Article contents
Immunolocalization and functional analysis of Opisthorchis viverrini-M60-like-1 metallopeptidase in animal models
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 April 2022
Abstract
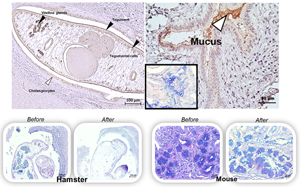
Host mucins have crucial physical roles in preventing the parasitic establishment and maturation, and also in expelling the invading parasites. However, some parasites utilize mucinase enzymes to facilitate the infection. Recently, we have identified a mucinase enzyme of the liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini, Ov-M60-like-1, which exhibits metallopeptidase activity against bovine submaxillary mucin substrate. Here, we aimed to study the localization of this enzyme in O. viverrini and the bile duct of hamsters using immunohistochemistry and functional analysis by mucin digestion in hamsters and mice tissues. The results showed that Ov-M60-like-1 was detected strongly in the tegument, tegumental cells, vitelline glands and mature eggs with miracidium. Expression in the gut, ovary and testis of the parasite was moderate while parenchyma showed slight colour intensity. In addition, the mucinase was also detected in the host biliary epithelial cells and goblet cells surrounding the worm. The mucinase assay revealed that the Ov-M60-like-1 could digest neutral mucin in the parenchyma, testis and seminal receptacle, but not the mucin in the tegument, tegumental cells and vitelline glands of the worm. The enzyme can also digest mucin in the cholangiocytes and modified the mixture type in the bile duct goblet cells of the infected hamsters, a susceptible host. In contrast, the enzyme was unable to digest neutral, acid and mixture mucin in the bile duct of the mice, a non-susceptible host. These findings indicate that Ov-M60-like-1 may have functions in both housekeeping tasks and host–parasite interactions, especially in modification of host susceptibility.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Parasitology , Volume 149 , Special Issue 10: Foodborne Trematodes – time to rise from neglected status , September 2022 , pp. 1356 - 1363
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
- 3
- Cited by



