs that remove the adults from the host. The reliance on anthelmintics has resulted in the widespread development of resistant nematodes, especially in livestock parasites, some of which are resistant to 1 or more major classes of anthelmintic drugs (Kaplan, Reference Kaplan2004, Reference Kaplan2020; Wolstenholme et al., Reference Wolstenholme, Fairweather, Prichard, von Samson-Himmelstjerna and Sangster2004; Kaplan and Vidyashankar, Reference Kaplan and Vidyashankar2012). Recent studies by us (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019) and others (Hess et al., Reference Hess, Millward, Rudinsky, Vincent and Marsh2019; Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019) have reported the emergence of multi-anthelmintic drug-resistant (MADR) Ancylostoma caninum hookworms which have spread to the general companion dog population from retired greyhounds (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019; Jimenez Castro and Kaplan, Reference Jimenez Castro and Kaplan2020; Balk et al., Reference Balk, Mitchell, Hughes, Soto Nauto, Rossi and Ramirez-Barrios2023; Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). Most of these hookworm isolates are resistant to the 3 major classes of anthelmintics used for treatment: the benzimidazoles (BZ), the macrocyclic lactones (ML) including ivermectin (IVM), and the imidazothiazoles/tetrahydropyrimidines levamisole and pyrantel (PYR). Of these, a molecular mechanism of resistance is known only for BZ resistance. In GINs infecting livestock, resistance is associated with mutations in 1 of 3 amino acids in isotype 1 of the β-tubulin gene: a phenylalanine to tyrosine mutation in codons 167 or 200, or a glutamate to alanine or leucine change in codon 198, with the 167 and 200 mutations occurring more frequently (Kwa et al., Reference Kwa, Veenstra and Roos1994; Silvestre and Cabaret, Reference Silvestre and Cabaret2002; Ghisi et al., Reference Ghisi, Kaminsky and Maser2007; Vercruysse et al., Reference Vercruysse, Albonico, Behnke, Kotze, Prichard, McCarthy, Montresor and Levecke2011). Recently, several additional mutations in codon 198 found at low frequencies in parasitic nematode populations have been shown to confer resistance to BZ in Caenorhabditis elegans (Avramenko et al., Reference Avramenko, Redman, Melville, Bartley, Wit, Queiroz, Bartley and Gilleard2019; Dilks et al., Reference Dilks, Hahnel, Sheng, Long, McGrath and Andersen2020, Reference Dilks, Koury, Buchanan and Andersen2021; Mohammedsalih et al., Reference Mohammedsalih, Krucken, Khalafalla, Bashar, Juma, Abakar, Abdalmalaik, Coles and von Samson-Himmelstjerna2020). Resistance to benzimidazoles has been reported in populations of A. caninum across the country, with varying frequencies of the 167 alleles as well as the recently reported novel Q134H mutation (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021; Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019; Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). Both the F167Y and Q134H mutations were definitively confirmed to impart BZ resistance using C. elegans as a surrogate (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019; Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). The mechanisms of resistance to IVM and PYR are currently unknown. Recently, several quantitative trait loci have been linked to ivermectin resistance in GINs, and the putative transcription factor cky-1 has been identified as a possible mediator of IVM resistance (Choi et al., Reference Choi, Bisset, Doyle, Hallsworth-Pepin, Martin, Grant and Mitreva2017; Doyle et al., Reference Doyle, Illingworth, Laing, Bartley, Redman, Martinelli, Holroyd, Morrison, Rezansoff, Tracey, Devaney, Berriman, Sargison, Cotton and Gilleard2019; Doyle et al., Reference Doyle, Laing, Bartley, Morrison, Holroyd, Maitland, Antonopoulos, Chaudhry, Flis, Howell, McIntyre, Gilleard, Tait, Mable, Kaplan, Sargison, Britton, Berriman, Devaney and Cotton2022, Laing et al., Reference Laing, Doyle, McIntyre, Maitland, Morrison, Bartley, Kaplan, Chaudhry, Sargison, Tait, Cotton, Britton and Devaney2022). Pyrantel resistance in A. caninum has been associated with alterations of nematode acetylcholine receptor subunit expression levels (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Coleman, Traub, McCarthy and Kotze2009), but the underlying genetic mutation is unknown.
When third-stage infective larvae (iL3) of A. caninum are incubated with a host-mimicking signal in vitro, they resume feeding over a period of 24 h, which has been termed larval activation (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1990, 1991a; Hotez et al., Reference Hotez, Hawdon and Schad1993). Activation is thought to represent initial steps in the transition to the parasitic stage of the life cycle, and is analogous to feeding associated with recovery of the analogous C. elegans dauer larva from developmental arrest (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon, Schad, Toft, Aeschlimann and Bolis1991a; Hotez et al., Reference Hotez, Hawdon and Schad1993; Crook, Reference Crook2014). The molecular components of the A. caninum activation pathway are highly conserved with those of the C. elegans dauer pathway, and include cGMP and insulin-like signalling (ILS) pathways (Tissenbaum et al., Reference Tissenbaum, Hawdon, Perregaux, Hotez, Guarente and Ruvkun2000; Hawdon and Datu, Reference Hawdon and Datu2003; Brand and Hawdon, Reference Brand and Hawdon2004; Gao et al., Reference Gao, Frank and Hawdon2009; Reference Gao, Wang, Martin, Abubucker, Zhang, Mitreva and Hawdon2010; Kiss et al., Reference Kiss, Gao, Krepp and Hawdon2009; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Zhou, Motola, Gao, Suino-Powell, Conneely, Ogata, Sharma, Auchus, Lok, Hawdon, Kliewer, Xu and Mangelsdorf2009). Here a triple resistant isolate of A. caninum that exhibits an alternate activation phenotype compared to our susceptible isolate is described.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
All experiments involving animals were conducted in strict accordance with the recommendations of the National Institute of Health (USA) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Animal Welfare Act (National Research Council, 2011; USDA, 2018). The animal protocol used in this study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of The George Washington University (USA).
Parasites and reagents
Wild-type laboratory isolate WMD and multidrug-resistant isolate KGR were described previously (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). The KGR isolate used here is resistant to thiabendazole (TBZ) and IVM. Multidrug-resistant BCR was isolated from a retired racing greyhound, which was raised in Kansas and raced in Florida, in October 2019. The dog had a history of recurring hookworm infections, and had been treated with Drontal Plus (praziquantel/pyrantel pamoate/febantel) prior to adoption. Infective third-stage larvae (iL3s) reared from eggs collected from feces of the infected dog were used to infect a hookworm naïve beagle. All isolates were maintained in beagles as described previously (Schad, Reference Schad and Meerovitch1982; Krepp et al., Reference Krepp, Gelmedin and Hawdon2011). Thiabendazole, ivermectin, pyrantel pamoate, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 8-bromo-cGMP were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Moxidectin (MOX) was a gift from Zoetis (Kalamazoo, MI, USA).
Larval development assay
Larval development assays (LDA) were performed as described in Kitchen et al. (Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019) with slight modifications. Briefly, stock concentrations of 10 mm IVM, 10 mm MOX and 10 mg mL−1 PYR were serially diluted 2-fold in 1% DMSO to concentrations twice the desired final concentration. For each drug concentration and control, 1.56 × 108 cells of ampicillin-resistant OP50 and 100 L1s in nematode handling buffer BU (50 mm Na2HPO4, 22 mm KH2PO4, 70 mm NaCl, pH 6.8) (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1991b) with ampicillin in a volume of 250 μL were added to duplicate wells of a 24-well tissue culture plate. In total, 250 μL of the appropriate drug concentration or 1% DMSO for controls was added to the wells. The final concentrations of IVM were between 1000 and 1.95 nm, and the final concentrations of PYR were between 168.2 and 0.33 mm. Plates were incubated at 27°C for a minimum of 7 days, after which 100 μL of Lugol's iodine was added to each well, and the number of larvae that had reached the iL3 stage and the number that did not reach the iL3 stage (L1 + L2) was counted. The percentage developing across all replicates was determined using the formula iL3total/((L1 + L2)total + iL3total) × 100. The percentage of larvae developing to the iL3 was normalized to the average development of iL3 in control wells. Three biological replicates with 2 technical replicates for each concentration were performed for each hookworm isolate. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated by plotting the average percentage of larvae developing to the iL3 stage against the log of the drug concentration. The resulting curve was analysed using the sigmoidal dose–response (variable slope) function in GraphPad Prism (ver. 9, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) to generate the IC50. Resistance ratios (RRs) at the IC50 concentrations for each drug were calculated by dividing the resistant isolate IC50 values by the corresponding wild-type values.
Egg hatch assay
Egg hatch assays (EHAs) were performed as described (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019) except that 3-fold dilutions of TBZ between 50 and 0.002 mm were used, and Lugol's iodine was not added to wells before counting. A minimum of 4 biological replicates with 3 technical replicates per concentration were performed for each isolate.
Fecal egg count reduction test (FECRT)
After 101 days of infection, the laboratory dog infected with the BCR isolate was treated orally with pyrantel pamoate (5 mg kg−1). Both prior to and following treatment, fecal egg counts (FEC) were regularly performed by homogenizing 2 g of feces in 60 mL of saturated salt solution and counting the eggs using a McMaster slide. The number of observed eggs was multiplied by 100 to determine the eggs per gram (EPG). The average EPG during the week prior to treatment and the average EPG on days 9, 10 and 11 post treatment were determined. A second dog infected with the KGR isolate was treated orally at day 37 post-infection with 5 mg kg−1 pyrantel pamoate, and the average EPG 3 days prior to treatment and on days 10, 11 and 12 post treatment were calculated. The equation ((pre-treatment FEC – post-treatment FEC)/(pre-treatment FEC)) × 100 to determine reduction in fecal egg count (FECR). Third-stage larvae from the first passage after pyrantel (BCR (P1)) were collected for genetic analysis.
β-tubulin codon 167 relative allele frequency determination
The relative frequency of the β-tubulin codon 167 resistant and susceptible alleles was determined according to Kitchen et al. (Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). Briefly, genomic DNA was isolated from each isolate using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). Separate quantitative polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) containing Brilliant II SYBR Green QPCR Master mix (Agilent Technology, Santa Clara, CA, USA), 10 ng of genomic DNA, a common reverse primer (5′-gctggcgccttcgccttttc-3′) and a forward primer designed to amplify either the susceptible wild-type allele (5′-gataggatcatgtcctcgtt-3′) or the resistant mutant allele (5′-gataggatcatgtcctcgta-3′) of the tbb-iso-1 gene were performed on a CFX96 detection system (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's suggested conditions. Relative allele frequencies were calculated using the formula:
where ΔCt = (Ct of allele1-specific PCR)–(Ct of allele2-specific PCR). Ct values were the mean of at least 3 technical replicates (Germer et al., Reference Germer, Holland and Higuchi2000).
As part of a larger study, we have sequenced the genomes of KGR, BCR, BCR (P1) and WMD isolates (data not shown). A pool-seq approach (Schlotterer et al., Reference Schlotterer, Tobler, Kofler and Nolte2014; Choi et al., Reference Choi, Bisset, Doyle, Hallsworth-Pepin, Martin, Grant and Mitreva2017) was employed to ascertain the allele frequencies of β-tubulin isotype 1 (tbb-iso-1) mutations F167Y (TTC>TAC) and Q134H (CAA>CAT) in KGR, BCR and WMD isolates. Only sites with a log-likelihood ratio of polymorphism greater than 22 (-p 22) were retained for allele frequency analysis. The sequences are available under BioProject PRJNA72585 (accession numbers SRR26411280 -SRR26411283).
cDNA synthesis and β-tubulin isotype 1 (tbb-iso-1) sequencing
Total RNA was isolated from approximately 10 000 BCR iL3 using Trizol (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA USA ) and cDNA synthesized as described previously (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). The tbb-iso-1 cDNA was PCR amplified using primers SHH282 (5′-atgcgtgagatcgtgcatgt-3′) and SHH286 (5′- ctactcctcggggtaagcct-3′), and pooled reactions purified using the Nucleospin Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Takara, San Jose, CA USA). Purified amplicons were Sanger sequenced by MCLAB (South San Francisco, CA ) using primers SHH282 (5′-atgcgtgagatcgtgcatgt-3′), SHH283 (5′-gcaaagaggcggaagg-3′), SHH284 (5′-caacagagaacgaagacatg-3′), SHH285 (5′-tttgctccactttcggc-3′) and SHH286 (5′- ctactcctcggggtaagcct-3′). The BCR tbb-iso-1 cDNA sequence was submitted to GenBank with the accession number MZ889668.
Larval activation assay
Infective L3 were recovered from coprocultures by a modified Baermann technique 7–10 days post-culture and stored for up to 3 weeks in BU at 22°C until used for activation studies. Ancylostoma caninum iL3 were activated under host-like conditions as described previously (Hawdon et al., Reference Hawdon, Narasimhan and Hotez1999). Briefly, iL3 collected from coprocultures were decontaminated with 1% (v/v) HCl in BU buffer for 30 min at 22°C. Approximately 250 iL3 were incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 24 h in 0.1 ml RPMI1640 tissue culture medium supplemented with 25 mm HEPES pH 7.0 and antibiotics (RPMI-c) in individual wells of 96-well microtiter plates (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1990). Activated L3 were stimulated by inclusion of 10% (v/v) canine serum and 15 mm S-methyl-glutathione (GSM; Sigma) or 10 mm 8-bromo-cGMP (Sigma) dissolved in RPMI-c (Hawdon et al., Reference Hawdon, Jones, Perregaux and Hotez1995; Hawdon and Datu, Reference Hawdon and Datu2003). Negative control (non-activated) L3 were incubated in RPMI-c without the stimuli. Treatments were done in triplicate, and the percentage of feeding larvae was determined as described (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1990). To monitor feeding, 100 μL of 2.5 mg mL−1 fluorescein-labelled bovine serum albumin (Sigma) was added to the wells at 24 h and incubated for 2–3 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. After incubation, the labelled larvae were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Feeding larvae, as evidenced by the presence of fluorescence in the lumen of the oesophagus and intestine, were counted and expressed as a percentage of the total larvae counted. A minimum of 50 total larvae were counted. To perform the larval activation inhibition assay (LAIA) to detect PYR resistance, WMD and BCR iL3 were incubated as described above together with increasing concentrations of PYR, and feeding determined at 24 h.
Statistical analyses
Tests for statistical significance were conducted in GraphPad Prism (ver. 9, GraphPad Software, La Jolla CA USA). A 1-tailed t-test was used to calculate the significance between average BCR and WMD feeding behaviours in the LAIA. A pairwise ANOVA was used to compare feeding behaviours of BCR, KGR and WMD in the presence of serum stimulus or 8-bromo-cGMP. A 1-way ANOVA was used to compare the feeding behaviours of BCR and WMD in the presence of serum stimulus and various concentrations of pyrantel.
Results
Resistance assays
A member of the Microbiology, Immunology, and Tropical Medicine department at The George Washington University had recently adopted a 3.6-year-old retired racing greyhound (named ‘Bean Counter’) with a history of a hookworm infection that was refractory to treatment with several anthelmintic regimens. Our recent report (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019), as well as that of others (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021), on multidrug-resistant hookworms isolated from greyhounds led us to predict the Bean Counter's hookworms were also multidrug resistant. To further investigate and characterize the isolate, a naïve beagle pup was infected with iL3 reared from Bean Counter's feces to establish the ‘BCR’ (Bean Counter-resistant) isolate in the lab.
Resistance of the BCR isolate to the BZ anthelmintic TBZ was measured using an EHA. A distinct rightward shift along the x-axis in the dose–response curve is seen in both resistant isolates (KGR and BCR) when compared to the wild-type WMD (Fig. 1). The BCR isolate was over 4 times more resistant to TBZ than KGR, with an IC50 of 40.08 μ m compared to 8.76 μ m for KGR. The RR, calculated by dividing the IC50 of the resistant isolate by the IC50 of the susceptible (WMD) isolate, of BCR was 105.5 compared to 23.1 in KGR (Table 1, Fig. 1).

Figure 1. Dose–response curves of Ancylostoma caninum isolates to thiabendazole (TBZ) using the egg hatch assay (EHA). Each point represents a minimum of 6 replicates from 3 independent experiments (WMD n = 59, KGR n = 60, BCR n = 62). The curves were analysed using the sigmoidal dose–response (variable slope) function in GraphPad Prism (ver. 9) to generate the IC50 values reported in Table 1.
Table 1. Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and resistance ratios (RR) of Ancylostoma caninum WMD, KGR and BCR isolates to thiabendazole, ivermectin and pyrantel pamoate

TBZ, thiabendazole; IVM, ivermectin; PYR, pyrantel pamoate; WMD, susceptible isolate; KGR, previously reported resistant isolate; BCR, resistant isolate; SE, standard error of the logIC50 reported by Graphpad Prism (ver 9); n = average number of larvae per replicate. IC50 values (μM) were generated by analysis of dose–response curves determined by larval development assays (LDA) and resistance ratio (RR) generated by dividing resistant isolate IC50 by WMD wild type IC50.
Next, an LDA assay was used to determine if BCR was resistant to IVM, MOX and PYR. As shown in Fig. 2A, the dose–response curves for KGR and BCR are again shifted rightward, indicating that both isolates are resistant to IVM. The IC50 of the KGR isolate was 233.7 nm and the RR was 14.9, nearly twice that of the BCR with an IC50 of 127.0 nm and RR of 8.1 (Table 1). BCR worms were profoundly resistant to the MOX (IC50 425.1 nm, RR 101), a newer member of the ML drug family (Fig. 2B). However, when BCR was tested for PYR resistance using the LDA, no significant resistance could be demonstrated (BCR RR = 1.5, KGR RR = 1.3) (Fig. 2C). The inability to detect PYR resistance using the LDA has been reported previously (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Coleman, McCarthy and Kotze2008; Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019). Given the co-occurrence of PYR with BZ and IVM resistance in greyhounds, a FECRT was performed following PYR treatment. Treatment of a BCR-infected dog with a standard dose of PYR (5 mg kg−1) had no effect on the infection. The average FEC the week prior to treatment was 1950 EPG, while the average FEC on days 9–11 post-treatment was 2833 EPG (FECR = −45.2%). Conversely, treatment of a KGR-infected dog reduced the egg count significantly, from 1200 EPG pre-treatment to 233 EPG 10–12 days post-treatment (FECR = 80.6%) (Fig. 3). To confirm PYR resistance in BCR, an LAIA was used, which is a modification of the in vitro larval feeding inhibition assay (LFIA) (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Coleman, McCarthy and Kotze2008). As shown in Supplementary Fig. 1, concentrations of pyrantel greater than 20 μg mL−1 significantly inhibited feeding of WMD L3 compared to BCR. The 100 μg mL−1 concentration was selected for the assay because of the highly significant (P < 0.01) feeding difference between the resistant and susceptible isolates. At a PYR concentration of 100 μg mL−1, 27 ± 5% of BCR L3 were feeding, whereas 2 ± 1.6% of WMD L3 fed (Fig. 2D). Together these results indicated that the BCR isolate is resistant to PYR in addition to TBZ, IVM and MOX.

Figure 2. Dose–response curves of Ancylostoma caninum isolates WMD (sensitive), KGR (double resistant) and BCR (triple resistant) using a larval development assay (LDA) and a larval activation inhibition assay (LAIA). Dose–response curves to (A) ivermectin (IVM), (B) moxidectin (MOX) and (C) pyrantel (PYR) determined by LDA. The curves were analysed using the sigmoidal dose–response (variable slope) function in GraphPad Prism (ver. 9) to generate the IC50 values reported in Table 1. Each point represents a minimum of 6 replicates from 3 independent experiments. (D) In vitro larval activation inhibition assay (LAIA) for PYR resistance. Third-stage infective larvae (iL3) of susceptible WMD and resistant BCR isolates were incubated with 100 μg mL−1 PYR overnight at 37°C, then assayed for activation. The mean of 4 (WMD) or 6 (BCR) replicates from 2 or 3 independent experiments were analysed by 1-tailed t-test in GraphPad Prism. **P < 0.01.

Figure 3. Fecal egg counts (FEC) in BCR and KGR isolates. (A) FEC were performed over the course of infection for a dog infected with the BCR hookworm isolate and (B) the KGR isolate to test for pyrantel resistance. The red arrow marks when pyrantel treatment was administered. BCR and KGR were treated at 101- and 37-days post-infection, respectively. Blank areas marked with red asterisks indicate days when the FEC was not measured.
Sequencing of the BCR β-tubulin isotype 1 gene
BZ resistance in parasitic nematodes is most frequently associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 1 of 3 codons in the β-tubulin isotype 1 (F200Y, E198L, F167Y) (Kwa et al., Reference Kwa, Kooyman, Boersema and Roos1993a, Reference Kwa, Veenstra and Roos1993b, Reference Kwa, Veenstra and Roos1994; Beech et al., Reference Beech, Prichard and Scott1994; Elard and Humbert, Reference Elard and Humbert1999; Silvestre and Cabaret, Reference Silvestre and Cabaret2002; Ghisi et al., Reference Ghisi, Kaminsky and Maser2007; Kotze et al., Reference Kotze, Cowling, Bagnall, Hines, Ruffell, Hunt and Coleman2012; Hahnel et al., Reference Hahnel, Zdraljevic, Rodriguez, Zhao, McGrath and Andersen2018). More recent work has identified an SNP in another codon (Q134H) in the β-tubulin isotype 1 of A. caninum (Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). To date, all hookworm isolates resistant to benzimidazole anthelmintics have exhibited the F167Y or Q134H mutation (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021; Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019; Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). To determine if any of these mutations were present in BCR-resistant worms, the tbb-iso-1 cDNA was amplified and sequenced and compared to the A. caninum Baltimore isolate (GenBank accession number DQ059758), our previous resistant isolate KGR (MH253569) (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019) and our susceptible isolate WMD (MH253570) sequences. Thirteen synonymous mutations and a single non-synonymous SNP that changed TTC (Phe) to TAC (Tyr) in amino 167 of the BCR isolate were found (Fig. 4). This SNP has been associated with BZ resistance in several strongylid nematodes, including hookworms (Silvestre and Cabaret, Reference Silvestre and Cabaret2002; Albonico et al., Reference Albonico, Wright and Bickle2004; Schwenkenbecher et al., Reference Schwenkenbecher, Albonico, Bickle and Kaplan2007; Vercruysse et al., Reference Vercruysse, Albonico, Behnke, Kotze, Prichard, McCarthy, Montresor and Levecke2011; Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021; Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019), and imparted TBZ resistance to C. elegans edited to contain the corresponding mutation in the ben-1 gene (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). No mutations were found at amino acid 134, 198 or 200 of tbb-iso-1 in BCR using this sequencing approach.

Figure 4. Sequences of β-tubulin isotype 1 cDNAs from 4 Ancylostoma caninum isolates. (A) DNA sequences. The non-synonymous mutation in codon 167 associated with benzimidazole resistance is shaded grey. A synonymous mutation in codon 165 of the BAL sequence is underlined. There were no mutations in codons 134, 182, 198 and 200, which have been associated with resistance to benzimidazoles, detected using this technique. (B) Protein translation of the relevant region of the β-tubulin isotype 1 sequence. The F167Y mutation is highlighted. BAL, Baltimore isolate reference genome (DQ059758; Bioproject PRJNA72585); WMD, thiabendazole-susceptible isolate (MH253570); KGR, thiabendazole-resistant isolate (MH253569); BCR, thiabendazole-resistant isolate (MZ889668).
Considering the relatively high frequency of the Q134H allele reported in canine populations, the limitations in our sequencing approach and large differences in RRs between KGR and BCR isolates (above), the recently sequenced genomes of WMD, KGR, BCR and BCR (P1) were interrogated for the presence of the Q134H allele. Examination of the tbb-iso-1 gene for mutations revealed both the F167Y (TTC>TAC) and Q134H (CAA>CAT) alleles. The alleles were not observed together on the same haplotype, suggesting they occur in a trans configuration (Supplementary Fig. 2).
Resistant allele frequencies
Previously, the frequency of the 167 resistant alleles (TAC) was found to be fixed at 100% in our KGR isolate (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). To determine the frequency of the TAC allele in BCR, a sensitive quantitative PCR assay was used to measure the relative ratio of the susceptible allele to the resistant allele (Germer et al., Reference Germer, Holland and Higuchi2000; Schwenkenbecher et al., Reference Schwenkenbecher, Albonico, Bickle and Kaplan2007; Kotze et al., Reference Kotze, Cowling, Bagnall, Hines, Ruffell, Hunt and Coleman2012; Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019). The allele frequencies in WMD, KGR and the first passage of BCR were determined. As shown in Table 2, the frequency of the resistant allele in WMD was <1%, but 99.97% in KGR. In larvae recovered from the first BCR infection, the frequency of the resistant allele was 76.3%, indicating the presence of heterozygotes in the population. Next, the allele frequencies in the original Bean Counter iL3 from the same batch used to establish the BCR isolate were measured. The allele frequencies in these Bean Counter larvae were 44.1 and 55.9% for the susceptible and resistant allele, respectively. This indicates that the frequency of the TAC-resistant allele increased from 56 to 76% with passage of the isolate in vivo in the absence of anthelmintic treatment.
Table 2. Frequency of wild-type and resistant β-tubulin F167Y allele in hookworm isolates

Allele frequencies were calculated using the formula frequency = 1/(2ΔCt + 1). Cycle threshold (Ct) values are the mean of 4 technical replicates. ΔCt = Ct−sen–Ct−res. WMD, susceptible isolate; KGR, double-resistant isolate; BCR, triple resistant isolate; Bean Counter, larvae from the infected greyhound that was the source of isolate BCR.
Based on the number of reads that support each allele (i.e. allele counts) in our genomic sequence data, the allele frequency of tubulin mutations in each of the isolates was estimated. The frequency of the TAC resistance mutation in codon 167 was 96.4% (54/56 reads) in KGR and 84.0% (21/25) in BCR. As the number of reads in the BCR sequences was reduced due to bacterial contamination, we also estimated the TAC allele frequency in BCR (P1), which was derived from iL3 collect from the first passage of BCR following treatment with PYR for the FECRT. The frequency of the TAC allele was 81.8% (99/121) in BCR (P1). The allele frequencies from the genomic sequences were similar to the allele frequencies determined by quantitative PCR (99.97 and 76.3%, respectively). The frequency of the TAC mutation in WMD was zero (0/55). The CAT resistance mutation in codon 134 was present in 16.0% (4/25) of the reads in BCR and 18.2% (26/143) of the reads in BCR (P1) but was absent (0/53 and 0/54) in KGR and WMD, respectively.
Altered activation phenotype
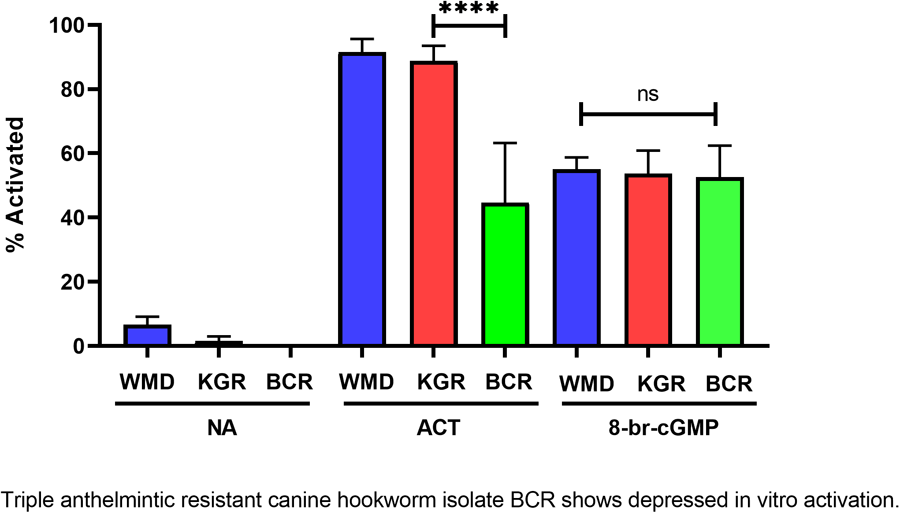
Feeding by infective L3 of hookworms and other nematodes in response to host-like stimuli in vitro has been termed larval activation (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1990, 1991a). Due to its similarity to recovery from the dauer stage in C. elegans, hookworm larval activation is believed to represent an early step in the transition to parasitism that occurs during infection of a permissive host (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon, Schad, Toft, Aeschlimann and Bolis1991a; Hawdon and Hotez, Reference Hawdon and Hotez1996). The activation pathway in hookworms is highly conserved with recovery from the dauer stage in C. elegans, and is mediated by both cGMP and ILS pathways (Tissenbaum et al., Reference Tissenbaum, Hawdon, Perregaux, Hotez, Guarente and Ruvkun2000; Hawdon and Datu, Reference Hawdon and Datu2003; Brand and Hawdon, Reference Brand and Hawdon2004; Gao et al., Reference Gao, Frank and Hawdon2009; Kiss et al., Reference Kiss, Gao, Krepp and Hawdon2009; Gelmedin et al., Reference Gelmedin, Brodigan, Gao, Krause, Wang and Hawdon2011) (Fig. 5A). When BCR iL3 were tested in our activation assay, their maximum feeding level was significantly lower (approximately 40–50%) than the feeding level of the wild-type WMD and the double-resistant KGR isolates (Fig. 5B). Exogenous cGMP (as 8-bromo-cGMP) initiated feeding similarly in all isolates (Fig. 5B), indicating that the signalling pathway downstream of the cGMP step is functioning normally in BCR worms, and that the defect causing decreased activation is upstream, likely in the membrane guanylyl cyclase (mGC) itself, as mGC is believed to be the first molecule in the activation pathway (Fig. 5A) (Murakami et al., Reference Murakami, Koga and Ohshima2001).

Figure 5. Altered feeding response in pyrantel-resistant BCR isolate. (A) General activation pathway. (B) Hookworm iL3 from each isolate were incubated in medium alone (NA), serum stimulus (ACT) or 15 mm 8-bromo-cGMP for 24 h, after which the number of activated (feeding) iL3 was determined. Experiments were done in triplicate and repeated twice, so that each value is the mean ± s.d. of 9 replicates, and analysed by pairwise ANOVA. ****P < 0.0001. mGC, membrane guanylyl cyclase; MuscR, muscarinic receptor; InsR, insulin receptor, FOXO, forkhead transcription factor.
Discussion
Domestic dogs are the most common companion animal, with an estimated 700 million worldwide (Hughes and Macdonald, Reference Hughes and Macdonald2013). This popularity comes with the potential for zoonotic exposure of people to canine parasites and risk of disease from these parasites. Hookworms are one of the greatest zoonotic concerns presenting significant risk to human health (Otranto et al., Reference Otranto, Dantas-Torres, Mihalca, Traub, Lappin and Baneth2017). The most common zoonotic species, A. caninum, is found in wild and domestic canids around the world. Ancylostoma caninum causes follicular cutaneous larva migrans (CLM), an intensely pruritic skin infection, in humans exposed to infective larvae. While the prevalence of CLM in the United States is unknown, it is thought to be second behind pinworm among helminth infections in developed countries (Robles and Habashy, Reference Robles and Habashy2020). Other zoonotic diseases caused by hookworms include eosinophilic enteritis resulting from a single immature adult worm establishing in the intestine, and diffuse unilateral subacute neuroretinitis, a serious infection caused by infective larvae migrating through the eye (Hawdon and Wise, Reference Hawdon, Wise, Strube and Mehlhorn2021). Patent infections in humans infected with A. caninum have been recently identified, suggesting that infections in humans are more common than previously thought (Ngcamphalala et al., Reference Ngcamphalala, Lamb and Mukaratirwa2019; Furtado et al., Reference Furtado, Dias, Rodrigues, Silva, Oliveira and Rabelo2020; Hawdon and Wise, Reference Hawdon, Wise, Strube and Mehlhorn2021).
Pet dog ownership in the United States is at the highest level ever reported; 45% of households own a dog, totalling 83 to 89 million animals (American Veterinary Medical Association, 2022). Ancylostoma caninum is the most prevalent and significant intestinal nematode of dogs in the United States (Little et al., Reference Little, Johnson, Lewis, Jaklitsch, Payton, Blagburn, Bowman, Moroff, Tams, Rich and Aucoin2009), and its prevalence has increased significantly over the last 5 years (Drake and Carey, Reference Drake and Carey2019; Sweet et al., Reference Sweet, Hegarty, McCrann, Coyne, Kincaid and Szlosek2021). Heavy infection causes severe, often fatal anaemia in puppies, and malnutrition and failure to thrive in older dogs. A recent retrospective survey found that hookworms were the most prevalent canine helminth parasite in 9 US states at approximately 5.6%, ranging as high as 11.9% in Georgia (Sobotyk et al., Reference Sobotyk, Upton, Lejeune, Nolan, Marsh, Herrin, Borst, Piccione, Zajac, Camp, Pulaski, Starkey, von Simson and Verocai2021). Hookworm prevalence has been increasing (Drake and Carey, Reference Drake and Carey2019; Nagamori et al., Reference Nagamori, Payton, Looper, Apple and Johnson2020), possibly reflecting the emergence of multiple anthelmintic-resistant hookworm isolates like BCR reported here in greyhounds and spreading to the general pet dog population (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021; Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019; Jimenez Castro and Kaplan, Reference Jimenez Castro and Kaplan2020; Balk et al., Reference Balk, Mitchell, Hughes, Soto Nauto, Rossi and Ramirez-Barrios2023; Leutenegger et al., Reference Leutenegger, Lozoya, Tereski, Savard, Ogeer and Lallier2023; Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). Increasing prevalence of MADR A. caninum has serious implications both for canine companion health and for zoonotic infections (Hawdon and Wise, Reference Hawdon, Wise, Strube and Mehlhorn2021). Indeed, the BCR isolate is profoundly resistance to the 3 classes of anthelmintic that are currently used for treatment of canine and zoonotic hookworm infections, which will complicate treatment of hookworm infections should they become widespread.
The IC50 of BCR to TBZ is nearly 5 times that of our previously reported resistant KGR isolate in an EHA (40.1 vs 8.76 μ m, RR 106 vs 23). The BCR is significantly more resistant than most of the previously published MADR A. caninum isolates that had not undergone selection in the lab (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021). Increased resistance of BCR relative to KGR is interesting, as frequency of the resistant F167Y allele is lower in the BCR isolate (76.3%) than in KGR, where it is essentially fixed (99.97%). A possible explanation for this difference is the presence of a recently identified mutation in codon 134 (CAA>CAT, Q134H) found at low frequency in the BCR, but not the KGR, isolate. However, introduction of this mutation into C. elegans ben-1 conferred a similar level of resistance as the ben-1 null allele (Venkatesan et al., Reference Venkatesan, Jimenez Castro, Morosetti, Horvath, Chen, Redman, Dunn, Collins, Fraser, Andersen, Kaplan and Gilleard2023). In C. elegans, additional mutations in canonical residues of the ben-1 gene have been identified that confer resistance (Dilks et al., Reference Dilks, Hahnel, Sheng, Long, McGrath and Andersen2020, 2021), and there are other non-tubulin mutations suspected to influence BZ resistance (Zamanian et al., Reference Zamanian, Cook, Zdraljevic, Brady, Lee, Lee and Andersen2018), although mutagenesis screens in C. elegans yielded either no mutations outside of the ben-1 gene, or a single non-tubulin mutation that was only weakly resistant (Driscoll et al., Reference Driscoll, Dean, Reilly, Bergholz and Chalfie1989; Pallotto et al., Reference Pallotto, Dilks, Park, Smit, Lu, Gopalakrishnan, Gilleard, Andersen and Mains2022).
Unlike TBZ resistance, resistance of the BCR isolate to IVM in the LDA was 54% lower than KGR (127.0–233.7 μ m), with IC50 RRs of 8.1 and 14.9, respectively. Previously, a higher IVM RR for KGR was reported (Kitchen et al., Reference Kitchen, Ratnappan, Han, Leasure, Grill, Iqbal, Granger, O'Halloran and Hawdon2019), which was likely due to technical differences in performance of the assays. The IC50 and RR values for IVM reported herein are more similar to those reported by Jimenez Castro et al. (Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019). The BCR isolate is highly resistant to MOX, a newer, more potent macrocyclic lactone drug. Resistance to MOX appears to develop in a stepwise process, beginning with resistance to IVM (Kaplan et al., Reference Kaplan, Vidyashankar, Howell, Neiss, Williamson and Terrill2007). For example, IVM-resistant, MOX-naïve Haemonchus contortus were found to be susceptible to MOX (Craig et al., Reference Craig, Hatfield, Pankavich and Wang1992; Oosthuizen and Erasmus, Reference Oosthuizen and Erasmus1993). However, IVM-resistant populations quickly obtain resistance to MOX with regular treatment. In addition to BCR, multiple MADR A. caninum isolates from greyhounds exhibit high levels of MOX resistance (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021), most likely as a result of treatment of adopted greyhounds with MOX-containing heartworm preventative formulations. We obtained infective larvae from the greyhound Bean Counter and established the BCR isolate prior to any treatments with MOX-containing formulations by his adopter. We cannot rule out exposure to MOX prior to his adoption, as medical records for those periods were unavailable. In any case, resistance to MOX further complicates treatment of dogs or humans infected with MADR hookworms.
Previous isolates have been reported to be resistant to PYR in addition to BZ and MLs (Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019, Reference Jimenez Castro, Venkatesan, Redman, Chen, Malatesta, Huff, Zuluaga Salazar, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2021, Reference Jimenez Castro, Durrence, Durrence, Giannechini, Collins, Dunn and Kaplan2022). Our LDA assay using PYR failed to discriminate between the susceptible and BCR isolates (Fig. 2C). Lack of discrimination in LDA for PYR has been reported previously, necessitating the use of the FECRT to confirm resistance to PYR (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Kotze, McCarthy and Coleman2007; Jimenez Castro et al., Reference Jimenez Castro, Howell, Schaefer, Avramenko, Gilleard and Kaplan2019; Jimenez Castro and Kaplan, Reference Jimenez Castro and Kaplan2020). The FECRT compares pre- and post-treatment mean egg counts to determine anthelmintic susceptibility. Our results indicated that the BCR isolate was highly resistant to PYR, as illustrated by a negative FECR, whereas the KGR isolate was much more susceptible, with an FECR of 80.6%. There are several disadvantages to the FECR test, most notably the need to infect dogs. Furthermore, the low sample size (n = 1) and other deviations from recommended guidelines for FECR tests (Kaplan et al., Reference Kaplan, Denwood, Nielsen, Thamsborg, Torgerson, Gilleard, Dobson, Vercruysse and Levecke2023) used here limit interpretation somewhat. In addition to the LDA, other in vitro tests have been used in attempts to determine PYR sensitivity, with mixed results (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Coleman, McCarthy and Kotze2008). To confirm our results, a larval arrested morphology assay was attempted first, which in our hands was difficult to interpret (not shown). Next, an LAIA, which is a modified version of the LFIA described by Kopp et al. (Reference Kopp, Coleman, McCarthy and Kotze2008), was used. The LFIA, originally adapted from the hookworm activation assay (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1990), uses the inhibition of iL3 feeding, or activation, as an indicator of PYR sensitivity. In the modified LAIA, the iL3 and increasing PYR concentrations were incubated together initially and feeding determined approximately 24 h later rather than adding PYR following the initial 24 h incubation as described (Kopp et al., Reference Kopp, Coleman, McCarthy and Kotze2008). Using this assay, a significant difference (P < 0.01) between feeding by BCR and WMD larvae was found at 100 μg mL−1 PYR, confirming that BCR is resistant to PYR.
When developmentally arrested hookworm iL3 enter a permissive host, a host-specific signal initiates the resumption of development, which culminates in the adult stage in the intestine. Early steps in this process can be modelled in vitro. When A. caninum iL3 are exposed to a low molecular weight canine serum fraction and a glutathione analogue (F + G), they resume feeding, or ‘activate’, within 6 h, and reach 90% of the iL3 population feeding by 16 h (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon and Schad1992; Hawdon and Hotez, Reference Hawdon and Hotez1996). Activation is thought to represent an early step in infection and is biologically analogous to recovery from the developmentally arrested dauer stage of the model nematode C. elegans (Hawdon and Schad, Reference Hawdon, Schad, Toft, Aeschlimann and Bolis1991a; Hawdon and Hotez, Reference Hawdon and Hotez1996). Dauer arrest in C. elegans is facultative, occurring in response to overcrowding, mediated by the concentration of ascaroside pheromones, and lack of food (Hu, Reference Hu2007; Ludewig and Schroeder, Reference Ludewig and Schroeder2013). Dauer recovery occurs in response to food and lower nematode density and is regulated by the mGC DAF-11 expressed in amphidial neurons ASI, ASJ and ASK (Hanna-Rose and Han, Reference Hanna-Rose and Han2000). DAF-11 binds a bacterial food signal, initiating cGMP synthesis and subsequent signalling through a conserved ILS pathway to cause recovery (Tissenbaum et al., Reference Tissenbaum, Hawdon, Perregaux, Hotez, Guarente and Ruvkun2000; Murakami et al., Reference Murakami, Koga and Ohshima2001; Chung et al., Reference Chung, Schmalz, Ruiz, Gabel and Mazur2013). The dauer pathway is well-studied genetically and biochemically, and the molecular components of the pathway have been identified (Riddle and Albert, Reference Riddle, Albert, Riddle, Blumenthal, Meyer and Priess1997; Hu, Reference Hu2007). Furthermore, the pathway is conserved in GINs, and hookworm iL3 activation is mediated by ILS (Tissenbaum et al., Reference Tissenbaum, Hawdon, Perregaux, Hotez, Guarente and Ruvkun2000; Brand and Hawdon, Reference Brand and Hawdon2004; Gao et al., Reference Gao, Frank and Hawdon2009; Kiss et al., Reference Kiss, Gao, Krepp and Hawdon2009; Wang et al., Reference Wang, Zhou, Motola, Gao, Suino-Powell, Conneely, Ogata, Sharma, Auchus, Lok, Hawdon, Kliewer, Xu and Mangelsdorf2009; Gelmedin et al., Reference Gelmedin, Brodigan, Gao, Krause, Wang and Hawdon2011; Zhi et al., Reference Zhi, Zhou, Melcher, Motola, Gelmedin, Hawdon, Kliewer, Mangelsdorf and Xu2012) and cGMP signalling (Hawdon and Datu, Reference Hawdon and Datu2003) as in C. elegans (Birnby et al., Reference Birnby, Link, Vowels, Tian, Colacurcio and Thomas2000).
When the BCR isolate iL3 were tested for their ability to activate in vitro, they resumed feeding in response to the activation stimulus at levels approximately half that of the WMD and KGR isolates. This altered phenotype is likely caused by a defect at or upstream of the DAF-11/mGC step, as BCR activation in response to exogenous cGMP is unaffected (Fig. 5). While the activation signal is thought to bind to the extracellular domain of the hookworm mGC, it is possible that the signal binds to an upstream G protein-coupled receptor which subsequently signals through the mGC.
Evolutionary theory assumes that the evolution of drug resistance is associated with a fitness trade-off, usually one that is deleterious in the absence of selection (Durão et al., Reference Durão, Balbontín and Gordo2018; Hodgkinson et al., Reference Hodgkinson, Kaplan, Kenyon, Morgan, Park, Paterson, Babayan, Beesley, Britton, Chaudhry, Doyle, Ezenwa, Fenton, Howell, Laing, Mable, Matthews, McIntyre, Milne, Morrison, Prentice, Sargison, Williams, Wolstenholme and Devaney2019). The altered activation phenotype may be evidence of such a trade-off whereby a defect or change in sensitivity in the mGC is a consequence of the mutations that also impart resistance. This defect could render the resistant population of hookworms less capable of resuming feeding in the presence of host serum compared to the susceptible strain. If activation is required for the transition to parasitism, then the depressed activation phenotype described here may affect the ability of MADR hookworms to infect their host. While these results are from a single resistant isolate, if this altered phenotype is found to be consistently associated with, or the result of, multi-anthelmintic resistance, it could serve as a marker for resistance, particularly if it is associated with resistance to a particular anthelmintic. If so, it may provide useful insights into anthelmintic resistance in A. caninum. In any case, further research into the biology and mechanism of anthelmintic resistance in hookworms is warranted.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182023001385.
Data availability statement
Pool-seq data have been deposited into the Sequence Read Archive database (SRA, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) under BioProject PRJNA72585. The accession numbers are SRR26411280 (WMD), SRR26411281 (KGR), SRR26411283 (BCR) and SRR26411282 (BCR P1).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Sue Holzmer, Kristina Kryda, Jessica Rodriguez and Molly Savadelis of Zoetis for the donation of moxidectin and Sterling Cherise for maintenance of hookworms. We also thank Alice Wolfkill and the late Bean Counter for their valuable contributions.
Author contributions
E. L. M. conceived the research, performed experiments, analysed data, prepared the figures, maintenance and infections of animals and edited the manuscript. E. G. performed experiments, analysed data, maintenance and infections of animals and edited the manuscript. Y.-J. C. analysed genomic sequencing and edited the manuscript. M. M. contributed to funding acquisition, analysed genomic sequencing and edited the manuscript. D. M. O. conceived the research, funding acquisition and edited the manuscript. J. M. H. conceived and supervised the research, funding acquisition, wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Financial support
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under award number R21AI137771 to J. M. H. and D. M. O., R01AI144161 to M. M. and a grant from Zoetis Animal Health to J. M. H. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the sponsors. The sponsors had no role in the study design, collection, analysis or interpretation of data, writing the manuscript or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
None.
Ethical standards
All experiments involving animals were conducted in strict accordance with the recommendations of the National Institute of Health (USA) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Animal Welfare Act. The animal protocol used in this study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of The George Washington University (USA).