Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2011
Highly crystalline, textured thin films of LiCoxAl1-xO2 (x=0, 0.5) have been grown by pulsed laser deposition. Films of both stoichiometries were dense and uniaxially textured with Li, Co (or Co, A1) layers parallel to the substrate. It was found that crystal quality depended strongly on oxygen partial pressure, substrate temperature, and substrate material. The deposition of LiCo0.5Al0.5O2 is also highly dependent upon laser fluence, requiring at least 12.8 J/cm2 for high quality films. Chemical diffusion measurements were performed over a wide range of lithium contents using the potentiostatic intermittent titration technique. Maximum and minimum effective 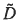 for LiCoO2 were 4.0 × 10−11 and 1.2 × 10−2 cm2/s, respectively, and for LiCo0.5A10.5O2, 2.2 × 10−12 and 8.0 × 10−17 cm2/s, respectively.
for LiCoO2 were 4.0 × 10−11 and 1.2 × 10−2 cm2/s, respectively, and for LiCo0.5A10.5O2, 2.2 × 10−12 and 8.0 × 10−17 cm2/s, respectively.