Published online by Cambridge University Press: 27 April 2012
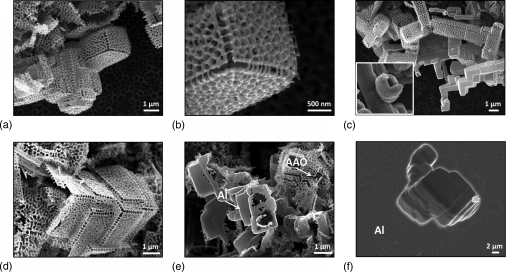
We report on the synthesis of unique tetragonal nanostructures from porous anodic aluminum oxide that enables geometrical three-dimensional (3D) microdesign of the porous surfaces. Scanning electron microscopy study revealed self-organization of hollow oxide nanostructures into hierarchical arrays. The formation of these structures has a localized nature and is associated with local electrical break-down during hard anodization of aluminum in oxalic acid solution. Moreover, in this communication we propose the mechanism of the nucleation and growth of complex 3D structures from porous anodic alumina.