Article contents
A Molecular Dynamics Study of Cu Segregation to the Σ11 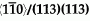 Grain Boundary In Al
Grain Boundary In Al
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2011
Abstract
We present results of molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies of Cu segregation to the Σ11 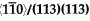 grain boundary (GB) in Al. The simulations were performed with Embedded Atom Method (EAM) potentials for Al and Al-Cu. The results predict that copper atoms tend to order along either side of the interface even at the pure symmetrical GB, forming alternating chains along the
grain boundary (GB) in Al. The simulations were performed with Embedded Atom Method (EAM) potentials for Al and Al-Cu. The results predict that copper atoms tend to order along either side of the interface even at the pure symmetrical GB, forming alternating chains along the 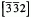 direction. The nucleation of the chains is driven by a change in the local atomic level stress induced by the pre-existing Cu atoms at the GB.
direction. The nucleation of the chains is driven by a change in the local atomic level stress induced by the pre-existing Cu atoms at the GB.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1996
References
- 3
- Cited by


