Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 February 2011
Mode-I fracture toughness studies were conducted on hydrogen-free tetrahedral amorphous diamond-like carbon (ta-C) MEMS specimens of various thicknesses. Mathematically sharp edge pre-cracks were generated through micro indentation on the Silicon dioxide sacrificial layer. An atomic force microscope (AFM) was employed to measure the precise length and orientation of each pre-crack. Upon wet etching and release the freestanding uniform width and varying thickness MEMS-scale specimens were tested in Mode-I using a custom-made micro-tensile tester. Fracture toughness values were computed from the test data using linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) for a finite width specimen with an edge crack in the fixed grip loading configuration. The average Mode-I fracture toughness for 0.5 micron thick specimens was found to be 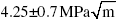 while the average mode-I fracture toughness for 1 micron specimens was
while the average mode-I fracture toughness for 1 micron specimens was 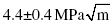 .
.